Aloe-derived Exosome Research and Application
Aloe vera-derived exosomes show potential benefits for a variety of applications, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, etc. Creative Biolabs is committed to providing professional scientific research services, focusing on helping clients with the isolation and functional exploration of plant exosomes, including Aloe vera-derived exosomes.
Isolation of Aloe vera-derived Exosomes
-
Wash aloe vera with distilled water.
-
Save Aloe Vera gel or Aloe Vera peel as desired and then mix with cold PBS.
-
Pulverize into aloe vera juice in the blender.
-
Filter the aloe vera juice mixture.
-
Remove tissue residue and cellular debris by differential centrifugation.
-
Wash and resuspend Aloe-derived exosomes.
-
Tangential flow filtration to concentrate the Aloe-derived exosome product.
Optimization of the isolation strategy: Large vesicles due to vesicle aggregation are easily removed and reduce the efficiency of drug delivery, making it necessary to optimize the isolation method to obtain high-quality exosomes.
-
Optimize the centrifugation time to balance the yield and quality of exosomes.
-
Optimize the ratio of Aloe vera juice to PBS to reduce the viscosity of the system to improve isolation efficiency and yield.
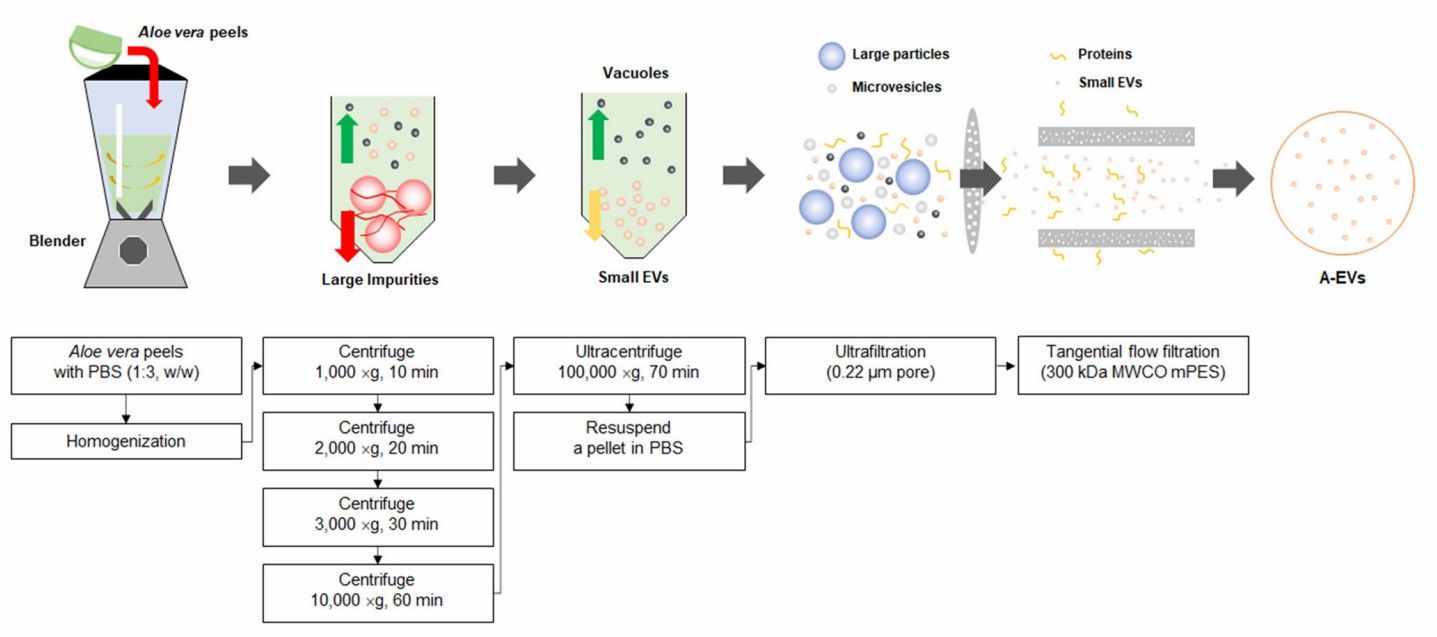 Fig. 1 Isolation of Aloe vera-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Isolation of Aloe vera-derived exosomes.1
Research on Aloe vera-derived Exosomes
|
Research item
|
Conclusion
|
|
Lipidomics analysis
|
-
Glucose ceramide is the major lipid type of Aloe exosomes and has the property of promoting or inducing membrane curvature in exosome formation and secretion.
-
Phosphatidic acid engages in exosome uptake processes by regulating membrane fission and fusion.
-
Components such as phosphatidylcholine and galactosyl diacylglycerol play roles in mitigating oxidation in exosome storage and stabilizing phospholipids in cryopreservation, respectively.
|
|
High performance liquid chromatography analysis
|
Aloe-emodin, aloesin, and β-sitosterol were detected in exosomes isolated from both Aloe vera gel and Aloe vera peel. these phytochemicals with antioxidant properties make Aloe vera exosomes suitable for use as stable drug carriers.
|
|
Stability assessment
|
Compared to liposomes, Aloe vera-derived exosomes showed better stability in the complex environment of peroxide radicals or detergents.
|
|
Safety Assessment
|
-
The results of the cell viability assay showed no significant cytotoxicity of Aloe vera-derived exosomes.
-
Hemolysis tests show that Aloe-derived exosomes are safe for red blood cells and can be administered by intravenous injection.
-
Serum pro-inflammatory factors and histologic staining revealed that Aloe vera-derived exosomes do not stimulate levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines or cause significant organ injury.
|
|
Efficacy in drug delivery applications
|
Aloe vera exosomes were able to deliver antitumor drugs, imparting excellent antitumor efficacy and exhibiting a wider range of penetration in the skin in a mouse melanoma tumor model that was independent of longer storage.
|
|
Evaluation of antioxidant activity
|
Aloe vera exosomes exert antioxidant effects by upregulating the expression of some antioxidant enzymes (HO-1, CAT, SOD) and mitigating cellular damage by the large number of free radicals generated by oxidative environmental stimuli.
|
|
Evaluation of pro-repair properties
|
Aloe exosomes exhibit good cytocompatibility and are taken up by cells through endocytosis mediated by lattice proteins, and cytoplasmic membrane microvesicles. In the wound healing cell assay, Aloe exosomes demonstrated pro-repair potential by promoting the growth and migration of epidermal cells and fibroblasts.
|
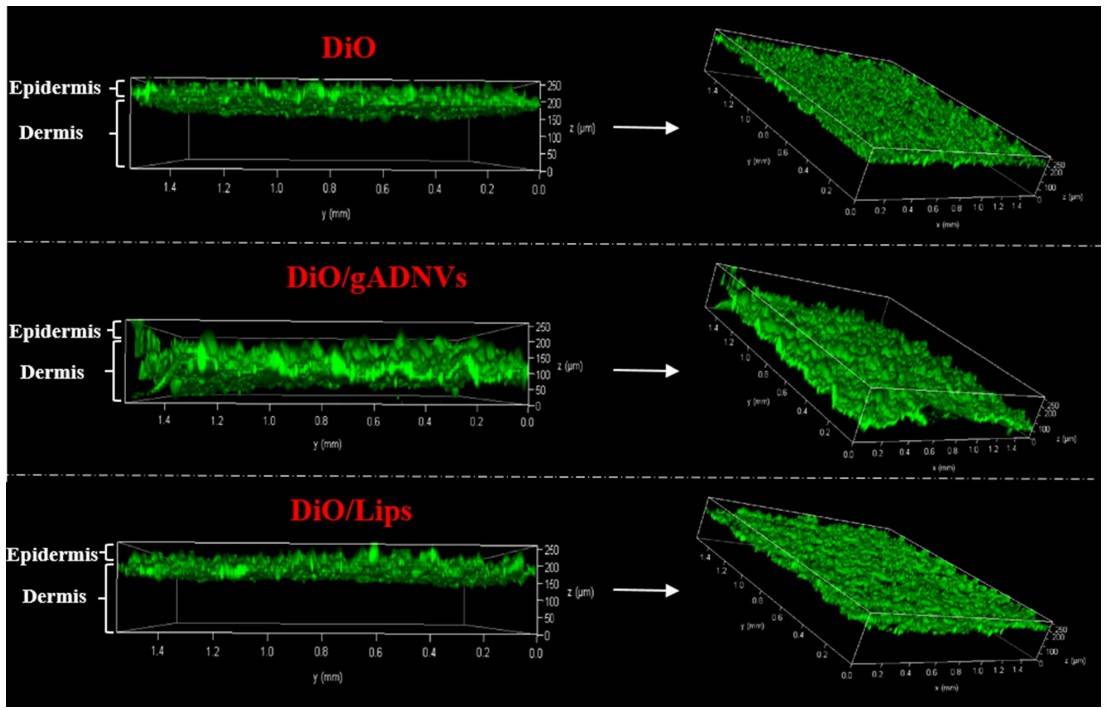 Fig. 2 Aloe-derived exosomes excel in skin permeation.2
Fig. 2 Aloe-derived exosomes excel in skin permeation.2
Aloe Vera exosomes have the potential to counteract oxidative damage to the skin caused by harsh environments and have great potential to be used in skin repair and anti-aging-related exosomes. Creative Biolabs provides professional services on plant-derived exosomes to help you evaluate the potential of exosomes including those from Aloe Vera. Please contact us for customized support for your project.
References
-
Kim, Min Kang, et al. "The antioxidant effect of small extracellular vesicles derived from aloe vera peels for wound healing." Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine 18 (2021): 561-571.
-
Zeng, Lupeng, et al. "Aloe derived nanovesicle as a functional carrier for indocyanine green encapsulation and phototherapy." Journal of Nanobiotechnology 19 (2021): 1-24.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Isolation of Aloe vera-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Isolation of Aloe vera-derived exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Aloe-derived exosomes excel in skin permeation.2
Fig. 2 Aloe-derived exosomes excel in skin permeation.2









