Custom Protein-Liposome Conjugation Services
Are you facing challenges such as poor drug solubility, off-target toxicity, or rapid degradation of your protein therapeutics? Creative Biolabs' Protein-Liposome Conjugation Service helps you improve drug efficacy, enhance stability, and achieve targeted delivery.
Introduction
Liposomes, microscopic vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers often stabilized by cholesterol, exhibit a unique amphiphilic structure enabling the encapsulation of both hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules. This inherent versatility, coupled with their biocompatibility, controlled release characteristics, and modifiable particle size, has led to their widespread use as delivery vehicles for pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and imaging agents. In recent years, advancements in protein-liposome conjugation, involving the incorporation of targeting moieties such as peptides and antibodies, further enhance the specificity of liposomal delivery, particularly for tumor-targeted therapeutics. This synergistic approach leverages the therapeutic or targeting potential of proteins with the advantageous drug delivery attributes of liposomes, resulting in improved pharmacokinetics, enhanced stability, reduced immunogenicity, and ultimately, increased therapeutic efficacy with minimized off-target effects.
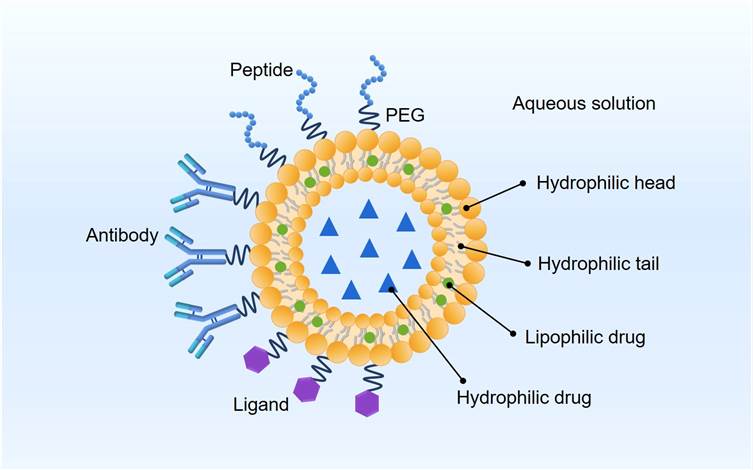 Fig.1 The main types of protein-modified liposomes.
Fig.1 The main types of protein-modified liposomes.
What Can We Do for Your Project?
Creative Biolabs specializes in the design and development of precisely engineered protein-liposome conjugates tailored to your specific research or therapeutic goals. We provide end-to-end solutions, transforming your proteins or peptides into advanced delivery systems with enhanced pharmacokinetic profiles and targeted action. Our service focuses on delivering conjugates that exhibit superior stability, controlled release characteristics, and optimized biological activity, enabling you to overcome common hurdles in drug development and biological research. We ensure each conjugate is meticulously characterized to meet stringent quality standards.
Types of Our Protein-Liposome Conjugation Service
Creative Biolabs offers specialized conjugation services tailored to different types of proteins and project needs:
Peptides are crucial to biological processes, governing growth, development, and metabolism. Their inherent biocompatibility, small size, high specificity, and ease of modification make them ideal for advanced therapeutic applications. We specialize in leveraging these properties by modifying liposomes with key peptide types, including:
- Homing Peptides: For precise targeting of specific cells, such as cancer cells.
- Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs): To enhance the intracellular uptake of liposomal cargo.
- Cell-Penetrating Homing Peptides: Combining targeted delivery with efficient cellular entry.
We meticulously optimize peptide conjugation to ensure maximum stability and optimal presentation, thereby maximizing the biological impact and therapeutic effect of your project.
We specialize in creating antibody-modified liposomes by conjugating monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies, or their fragments (e.g., Fab', scFv), to PEGylated liposomes. These actively targeted systems specifically bind to cell surface antigens, concentrating your liposomal drug delivery within target cells while minimizing off-target effects. The inclusion of PEGylation further enhances efficacy by prolonging circulation time. Our immunoliposomes are ideal for developing highly specific therapies (such as cancer treatments) and diagnostic agents, offering a powerful approach to precision medicine.
- Ligand-Liposome Conjugation:
Receptor-specific ligand modification is a powerful strategy for directing liposomes to target cells, such as cancer cells. Transferrin-liposome conjugates, for example, effectively exploit the higher transferrin receptor levels on tumor cells to achieve targeted cell kill. We empower your research by conjugating various other targeting ligands to liposomes. This capability facilitates highly adaptable targeting strategies aimed at specific cellular receptors or markers, offering a flexible and powerful method to improve therapeutic outcomes and expand the utility of your liposomal formulations.
Workflow
Our systematic and transparent workflow is meticulously managed by our experienced scientists, providing you with a clear path from the initial concept to the final product.
-
Required Starting Materials:
- Your Protein/Peptide: Purified protein or peptide of interest, typically >1 mg, with details on its concentration, buffer composition, and sequence (if available).
- Liposome Specifications: Desired lipid composition (e.g., DSPC, DOPE, cholesterol ratios), target vesicle size, surface charge, and any specific requirements for encapsulated cargo (drug, nucleic acid, imaging agent).
- Project Goals & Application: Detailed information about the intended application (e.g., in vitro cell targeting, in vivo drug delivery, diagnostic imaging), the target cell type or tissue, and any known receptor targets for the protein/peptide.
- Key Steps Involved:
| Steps | Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Consultation & Strategic Design | A comprehensive discussion of your project requirements, protein/peptide characteristics, desired liposome properties, and potential conjugation strategies. Our experts will assess feasibility and propose an optimal experimental design. | A detailed project plan, including chosen conjugation chemistry, liposome formulation parameters, analytical methods, timeline, and quotation. |
| Custom Liposome Formulation | Precise preparation of liposomes according to the agreed-upon lipid composition. This includes options for stealth liposomes (PEGylated) or ligand-targeted liposomes. | High-quality liposomes ready for conjugation. |
| Protein Modification (if required) & Conjugation Reaction | Chemical modification of the protein or liposome surface to introduce reactive groups, if not already present. Execution of the conjugation reaction using selected chemistry (e.g., maleimide-thiol, NHS-ester, click chemistry) under optimized conditions to maximize efficiency and preserve protein activity. | Crude protein-liposome conjugate mixture. |
| Purification of Protein-Liposome Conjugate | Rigorous purification of the conjugate from unreacted protein, free lipids, and other reaction by-products using appropriate techniques such as size exclusion chromatography (SEC) or dialysis. | Purified protein-liposome conjugates meeting predefined purity specifications. |
| Comprehensive Characterization & Quality Control | Extensive analysis of the final conjugate, including protein concentration, particle size and distribution (DLS), and zeta potential. Endotoxin testing and activity assays can be performed as required. | Fully characterized protein-liposome conjugate with a comprehensive Certificate of Analysis (COA). |
-
Final Deliverables:
- The purified, ready-to-use protein-liposome conjugate at the agreed-upon quantity, concentration, and formulation buffer.
- A comprehensive COA summarizing key quality attributes of the final product, including the liposome formulation, conjugation methodology, purification process, and all characterization data.
- Estimated Timeframe:
The typical timeframe for our protein-liposome conjugation service ranges from 6 to 12 weeks. This duration is contingent upon factors such as the complexity of the protein, the specifics of the liposome formulation, the chosen conjugation chemistry, and the extent of analytical characterization required. We will provide a more precise timeline after the initial project consultation.
FAQs
1. Q: What types of proteins are suitable for conjugation to liposomes using Creative Biolabs' service?
A: Creative Biolabs has extensive experience conjugating a diverse array of proteins, including full-length antibodies, antibody fragments (Fab', scFv), enzymes, cytokines, growth factors, and various peptides. The feasibility and optimal strategy depend on the protein's size, pI, surface chemistry, and stability. Reach out to our experts to discuss your protein.
2. Q: How does Creative Biolabs ensure that the conjugated protein retains its biological activity?
A: Preserving protein integrity and activity is a cornerstone of our service. We achieve this by: selecting mild and site-specific conjugation chemistries where possible, meticulously optimizing reaction conditions (pH, temperature, reactant ratios), and employing gentle purification methods.
3. Q: What is the minimum order quantity for a custom protein-liposome conjugate?
A: The minimum quantity for custom protein-liposome conjugate synthesis is 10 mg. This usually requires 1 mg of the initial protein/peptide. Please inquire about custom synthesis pricing if needed.
4. What is the shelf life of a protein-liposome conjugate?
A: Typically, a protein-liposome conjugate stored under optimal conditions (2-8°C, protected from light, and in a suitable buffer) has a shelf life of about 1-2 months. Lyophilized formulations may extend the storage life to 4-6 months.
5. Q: How does outsourcing protein-liposome conjugation to Creative Biolabs compare to developing them in-house?
A: While in-house development offers direct control, partnering with Creative Biolabs provides immediate access to specialized expertise, established and optimized protocols, custom formulation and advanced analytical instrumentation, and dedicated project management. This can significantly accelerate your research timelines, reduce R&D costs associated with establishing these capabilities internally, and ensure high-quality, consistently produced, and well-characterized conjugates. Let us handle the complexities so you can focus on your core research.
Creative Biolabs is your dedicated partner for cutting-edge protein-liposome conjugation services. We combine scientific rigor with a client-centric approach to deliver customized solutions that meet the demanding needs of modern biopharmaceutical research and development. Our expertise empowers you to enhance the efficacy, stability, and targeting of your protein-based therapeutics and diagnostics. Contact us for more information.
