Gold Nanoparticle Annotation
Creative Biolabs is committed to becoming a top team in the field of international nanomaterials, providing a series of gold nanoparticle products and solutions to global customers. We have an excellent scientific research team to serve you wholeheartedly.
Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
Gold is one of the most chemically stable elements, but nanoscale gold particles have special physical and chemical properties. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are a kind of nanomaterials, which are generally referred to as colloidal gold in biological research. Compared with other noble metal nanoparticles, the particle size of AuNPs is generally between 1 and 100 nm. Due to the surface plasmon resonance properties of AuNPs, AuNPs with different particle sizes will show different colors. The color of AuNPs varies from red to purple depending on the diameter, which lays a scientific foundation for the application of AuNPs. AuNPs have been shown to have higher biocompatibility and lower toxicity. In addition, AuNPs possess a unique photoelectric effect and large specific surface area, so that the biomolecules modified on their surface can maintain good activity.
 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of AuNPs.
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of AuNPs.
Bioconjugation of AuNPs
The unstable ligands covered on the surface of AuNPs, such as citrates, thiols, or other ligands adsorbed on the surface, can be replaced by ligand exchange reactions, resulting in hybrid monolayer-protected AuNPs. The covering efficiency of ligands on the surface of AuNPs was controlled by adjusting the reaction time and ligand ratio. In addition, if two or more functional ligands are introduced in the ligand exchange reaction, there will be a synergistic effect on the surface of AuNPs protected by the monolayer.
Biomolecules combined with AuNPs generally include proteins, enzymes, lectins, and biotoxins. Ligand exchange enables the indirect attachment of biomolecules on the surface of AuNPs. There are generally two ways of conjugation, covalent conjugation, and non-covalent conjugation. Non-covalent conjugation is a relatively simple way to couple AuNPs with biomolecules because it can be accomplished through different interactions, such as through specific conjugation affinity, electrostatic interaction, and hydrophobic interaction. Due to their facile release and reversible properties, these noncovalent interactions are widely used in drug delivery and biosensing. Additionally, covalent conjugation of biomolecules to AuNPs is more feasible when structurally stable conjugates are required (e.g., imaging). There are two main types of covalent bonding, one is the direct attachment of sulfhydryl molecules on the surface of AuNPs, and the other is the formation of covalent bonds (e.g., amine-ethyl carboxylate coupling and click reaction). Usually, these covalent bonds are between free molecules on the surface of AuNPs and bound thiolate ligands. The conjugation of AuNPs to biomolecules has been widely used in biological immunodetection, protein labeling, optical imaging, cancer therapy, medical diagnosis, and drug delivery.
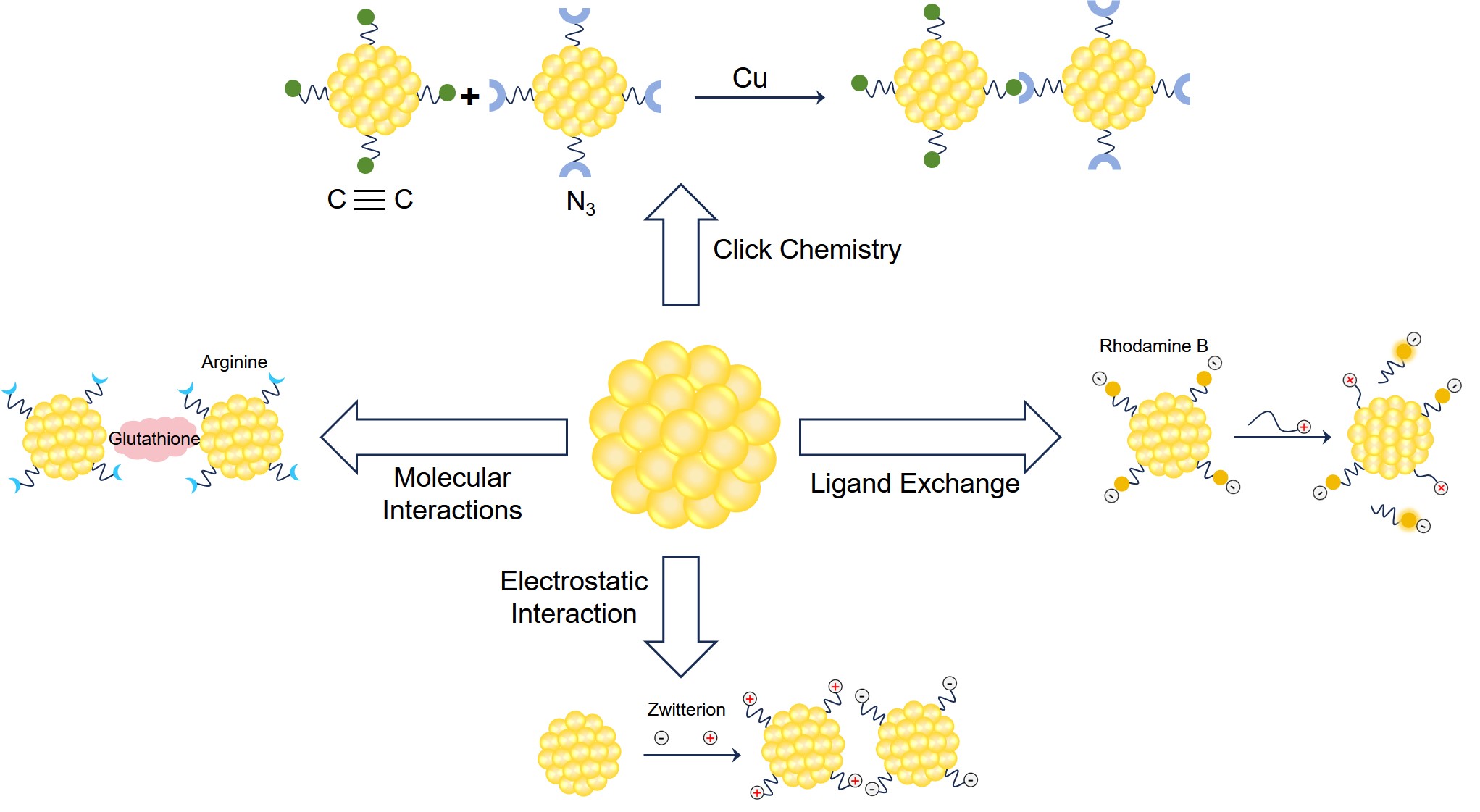 Fig.2 Strategies of surface chemistry for bioconjugation of AuNPs with small molecules.
Fig.2 Strategies of surface chemistry for bioconjugation of AuNPs with small molecules.
Creative Biolabs can provide water-soluble AuNPs, oil-soluble AuNPs, fluorescently labeled AuNPs, and AuNPs with special shapes, and can also provide customized services according to requirements of our clients. Our AuNPs products have uniform size, good dispersibility, non-agglomeration, high purity, and good stability. Numerous particle sizes and modifications are available for you to choose from. Please contact us if you have bioconjugation requirements for AuNPs.
