Extracellular Vesicle mRNA Sequencing Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
The mRNA sequencing for EVs serves to study the gene expression patterns regulated by EVs and their role in various biological processes. Creative Biolabs provides not only mRNA sequencing services for EVs, but also combines various analytical services such as exosome proteomics and cytokines profiling, assisting clients to acquire an understanding of mRNAs and their functions in EVs.
Introduction to mRNA Sequencing for EVs
-
mRNA sequencing of EVs is a laboratory procedure used to analyze the gene expression of EVs and their sources. It involves the sequencing of transcripts (mRNA) to measure the relative abundance of different mRNA molecules in EVs from multiple biological samples (e.g., tissues, cell lines, or single cells).
-
mRNA sequencing of EVs is often performed in combination with other techniques such as genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to access a more comprehensive insight into the function of EVs in regulating gene expression. Sequencing can provide more information about mRNAs present in EVs, identifying the type, proportion, and expression level of mRNAs, thus allowing scientists to more accurately learn about the biological processes they may be involved in and to better understand their roles.
-
mRNA sequencing can also be used to explore the complexity of expression regulation, determine the structure and function of mRNAs in EVs, and provide important information for clinical treatment and diagnosis. For example, mRNA sequencing for EVs can identify disease mechanisms, enable early diagnosis of disease and design of therapeutic strategies, and identify molecular targets for drug development. Secondly, it can also contribute to monitoring disease activity and evaluating drug efficacy, as well as monitoring changes in patient status. Finally, it can further explore cellular signal transduction pathways.
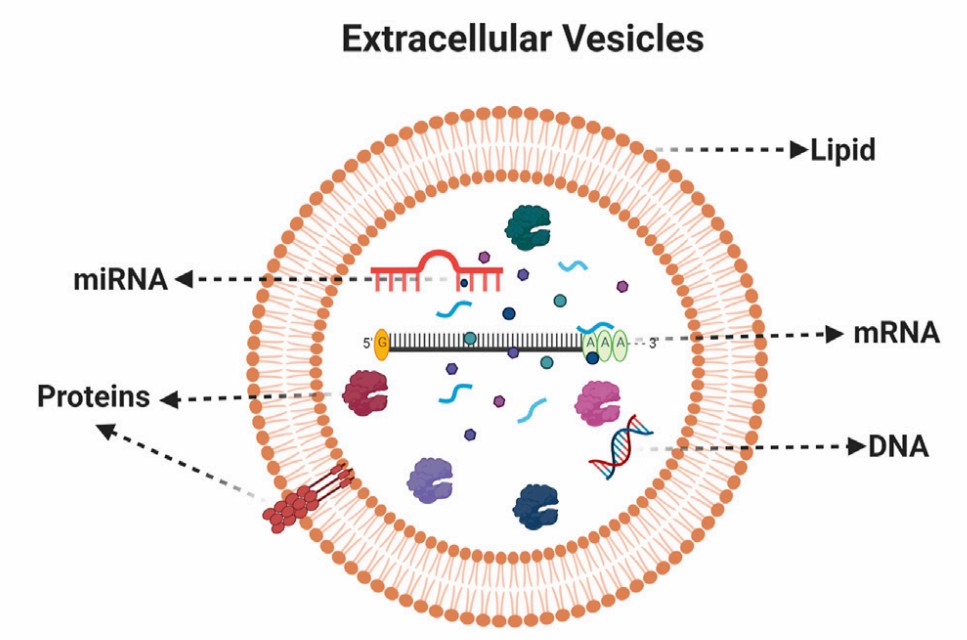 Fig.1 Composition of extracellular vesicles.1, 3
Fig.1 Composition of extracellular vesicles.1, 3
mRNA Sequencing Procedure for EVs at Creative Biolabs
-
The first step is to obtain samples. For EVs, samples can be cells, serum, or plasma from a variety of sources, and EVs can be separated based on characteristics such as lipid bilayer composition and size.
-
Secondly, separation and purification, to get enough mRNA in EVs, for sequencing.
-
Finally, make the actual sequencing, according to the requirements in terms of whole genome sequencing or target gene sequencing, to profile the mRNA information in EVs.
mRNA-seq Features
-
The mRNA-seq technique is commonly applied to reveal the function of genes, identify active genes, detect genes expressed at low levels, and compare differences between two samples or between one sample and a reference sample. It is often used to study the mRNA of EVs from different tissues and cellular sources, thus reflecting the differences in expressed genes in their donor to infer the functions and possible biological mechanisms of the genes involved.
-
It can also be available for locating RNA editing sites associated with EVs discovering novel genes and finding differential transcript levels, gene identification of mutation and rearrangement sites, and exploring sequence features. In addition, mRNA-seq allows for the detection and identification of transcription factor binding sites, as well as the generation of structural variants.
-
mRNA-seq accurately probes mRNAs and their distribution in EVs, allowing for greater insight into potential transcriptional events and their function. For example, it can be used to detect mRNAs within EVs that may be involved in cancer biological processes, including tumor-associated factors.
-
mRNA-seq can potentially lead to the identification of genes involved in extracellular EVs-based RNA molecules for other biological processes, such as inflammatory responses, immune responses, and lipid metabolism.
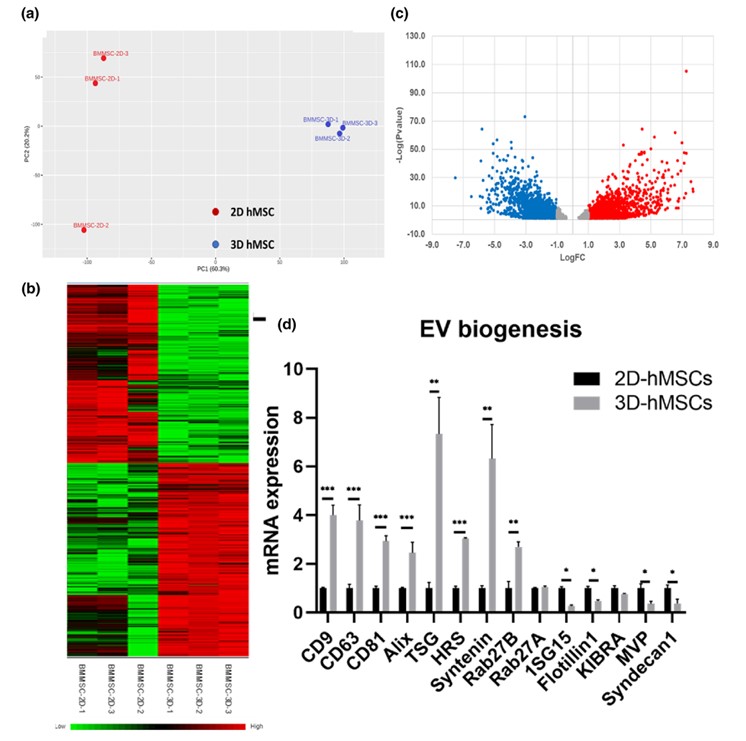 Fig. 2 mRNA sequencing of 2D vs. 3D hMSCs and EV biogenesis marker expression.2, 3
Fig. 2 mRNA sequencing of 2D vs. 3D hMSCs and EV biogenesis marker expression.2, 3
mRNA sequencing for EVs can identify mRNA species in EVs and the biological functions they are involved in, such as disease onset, immune and metabolic regulatory processes, etc. Creative Biolabs offers rapid-response mRNA sequencing services for EVs, and our dedicated experts are ready to advance your project. Please contact us for more information.
FAQs
Q: How is mRNA sequencing applied to extracellular vesicles?
A: mRNA sequencing of extracellular vesicles involves isolating EVs from biological fluids (such as blood or urine), extracting RNA from these vesicles, and then sequencing the mRNA transcripts present. This allows researchers to study the RNA content of EVs and understand their role in cellular signaling and disease.
Q: What are the potential applications of mRNA sequencing for extracellular vesicles?
A: Applications include biomarker discovery for various diseases, understanding disease mechanisms, monitoring treatment responses, and exploring the role of EVs in cell-to-cell communication.
Q: What are the advantages of using mRNA sequencing for studying extracellular vesicles?
A: mRNA sequencing provides high sensitivity and specificity in detecting RNA transcripts within EVs. It allows for unbiased profiling of RNA content, which can uncover novel biomarkers and pathways relevant to disease.
Q: How can you interpret the results of mRNA sequencing for extracellular vesicles?
A: Interpreting results involves analyzing differential gene expression, and identifying enriched pathways or biological functions. Bioinformatics tools and expertise are often required for comprehensive data analysis.
Q: What are some challenges associated with mRNA sequencing of extracellular vesicles?
A: Challenges include the small RNA yield from EVs, potential contamination from non-EV RNA, the heterogeneity of EV populations, and the need for sensitive detection methods to accurately profile low-abundance transcripts.
References
-
Gangadaran, Prakash, et al. "Application of cell-derived extracellular vesicles and engineered nanovesicles for hair growth: from mechanisms to therapeutics." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 10 (2022): 963278.
-
Yuan, Xuegang, et al. "Engineering extracellular vesicles by three‐dimensional dynamic culture of human mesenchymal stem cells." Journal of extracellular vesicles 11.6 (2022): e12235.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Composition of extracellular vesicles.1, 3
Fig.1 Composition of extracellular vesicles.1, 3
 Fig. 2 mRNA sequencing of 2D vs. 3D hMSCs and EV biogenesis marker expression.2, 3
Fig. 2 mRNA sequencing of 2D vs. 3D hMSCs and EV biogenesis marker expression.2, 3








