-
Validation of Entamoeba-derived exosomes carrying protein cargo.
Comparison of proteins in Entamoeba-derived exosomes and whole-cell lysates by protein gel electrophoresis showed that Entamoeba-derived exosomes were selectively enriched and depleted of some proteins. Gal/GalNAc lectin proteins were selectively enriched in exosomes, while cytosolic skeleton proteins were selectively depleted.
-
Proteomic profiling of Entamoeba-derived Exosome
Mass spectrometry profiling and GO analysis showed that Entamoeba-derived Exosome proteins hardly contain proteins associated with the plasma membrane, or compartments other than endosomes, but mainly encompass proteins associated with vesicle genesis, molecular binding and signaling.
-
RNA profiling of Entamoeba-derived Exosome.
PAGE assay revealed that Entamoeba-derived exosomes were selectively enriched for some 27-nt small RNAs and were able to protect the RNA cargo from RNase A digestion. Moreover, the presence of argonaute 2-2 protein and Tudor protein, which bind to small RNAs to mediate target gene silencing, was also confirmed in Entamoeba-derived exosomes by protein blotting, suggesting that these exosomal small RNAs mediate the RNAi process.
-
Functional assay of Entamoeba-derived exosomes.
The extent of the encystation process was indicated by luciferase signaling. Encysting Entamoeba-derived exosomes promoted E. invadens encystation, whereas exosomes derived from metabolically active Entamoeba trophozoites impeded encystation, suggesting a function for Entamoeba-derived exosomes to mediate parasite-to-parasite communication.
-
Entamoeba-derived exosomes affected ROS levels in neutrophils.
The ROS levels released in neutrophils were detected by a ROS fluorescent probe, and it was found that compared to neutrophil-derived exosomes and Entamoeba-derived exosomes, exosomes derived from co-cultures of neutrophils and Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites were capable of transfer higher levels of ROS.
-
Entamoeba-derived exosomes suppressed the respiratory burst and NET of neutrophils.
Pretreatment with Entamoeba-derived exosomes was found to significantly reduce chemical and biological stimulant-induced oxidative burst and NETosis in neutrophils by fluorescence quantification, whereas co-culture-derived exosomes were able to more substantially delay NETosis and reduce NET release.

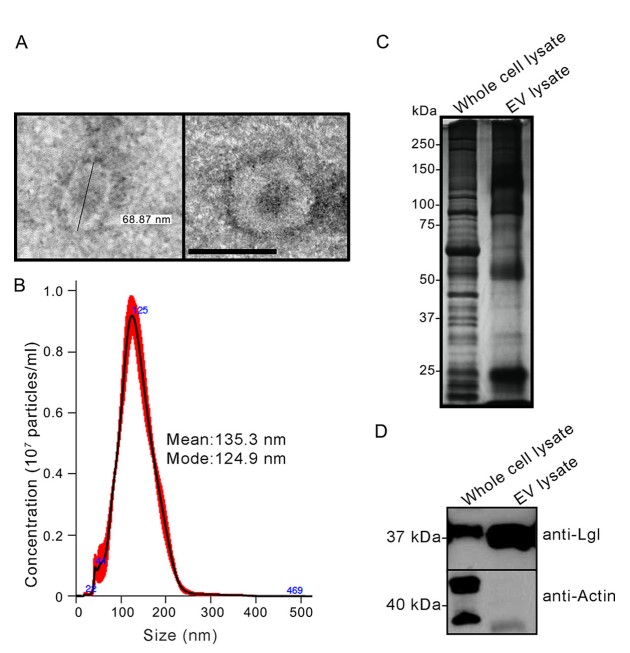 Fig. 1 Characterization of Entamoeba exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Characterization of Entamoeba exosomes.1
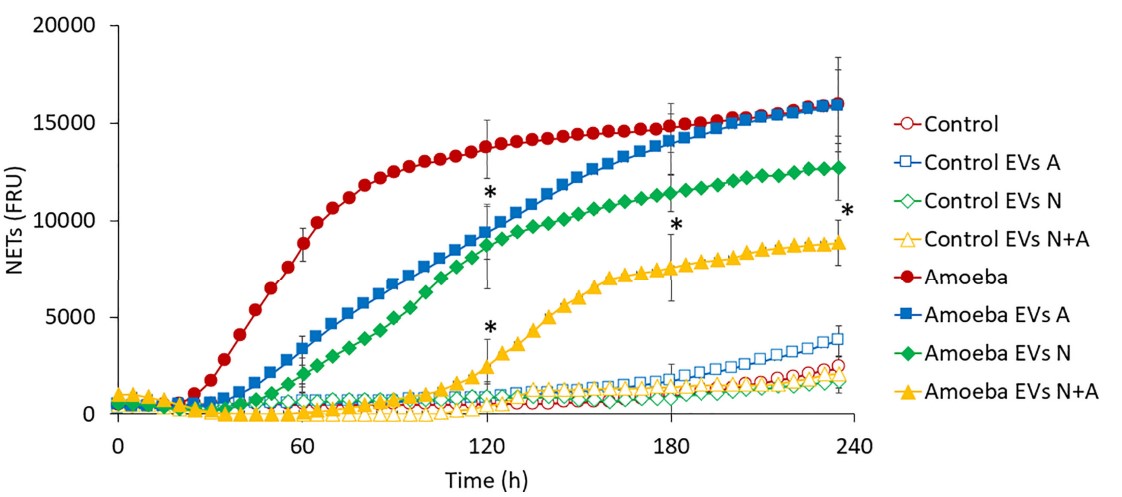 Fig. 2 Exosomes derived from Entamoeba regulated NETosis in Entamoeba histolytica-stimulated neutrophils.2
Fig. 2 Exosomes derived from Entamoeba regulated NETosis in Entamoeba histolytica-stimulated neutrophils.2








