Cleavable Linker Annotation
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a targeted therapeutic strategy that combines the benefits of both antibodies and small molecule drugs. It retains the advantages of antibodies in terms of pharmacokinetics, low side effects, and specificity, while releasing the drug in combination with the target site. However, the challenge of ADCs is to effectively bind the antibody to the drug and ensure its stability while still allowing for effective drug release at the target site. Therefore, the cleavability of the ADC linkers has become an important consideration. With years of experience in the biological field, Creative Biolabs is confident in providing a wide range of reliable bioconjugation services. In order to improve the stability and pharmaceutical efficacy of antibody-drug conjugates, our scientists in related fields are prepared to provide you with specialized and customized cleavable linkers-based bioconjugation services.
Cleavable Linkers
Cleavable linkers depend on intracellular processes to release cytotoxic molecules, including the reduction in the cytoplasm, exposure of the target to the lysosome, or cleavage by specific intracellular proteases. The cleavable linkers are classified into chemically labile linkers and enzymatically cleavable linkers.
Chemically Labile Linkers
Different chemically labile linkers can be employed in different intra-environmental contexts, such as in plasma and different cytoplasmic compartments. The stability and pharmacokinetics of these linkers can be adjusted by chemical modifications, such as the introduction of substituents.
-
Acid-Labile Linkers (Hydrazones)
Acid-labile linkers retain their integrality during systemic circulation in the plasma neutral pH environment, while proceeding hydrolysis and promoting drug release under the acidic environment of endosomes and lysosomes. -
Disulfide Linkers
In the absence of free sulfhydryl groups, disulfide linkers are stable in plasma. Taking advantage of the fact that they can be reduced by thiols that exist in the cell cytoplasm, such as glutathione, ADCs have been engineered to be conjugated to the disulfide linkers that remain stable in the circulation and selectively release drugs in the cytoplasm.
Enzymatically Cleavable Linkers
-
Peptide Linkers
Peptide linkers, as one of the linkers of ADCs, have better serum stability, longer serum half-life, and better control of drug release due to the low activity of lysosomal proteolytic enzymes in the blood and the high level of proteases in target cells, such as tumor tissues, where rapid enzymatic reactions can occur. -
β-Glucuronide Linkers
β-glucuronic acid-based linkers are an extension of the peptide-based linkers, which offer higher ADC stability. The lysosomal β-glucuronidase has low extracellular activity and is abundantly present in the lysosomes of tumor cells. β-glucuronide linkers can stably and selectively release active drugs in target cells by cleaving the β-glucuronidase glycosidic bond of the lysosomal β-glucuronidase. In addition, the highly hydrophilic nature of β-glucuronide linkers circumvents the aggregation of ADCs.
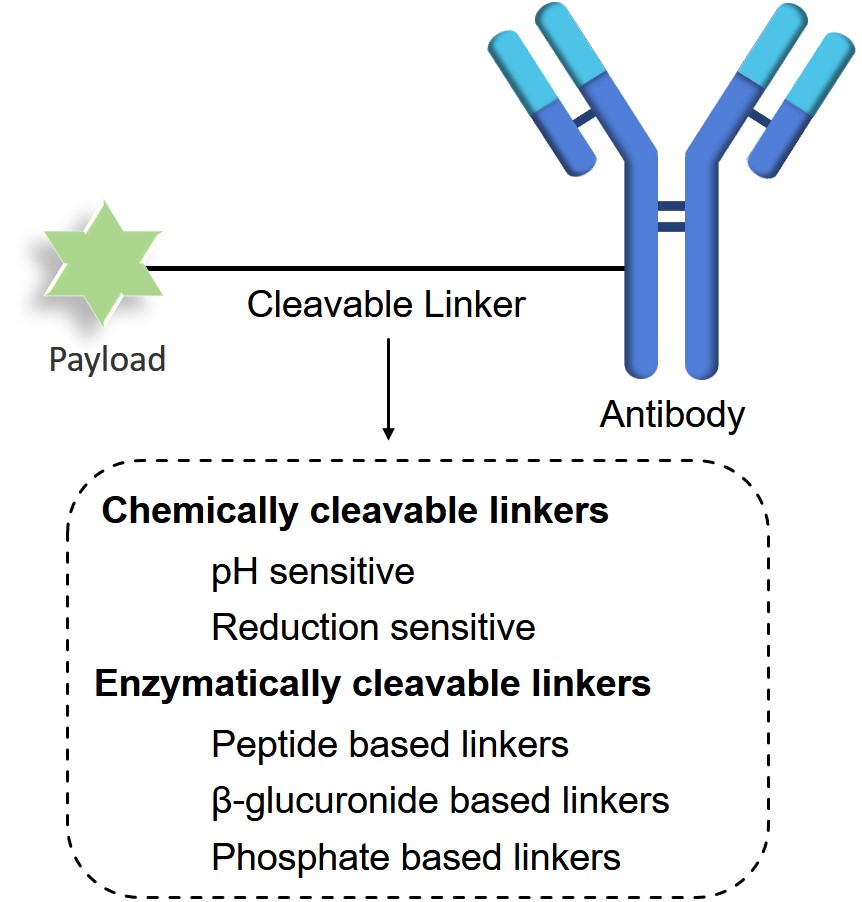 Fig.1 Classification of cleavable linkers.
Fig.1 Classification of cleavable linkers.
Creative Biolabs is committed to delivering high-quality biomarker services that facilitate the development of novel antibody-drug conjugates. We have the expertise to provide you with solutions to meet any of your research and development requirements. If you are interested in our cleavable linker-based bioconjugation services, please contact us for more detailed information.
Related Sections

