Extracellular Vesicle RNA Sequencing Services
Overview Services Features FAQs
RNA sequencing can serve to characterize the composition and function of EVs, as well as identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Creative Biolabs offers RNA sequencing and profiling services for multiple types of RNA in EVs, including transcriptome, miRNA, mRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA.
Overview
The investigation of the whole transcriptome of EVs in RNA sequencing enables the identification of genes expressed from the parental source of EVs, as well as the measuring of the abundance of specific transcripts, facilitating insight into the role played by EVs in health and disease. In addition, RNA sequencing serves to determine the amount of mRNA and non-coding RNA present in EVs, as well as to study post-transcriptional modifications of mRNA. These types of profiling can be used to identify biomarkers for diseases associated with EVs, examine the role of EVs in disease progression, and identify novel therapeutic targets and mechanisms.
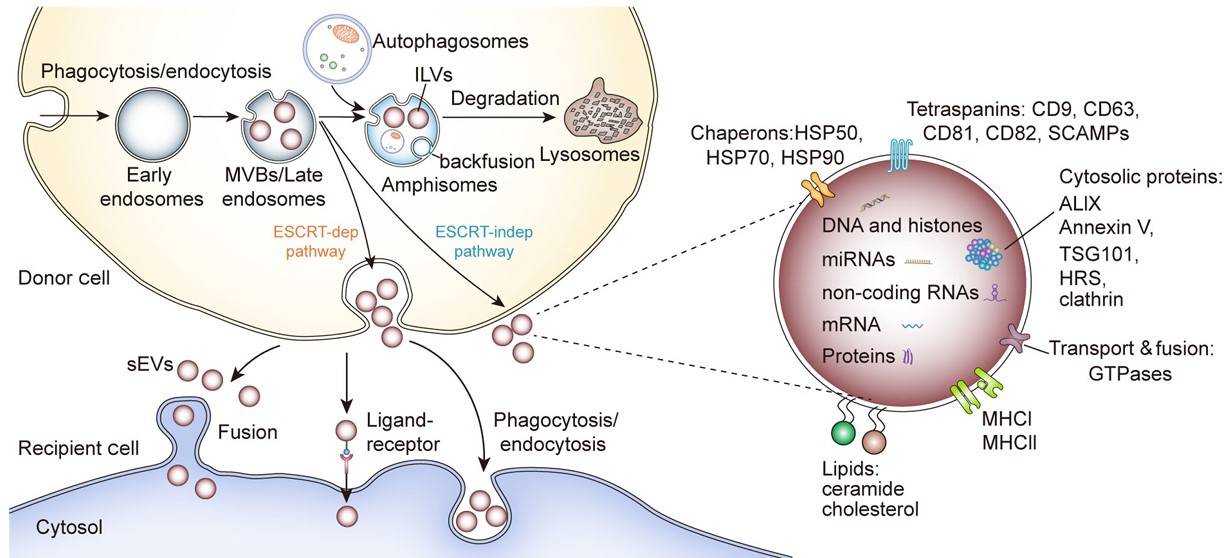 Fig.1 sEV biogenesis, cargo contents and uptake.1
Fig.1 sEV biogenesis, cargo contents and uptake.1
RNA Sequencing Services for EVs at Creative Biolabs
RNA sequencing services for EVs provide important insights into the nature of RNA cargo based on the intercellular transfer of EVs, contributing to the elucidation of the mechanisms by which EVs interact with their environment as well as the molecular mechanisms associated with their potential regulatory and therapeutic effects. Creative Biolabs offers the following RNA sequencing services for EVs, among others:
RNA Sequencing Procedures as below,
-
Isolation of EVs: EVs can be isolated from the sample using a variety of techniques, including ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography, and immunoaffinity purification.
-
Purification of RNA from EVs: RNA can be isolated from the isolated EVs using a variety of methods, including phenol-chloroform extraction and column-based purification.
-
cDNA Synthesis: Reverse transcription can be used to create cDNA from the purified RNA.
-
Library Preparation: cDNA libraries can be prepared for sequencing, using PCR-based methods.
-
Sequencing of Libraries: The libraries can be sequenced using either next-generation sequencing or Sanger sequencing.
-
Data Analysis: To find and measure expressed genes, bioinformatics techniques can be used to analyze the sequencing data.
Features
-
Comprehensive Analysis: Our RNA sequencing services are specifically tailored for EVs, providing a deep understanding of the RNA content within these tiny mediators of cell communication.
-
High-Throughput: Using state-of-the-art sequencing platforms, we offer high-throughput analysis, enabling the sequencing of millions of RNA molecules simultaneously, and helping you to uncover novel biomarkers and genetic signatures of EVs.
-
Customizable: Our service is customizable to meet your specific research needs. We can adjust our protocols accordingly, whether it's targeted sequencing, whole transcriptome analysis, or specific RNA types (e.g., miRNA, lncRNA).
-
Quality Control: Each step of our RNA sequencing process is subject to rigorous quality control measures to ensure the integrity and reliability of your data. This includes the validation of EV isolation methods, the integrity of the RNA, and the quality of the sequencing libraries.
RNA sequencing for EVs supports the exploration of the molecular composition of EVs and the biological processes they are involved in, helping to better understand the mechanisms of EV-mediated communication between cells and tissues, which can be used to develop new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Creative Biolabs offers RNA sequencing services with an innovative molecular analysis platform for EVs. Please contact us with your demands.
FAQs
Q: What types of RNA can be analyzed through your service?
A: Our service can analyze a wide range of RNA types including mRNA, microRNA (miRNA), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), and small interfering RNA (siRNA) among others, depending on the customer's specific needs and sample preparation.
Q: How are the extracellular vesicles isolated before sequencing?
A: The isolation of EVs depends on the sample source and the downstream application, but common techniques include ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography, and immunoaffinity capture. We can tailor the isolation method to match the RNA that is being targeted or the customer's specific requirements.
Q: How should the sample be prepared for RNA sequencing?
A: Our preparation starts with isolating high-quality RNA from EVs. This is followed by DNase treatment to remove DNA contaminants, RNA cleanup, and quantification. We can provide sample preparation services or guide you through the process if you prefer to handle it in-house.
Q: How is the data analyzed?
A: After sequencing, data is processed through a pipeline that involves quality control, alignment to a reference genome or transcriptome, and quantification of transcript abundances. We can offer differential expression analysis, pathway analysis, and more, depending on your research objectives. We can help with the understanding of the outcomes and offer customization options for the data analysis.
Q: Are there any limitations to RNA sequencing for extracellular vesicle analysis?
A: One limitation can be the low abundance of RNA in some EV samples. Additionally, the small size of some RNA species (e.g., miRNA) can sometimes pose challenges in library preparation and sequencing. Our skilled team and well-optimized processes, however, are prepared to tackle these difficulties.
Reference
-
Gao, Yanan, et al. "Small extracellular vesicles: a novel avenue for cancer management." Frontiers in Oncology 11 (2021): 638357. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 sEV biogenesis, cargo contents and uptake.1
Fig.1 sEV biogenesis, cargo contents and uptake.1









