With the rapid development of many pharmaceutical products, biosimilars (or biotherapeutics) are also prosperous in the bio-manufacturing industry. Biotherapeutics are widely used for their good histocompatibility and cell affinity. However, such externally introduced biological agents are still inevitably recognized and phagocytized by the immune system, causing serious adverse reactions or side effects. Therefore, studies on the immunogenicity of biological agents are very important and can effectively avoid the activation of immune cells in the body. Almost all biopharmaceutical products can cause certain anti-drug antibody (ADAs) reactions, which may reduce the efficacy of the drug or cause serious adverse reactions. Creative Biolabs owns a variety of testing methods and techniques to provide you with the most accurate data results in ADA evaluation.
For biopharmaceutical drug analysis, it is not an easy task to establish general methods to fit all drug evaluation and regulatory demands. It requires a lot of repeated “honing” of theoretical and practical experience. For some drugs with long half-life or drugs that require repeated administration, ADA is easy to form multiple immune complexes with the drug to be tested, which is not conducive to the detection of ADA. For example, multiple doses may interfere with the detection of ADA and drug targets or may be difficult to quantify by ADA interference pharmacokinetic (PK) studies and/or toxicokinetic (TK) studies, not conducive to preclinical studies.
 Fig.1 Free and partially bound PK assays. (Kelley, 2013)
Fig.1 Free and partially bound PK assays. (Kelley, 2013)
Regarding how to determine the presence of ADA in the sample, we can follow the steps:
The combination of ADA and PK detection methods brings new hopes and opportunities for the immunogenicity detection of preclinical biotherapeutics. Creative Biolabs can offer various detection methods and emerging technologies. If you are interested in immunogenicity testing, please contact us in time about more details and we will be glad to serve you.
Other optional SIAT® Anti-drug Antibodies (ADA) Assays:
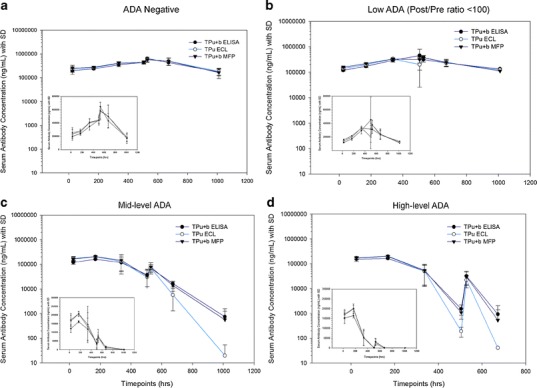 Fig. 2 Mean serum concentration–time profiles of TP measured using three different platforms and four ADA groups. (Theingi M. Thway, 2013)
Fig. 2 Mean serum concentration–time profiles of TP measured using three different platforms and four ADA groups. (Theingi M. Thway, 2013)
The study evaluates the impact of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) on pharmacokinetic (PK) assessments in a preclinical setting using Sprague Dawley rats administered with a humanized monoclonal antibody. It was observed that ADAs could significantly alter the measurement of therapeutic protein (TP) concentrations, affecting both 'bound' and 'unbound' TP measurements across different bioanalytical methods (ELISA, MFP, ECL). The presence of ADAs led to discrepancies in TP concentration measurements, especially at low TP concentrations, indicating ADA interference. Specifically, the study highlighted that ADAs could decrease TP concentration measurements by up to 99.8% in samples with high ADA levels, demonstrating a profound impact on PK exposure assessment. This indicates the necessity for accurate ADA assay development and validation in PK studies to ensure that ADA-induced alterations in drug concentration and exposure are correctly accounted for, ultimately influencing drug dosing and safety evaluations in clinical settings.
Anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) can significantly alter the pharmacokinetics (PK) and toxicokinetics (TK) of biologic therapies by affecting drug clearance and bioavailability. ADA assays in PK/TK analysis help identify whether ADAs are impacting drug efficacy, which is crucial for adjusting dosing strategies and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the therapy.
ADAs can bind to therapeutic proteins, potentially forming immune complexes that may accelerate drug clearance or alter its distribution. This interaction can reduce the effective concentration of the drug in circulation, leading to decreased efficacy or increased dosing requirements, which are critical factors in clinical management.
Common methods include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), electrochemiluminescence (ECL) assays, and radioimmunoassays (RIA). These techniques are chosen based on their sensitivity and specificity to detect ADAs, which can interfere with therapeutic protein measurements and PK/TK analysis.
High sensitivity in ADA assays ensures the detection of low levels of ADAs that might still significantly impact the pharmacokinetics of a drug. Early detection allows for timely intervention in therapeutic management, which is vital for maintaining drug efficacy and patient safety.
Proper validation of ADA assays ensures that these tests accurately reflect the presence and concentration of ADAs in patient samples. Reliable ADA assays are crucial for correct interpretation of PK/TK data, ensuring that changes in drug metabolism or clearance are appropriately attributed to immune responses.
The presence of high levels of ADAs can lead to a phenomenon known as 'immune clearance,' where the therapeutic protein is rapidly cleared from the circulation. This can lead to subtherapeutic drug levels, undermining the clinical efficacy and potentially leading to the failure of drug studies.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
