Arginase based Cancer Therapy
Small-molecule arginase inhibitors are currently described as promising therapeutic agents for the treatment of variety of diseases, including cancer. Arginase vaccination could induce Th1 inflammation at tumor sites where regulatory myeloid cells otherwise prevent lymphocyte infiltration. Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in the field of cancer vaccines and can provide arginase vaccine development for cancer therapy.
Biological Function of Arginase
Arginase is an enzyme that metabolizes L-arginine to L-ornithine and urea that was first discovered by Kossel and Dakin in 1904 in mammalian liver. It is a binuclear manganese metalloenzyme which catalyzes the hydrolysis of l-arginine to urea and ornithine. In addition to its essential role in the hepatic ornithine cycle, it also affects the immune systems in mice and humans. There are two types of arginase, and they are both products of distinct genes that are regulated independently and located on different chromosomes. There are two types of arginase which are products of different genes that are independently regulated and located on different chromosomes. Arginase I is dominant in the liver whereas Arginase II is expressed in brain, kidney, small intestine, monocytes, and macrophages.
Arginase participates in many inflammatory disorders by downregulating NO synthesis and inducing fibrosis and tissue regeneration. The fundamental mechanism of inflammation-associated immunosuppression is the suppression of the T-cell immune response by arginase-mediated l-arginine depletion in myeloid cells. This mechanism plays a important role in inflammation-associated immunosuppression. Pathogens can synthesize their own arginase to avoid immune reaction. Small-molecule arginase inhibitors are currently described as promising therapeutic agents for the treatment of variety of diseases, including diseases associated with pathogens, ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, allergic asthma, cardiovascular diseases, immune disorders, and cancer.
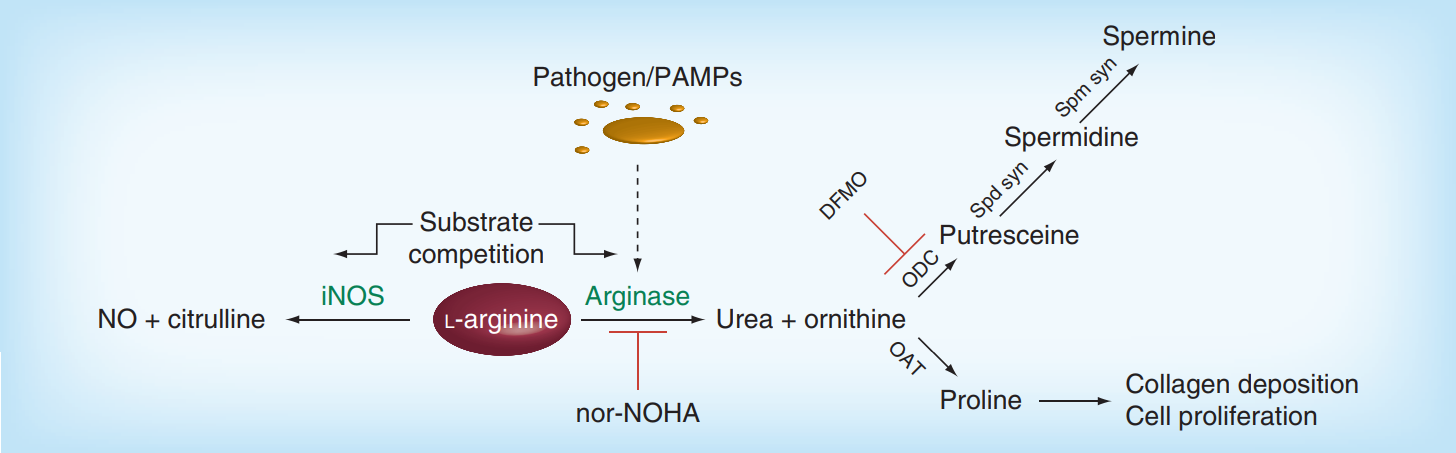
Fig.1 Mammalian arginine metabolism. (Ivanenkov YA. 2014)
Arginase Vaccine
Activation of arginase-specific T cells by therapeutic arginase vaccines is attractive because arginase-expressing myeloid cells are major players involved in the immunosuppressive microenvironment found in many tumors. These lesions have recently been defined as tumors with an “excluded” phonotype, indicating the exclusion of CD8+ T cells from tumor parenchyma. Arginase-expressing cells play a major role for the development of a permissive microenvironment because they prevent the proliferation of effector lymphocytes at the tumor site. Arginase-expressing cells act as inhibitors of Th1 inflammation, so in immune homeostasis, arginase-specific anti-Tregs can be used as the last attempt by the immune system to drive the reaction into the Th-1 response.
The arginase peptide vaccine could introduce T cell infiltration at the tumor site by specifically targeting arginase-expressing myeloid cells, such as tumor associated macrophages, neutrophils, and MDSCs. Th1 inflammation signals spontaneously result in the expansion of IDO-specific T cells, indicating a potential synergistic action of arginase with IDO-based vaccines. In this case, arginase vaccination could induce Th1 inflammation at tumor sites where regulatory myeloid cells otherwise prevent lymphocyte infiltration. This effect, in turn, induces IDO and can be further targeted by IDO-specific T cells. Hence, combinations of vaccine epitopes from arginase and IDO may be very beneficial and easy to implement in a clinical setting.
Creative Biolabs is a leader in the field of vaccine development and has focused on the cancer vaccines for years. We have experienced experts and advanced platforms that are able to provide excellent services. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Ivanenkov YA. (2014). “Small-molecule arginase inhibitors.” Pharm Pat Anal. 3(1): 65-85.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


