-
Widely distributed in various ecological niches such as waters, soils, and decaying plants.
-
Can cause immune dysfunction, resulting in keratitis, central nervous system inflammation, skin lesions, pulmonary infections, and diffuse systemic infections.
-
Besides the pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba itself, the presence of endosymbiotic pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, may enhance virulence.
-
Understanding the role of Acanthamoeba as an environmental host and the classes of pathogens that host Acanthamoeba facilitates the control of the health threats it conveys.
|
-
Acanthamoeba-derived exosomes contain cargo compositions that are related to the culture conditions of their parent trophozoites. For example, under nutrient-stress conditions, Acanthamoeba-derived exosomes were found to carry additional proteins compared to steady-state conditions.
-
The protein cargoes that Acanthamoeba-derived exosomes carry range from those associated with nutrient acquisition and digestion, amino acid metabolism, and cellular stress, to pathogenic proteases involved in the development of infectious diseases and cancers, as well as kinases and glycosidases that favor immune escape and colonization tropism.
-
Potential applications of Acanthamoeba-derived exosomes involve their use as vaccines, drug delivery vehicles, and feedstocks for biofuel production.
-
Studying the molecules carried within the Acanthamoeba-derived exosome that are involved in the infection establishment and the variation of cargo with the environmental conditions of trophozoite inhabitants could be favorable for the development of therapeutic strategies in which Acanthamoeba-derived exosomes serve as targets.
|

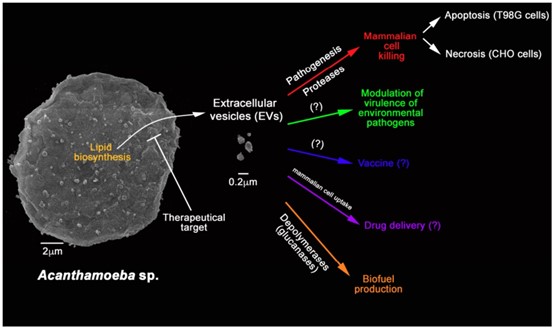 Fig. 1 Functions and applications of A. castellanii-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Functions and applications of A. castellanii-derived exosomes.1
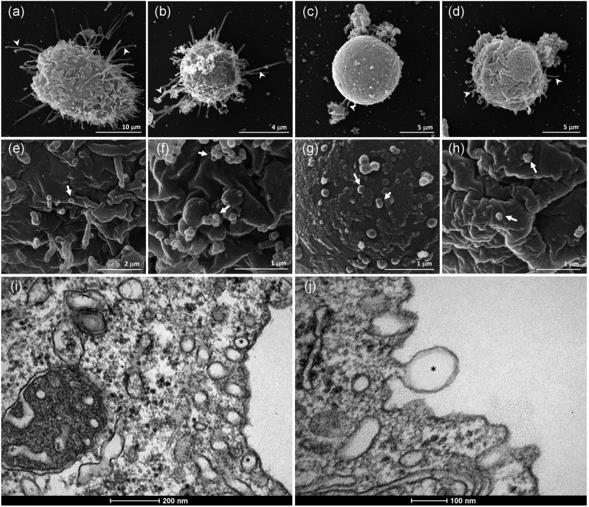 Fig. 2 Electron micrographs of exosomes generated from Acanthamoeba trophozoites.2
Fig. 2 Electron micrographs of exosomes generated from Acanthamoeba trophozoites.2








