CCL22 based Cancer Therapy
The targeting of chemokine expressing cells by therapeutic vaccination might present a broad therapeutic approach. Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in the field of cancer vaccines and can provide CCL22 based development services for the treatment of cancer.
Biological Function of CCL22
C-C motif chemokine 22 is secreted by macrophages and dendritic cells and elicits its action on its target cells by interacting with cell surface chemokine receptors such as CCR4. The gene which encoded CCL22 is located in human chromosome 16 in a cluster with other chemokines called CCL17 and CX3CL1. A few studies have demonstrated the importance of the macrophage-derived chemokine (CCL22) and its receptor CCR4 in the migration of Tregs. The macrophage-derived chemokine is produced constitutively by macrophages, monocyte-derived dendritic cells, activated natural killer (NK) cells, activated T cells, and epithelial cells. CCL22 plays a key role in a variety of diseases, including atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, and lymphoma. The role of CCL22 in malignant diseases has not been extensively studied.
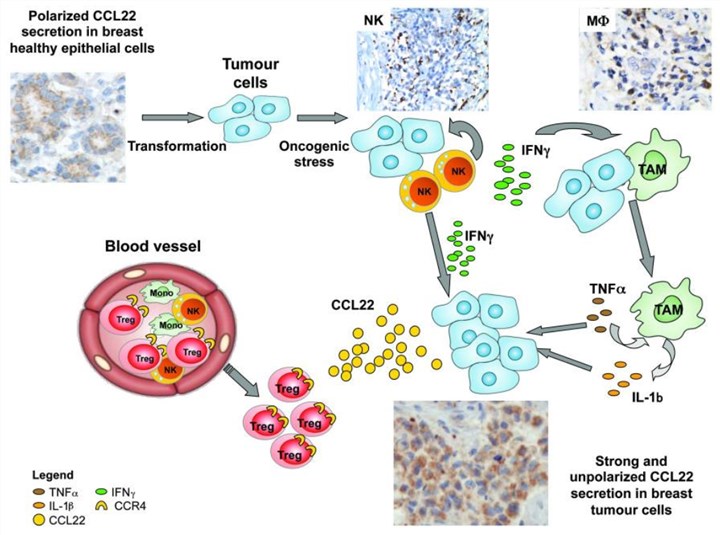
Fig.1 Scheme recapitulating the sequence of events leading to the strong non-polarized CCL22 production by tumor cells. (Ménétrier-Caux C. 2012)
CCL22 and Cancer
Tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages secrete the chemokine CCL22, which attracts and recruits Tregs to the microenvironment. The production of CCL22 correlates with the accumulation of Tregs in many solid cancers. It has been reported that several solid tumor cells, including ovarian, breast, prostate, gastric, and esophageal tumor cells, release CCL22. In tumors where CCL22 is not produced, Tregs do not infiltrate, regardless of whether these tumors produce other CCR4-binding chemokines such as CCL17. CCL22 production, therefore, is central to recruitment of Tregs into the tumor environment.
Development of CTLA-4 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy
CCL22-specific anti-Tregs are present in cancer patients. These cells recognize cells that express CCL22 by targeting the signal sequence of the CCL22 protein. CCL22-specific anti-Tregs recognize CCL22-expressing solid cancer cells, including colon and breast cancer cells. Moreover, CCL22-specific T cells lyse acute monocytic leukemia cells in a CCL22 expression-dependent manner. Interestingly, activation of CCL22-specific anti-Tregs reduces the level of CCL22 in the microenvironment in vitro. Recent research further indicates that therapeutic vaccination of mice against CCL22 leads to a CCL22-specific T cell response that results in the elimination of colon carcinoma in tumor-bearing mice, even though the tumor cells do not produce CCL22. Hence, therapeutic vaccination against CCL22 is another way to target cells in the tumor microenvironment and modulating the immunosuppressive environment. Therefore, this approach should be an attractive method to improve anti-cancer immunity in cancers that produce CCL22.
Creative Biolabs is a leader in the field of vaccine development and has focused on the cancer vaccines for years. We have experienced experts and advanced platforms that are able to provide excellent services. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Ménétrier-Caux C. (2012). “Innate immune recognition of breast tumor cells mediates CCL22 secretion favoring Treg recruitment within tumor environment.” Oncoimmunology. 1(5): 759-761.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


