PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade for Cancer Therapy
The emergence of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)/programmed death-1 (PD-1)-targeted therapy has demonstrated the importance of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction in inhibiting anti-cancer T-cell immunity in multiple human cancers. Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in the field of cancer vaccines and can provide PD-1/PD-L1 blockade development services for the treatment of cancer with durable responses and extended overall survival.
Biological Function of PD-1/PD-L1
The programmed cell death protein 1 receptor (PD-1) receptor was first described in the early 1990s because it was expressed during T cell hybridoma-induced apoptosis. Scientists have identified that engagement of PD-1 through its ligand, programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), negatively regulates T-cell-mediated immune responses. Early preclinical evidence indicated that activation of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling could serve as a mechanism for tumors to evade an antigen-specific T-cell immunologic response. Therefore, the hypothesis was developed that PD-1/PD-L1 blockade may be an effective cancer immunotherapy.
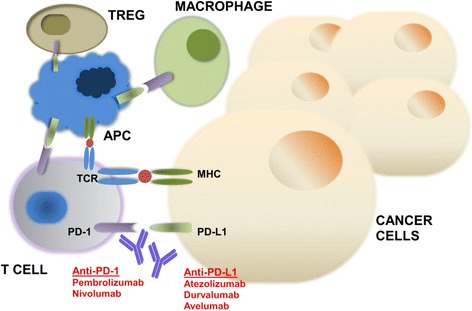
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. (Gong J. 2018)
PD-1/PD-L1 and Cancer
Cancer immunotherapies against the PD-L1/PD-1 axis of immune regulation have shown significant efficacy in a variety of cancers. In addition to clinical activity in historically immunogenic cancers such as melanoma and renal cell carcinoma (RCC), anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 agents can produce anti-cancer responses in a growing number of malignancies, including non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), urothelial carcinoma, triple-negative breast cancer, lymphoma, and head and neck cancer.
Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 Inhibitors as A Form of Cancer Immunotherapy
PD-1 expression on tumor infiltrating T cells is a major inhibitor of the spontaneous anti-tumor immune response in patients. As a regulatory molecule, PD-1 delivers inhibitory signals to T cells to make them functionally silent against their antigens. Its ligands are PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-L2 (B7-H2), which are expressed on tumor cells and on antigen-presenting cells, placental cells, and non-hematopoietic cells found in the inflammatory microenvironment. Expression of both PD-L1 and PD-L2 can be introduced by IFNs found in an inflammatory microenvironment. Thus, PD-1 and its ligands play an important role in the production of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that protects cancer cells from immune cell-mediated death. Therefore, PD-L1 helps protect malignant cells from immune destruction and it is expressed by many different cancer cell types. Blockade of either PD-1 or PD-L1 by monoclonal antibodies has produced outstanding clinical responses.
Early preclinical evidence provided the rationale for PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade as a potential form of cancer immunotherapy given that activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis putatively served as a mechanism for tumor evasion of host tumor antigen-specific T-cell immunity. Creative Biolabs is a leader in the field of vaccine development and has focused on the cancer vaccines for years. We have experienced experts and advanced platforms that are able to provide excellent services. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Gong J. (2018). “Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: a comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations.” J Immunother Cancer. 6(1):8.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


