Custom Small Molecule-Particle Conjugation Service
Constructs made by coupling small molecules to nano- or micro-diameter particles via affinity ligands have been widely used in diagnostic testing and drug development research procedures. In order to meet the various needs of our customers, Creative Biolabs provides flexible, stable and repeatable custom small molecule-particle conjugates services for clients all over the world.
Custom Small Molecule-Particle Conjugate
Small molecules are one of the most critical elements for biological functions, most drugs contain such molecules. The delivery of small molecules using nano- or micro-scale drug carriers has shown significant improvement in therapeutic efficacy and lower side effects, providing positive attributes for in vivo distribution and stabilization of small molecule drugs and improving adverse pharmacokinetics study. With the development of nanotechnology and microphase synthesis technology, materials science provides almost unlimited particle types of shapes and sizes for biological applications of nanomaterials, including amorphous particles, various fine geometric shapes or symmetric structures used as scaffolds organic structures. The choice of materials is also variable depending on the specific goals it is required to achieve, including polymers, copolymers, metals, semiconductors, superparamagnetic composites, and many others. In addition to their applications in drug development and delivery, nanoparticles and microparticles are also widely used in solid-phase assays, agglutination tests, magnetic separations, biosensing, and fluorescent labeling.
Metal Nanoparticles
The development of metal nanoparticles has been greatly accelerated with advances in nanotechnology and molecular cell biology. Specifically, gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) have been identified as important candidates for drug delivery particles due to their biocompatibility, ease of functionalization, and chemical and physical stability. The surface of Au-NPs has a strong binding affinity for amines, thiols and disulfides. Natural or other types of thiol groups can be bound to Au-NPs by the Au-thiol interactions. Therefore, most molecular drugs can be loaded on Au-NPs by thiol-containing ligands such as thioglycolic acid (TGA) and GSH, and Au-NPs can also be modified and encapsulated by fucoidan, galactose, and oligosaccharide. In conclusion, functionalized Au-NPs represent attractive and promising candidates for drug delivery due to their unique size, tunable surface functions, and controllable drug release.
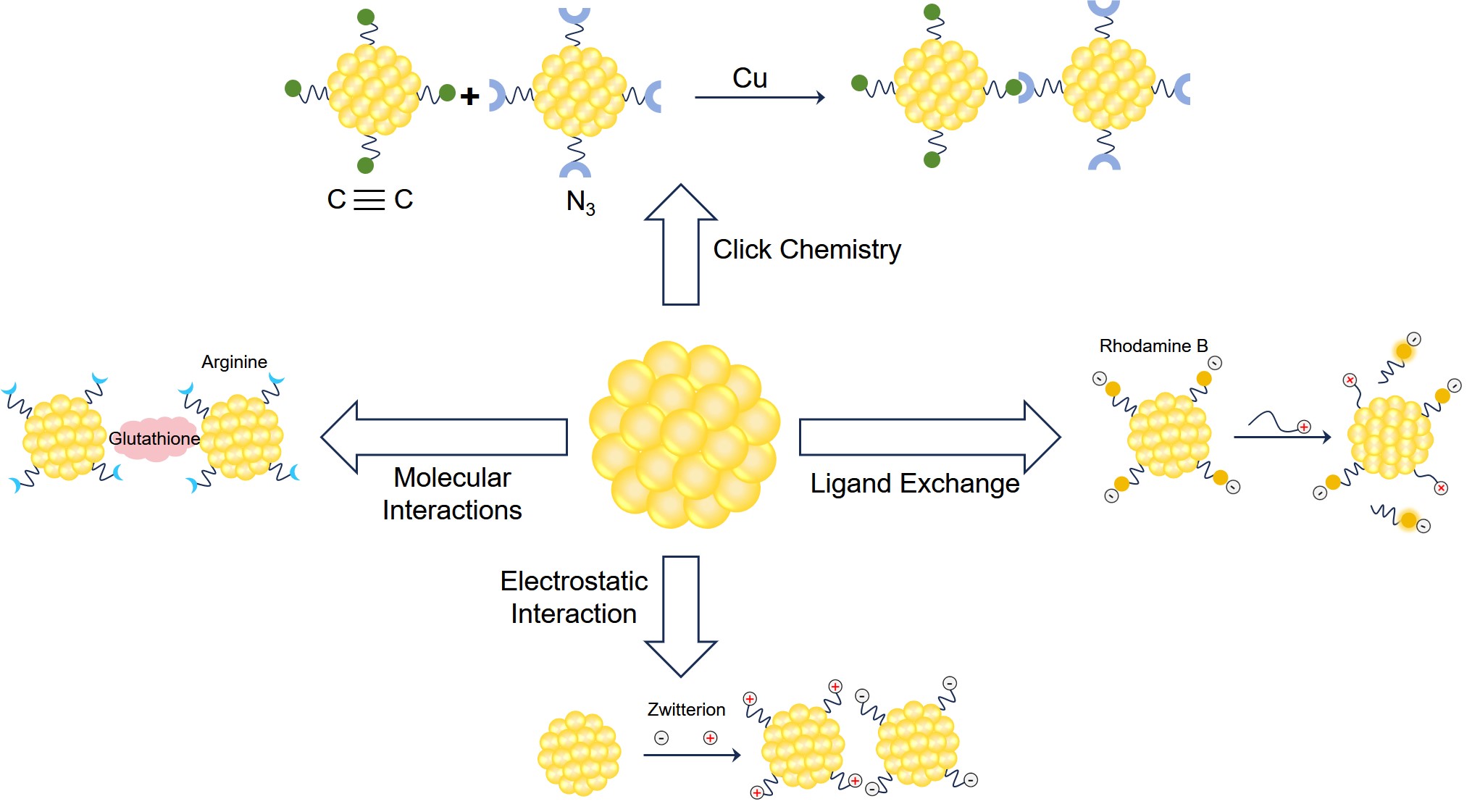 Fig.1 Strategies of surface chemistry for bioconjugation of AuNPs with small molecules.
Fig.1 Strategies of surface chemistry for bioconjugation of AuNPs with small molecules.
Superparamagnetic Composites
Iron oxide nanoparticles have been widely studied and successfully used in numerous applications due to their superparamagnetic properties. With the help of an external magnetic field, the drug-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles can accumulate directly at the tumor site and improve the effectiveness of drug release. The modification of iron oxide nanoparticles can be achieved by conjugating with PEG molecules. Fe3O4-NPs with citric acid coating can be conjugated with biocompatible PEG biscarboxymethyl ether to form spherical magnetic composites, which are then linked to specific molecules through hydrazone bonds. PEG carboxyl-poly(ε-caprolactone) can also PEGylate iron oxide nanoparticles, and the modified conjugates exhibit good biocompatibility and minimal cytotoxicity, as well as the ability to specifically target drug delivery to tumor cells when an external magnetic field is applied.
Polymer Particles
The emergence and development of organic electronics are attributed to the wide range of synthesizable conjugated polymers, including polystyrene (commonly used latex particles), polymethacrylate, poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate). Direct arylation polymerization can be used to generate reactive or functional groups on the particle surface for subsequent conjugation with affinity ligands after functional monomers are incorporated into the polymerization mix. In addition, traditional cross-coupling polymerization, such as Stille and Suzuki polymerization, is also common means of cross-linking polymer particles with various types of molecules.
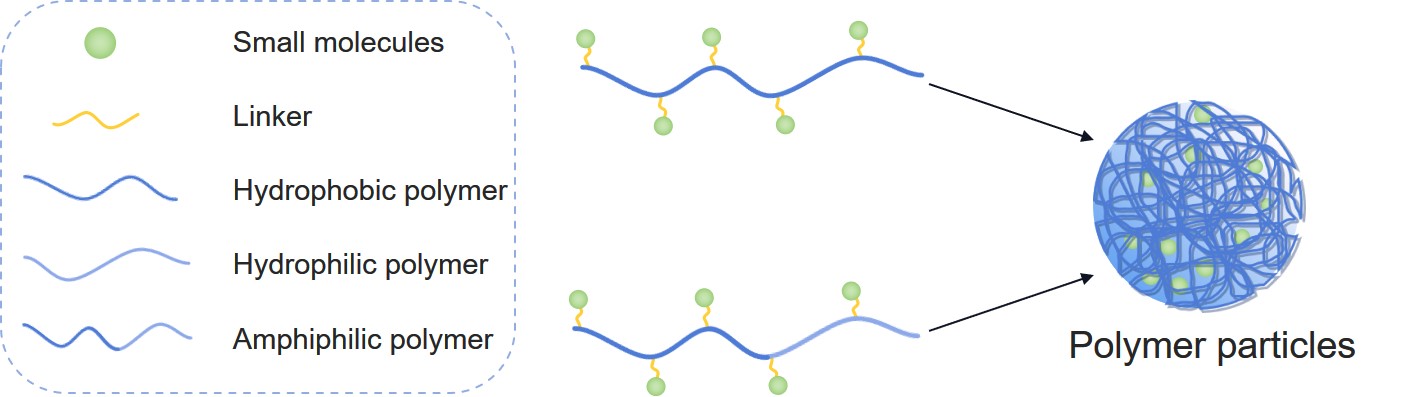 Fig.2 Two representative polymer-drug conjugates (PDCs).
Fig.2 Two representative polymer-drug conjugates (PDCs).
Other Particles
The chemical composition of particles used for drug delivery and biomonitoring is as varied as their shape. In addition to the above-mentioned nanoparticles, materials such as latex microspheres and liposomes are often used for conjugation with small molecules, and the optional small molecules and cross-linking methods are also different.
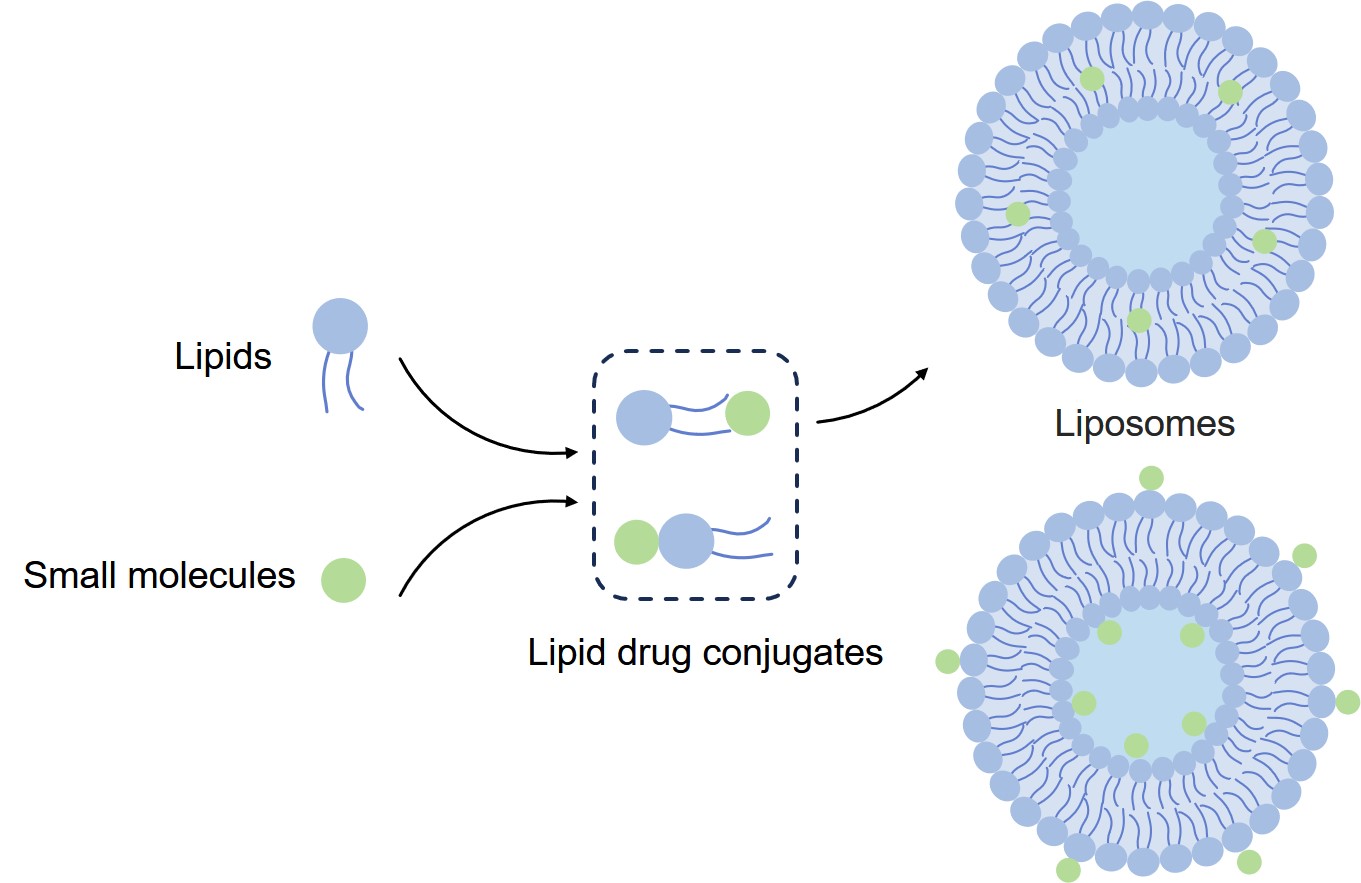 Fig.3 Conjugation strategies for liposomes and small molecules.
Fig.3 Conjugation strategies for liposomes and small molecules.
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to offering high-quality bioconjugation services to support projects of our clients globally. With our well-trained R&D team, we can achieve stable small molecule-particle conjugation through a variety of methods. Contact us to get more information about your project.
Recommended products
