Latex Nanoparticle Annotation
Latex nanoparticles, as polymeric particles, can be conjugated with drugs, antibodies, fluorescent markers, etc., and serve as important materials for drug delivery or fluorescent labeling. Based on our strong BioConjugation research platform and state-of-the-art technologies, Creative Biolabs offers a variety of services related to the BioConjugation of latex nanoparticles. Our experienced team is ready to provide you with customized and professional latex nanoparticle BioConjugation services.
Introduction of Latex Nanoparticles
Latex nanoparticles are polymeric particles consisting of polystyrene or copolymers of styrene, such as styrene/divinylbenzene, styrene/butadiene, styrene/acrylate, or styrene/vinyltoluene. Due to the polymeric diversity, the type of polymer monomer determines the properties of these nanoparticles, such as hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Hydrophilic polymers include poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG), poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA), poly (acrylic acid), etc. Polymer latexes can be artificially synthesized through emulsion, dispersion, precipitation, miniemulsion, or suspension polymerization.
Polymer particles can be further diversified by adding functional groups on their surface. Non-covalently adsorbed detergent molecules can add amphipathic character to the particle surface. In addition, the polymeric particle amphipathic characteristics can be modified by graft copolymerization, adsorptive coating, or through covalent attachment of another polymer type. The hydrophilic shell contributes to the ability to reduce particle aggregation in aqueous solutions and to maintain the separation and suspension of these particles in aqueous solutions. Polystyrene particles with hydrophilic surfaces can be used for cell attachment. Moreover, another method to hide the hydrophobic properties of the underlying surface while increasing the biocompatibility of the particles is to covalently attach short hydrophilic organic molecules, such as monoclonal antibodies and peptides, to the latex nanoparticles.
Applications
- The hydrophilic modification of the hydrophobic particle core helps to isolate its binding to proteins or other drug molecules for drug delivery. The advantage is that it can be used to control drug loading and release, protect drugs and other biologically active molecules from environmental influences, and improve their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.
- The high specificity, availability, and diversity of antibodies provide targeting capabilities and enhance biological activity, which are already widely used in the pharmaceutical and biomedical fields. The new BioConjugation technology allows the attachment of antibodies to different latex nanoparticle surfaces by conjugation. This new technology improves the targeting efficiency of antibodies and drug delivery while minimizing non-specific binding.
- Fluorescent polystyrene particles, polymer particles loaded with fluorescent inorganic nanoparticles or dyed latex nanoparticles can be used in multiplexed detection systems using suspension arrays, which play an important role in imaging and diagnostics, drug discovery, hydrodynamic studies, and phagocytosis studies.
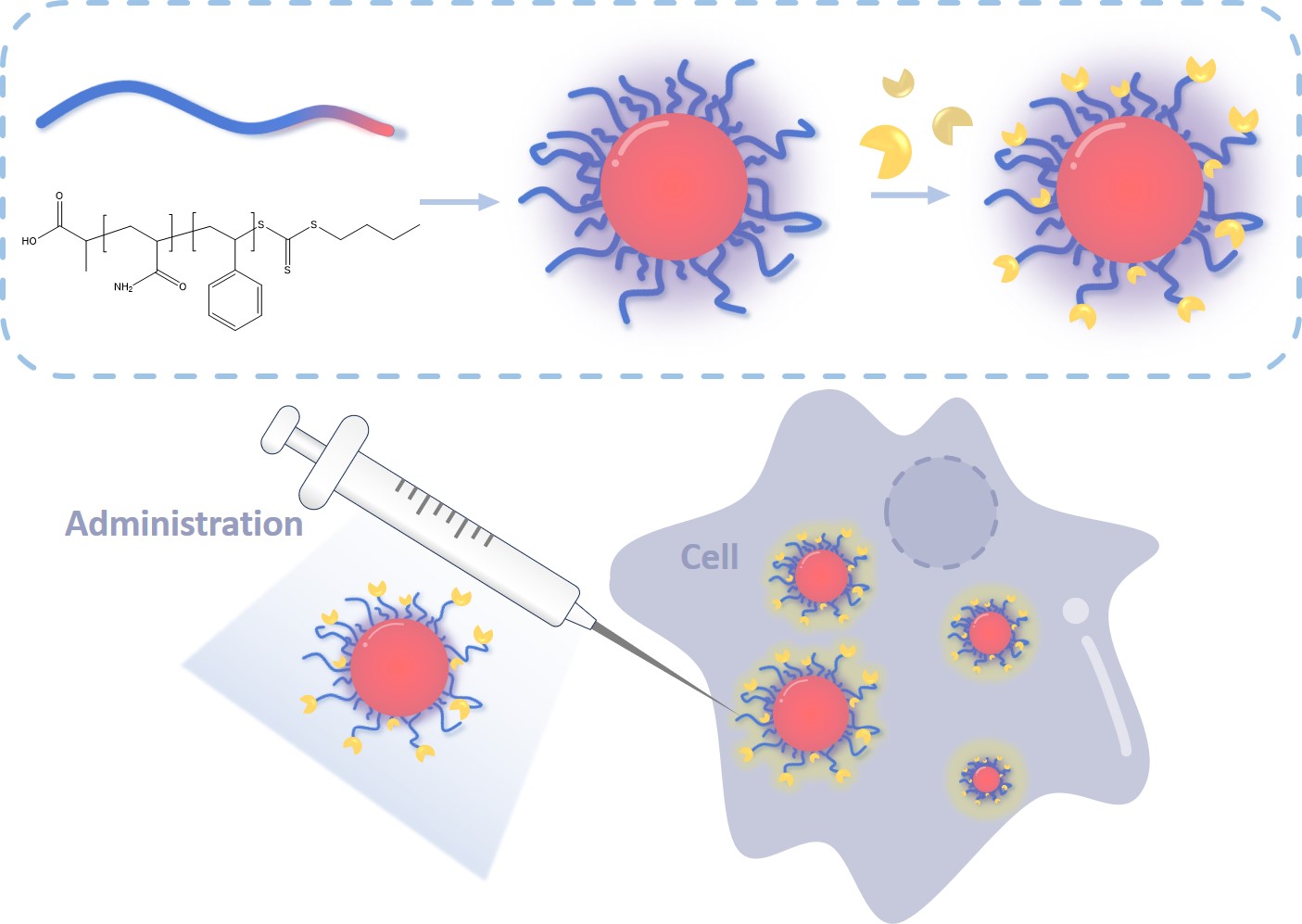 Fig.1 Latex nanoparticles can be used as drug delivery carriers and be fluorescently labeled.
Fig.1 Latex nanoparticles can be used as drug delivery carriers and be fluorescently labeled.
As a leading service provider in the field of biopharmaceuticals, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing dependable bioconjugation services to support the discovery of latex nanoparticle-based targeted drugs and fluorescent markers. If you intend to learn more about our latex nanoparticle BioConjugation services and customize your programs, please do not hesitate to contact us.
