Tea-derived Exosome Research and Application
Tea-derived exosome is a natural bioactive substance with good biocompatibility and bioactivity that has promising prospects for extensive applications. It can be used as a drug vehicle, nutritional supplement, functional food, and cosmetic additive in medical, nutritional, and cosmetic fields, etc. Creative Biolabs has experienced scientists in the field of exosomes and can help clients explore tea-derived exosomes in depth.
Isolation Strategy
-
Breaking of tea cells: Tea cells first need to be broken to release their contents. This can be done by physical methods (e.g. ultrasonic breaking), chemical methods (e.g. using solvents), or biological methods (e.g. using enzymes).
-
Coarse separation: The exosomes then need to be coarsely separated. This can be achieved by different methods such as high-speed centrifugation, ultrafiltration, or affinity chromatography. These methods are able to separate exosomes from other cellular debris and macromolecules based on their different physical and chemical properties.
-
Purification: After crude separation of exosomes, they need to be purified. There are two main methods of purification: immunoaffinity chromatography and density gradient centrifugation. Immunoaffinity chromatography is able to separate exosomes based on the interaction between specific antigens and antibodies on the surface of the exosomes, while density gradient centrifugation separates exosomes based on their different sizes and densities.
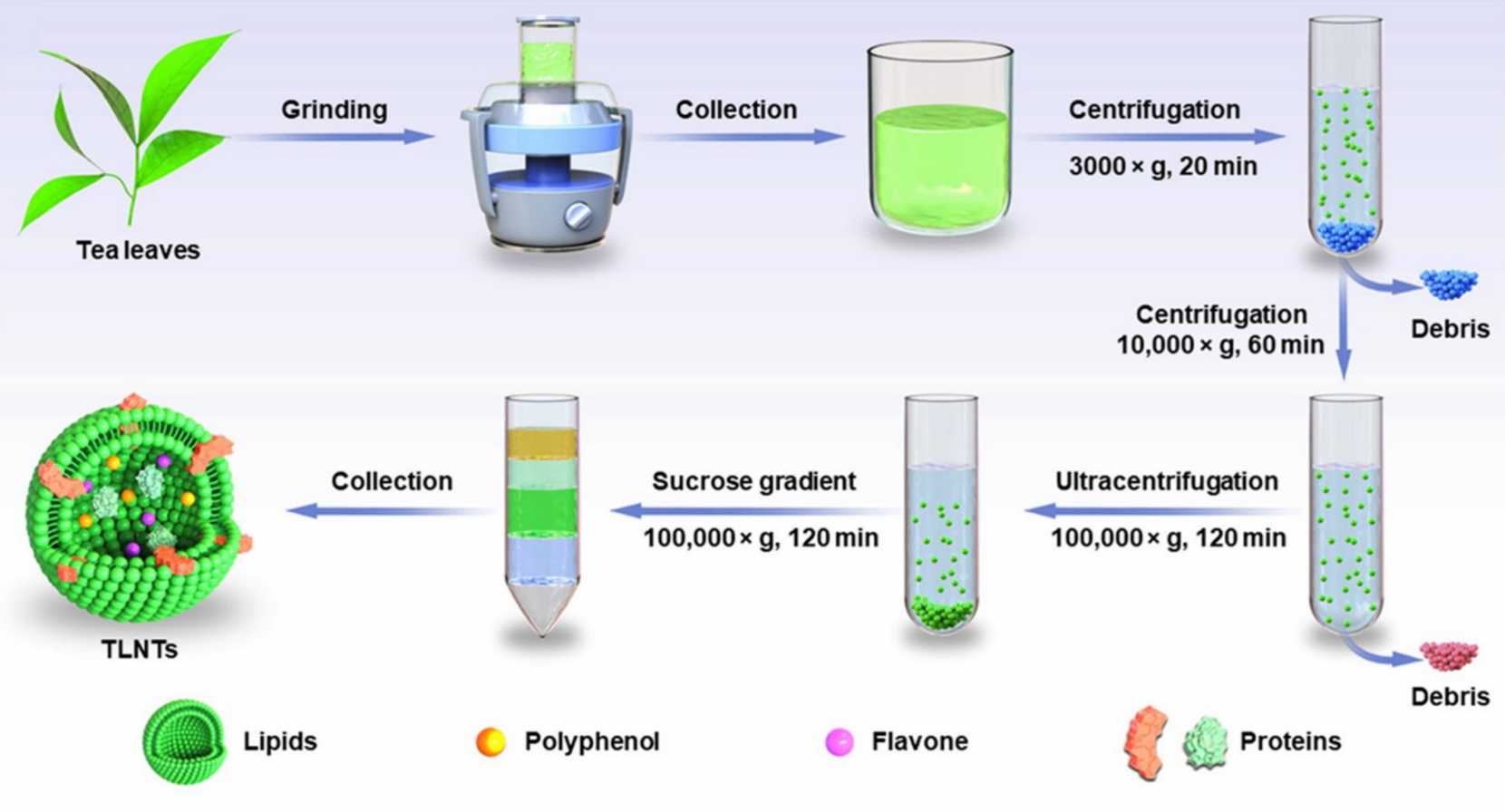 Fig. 1 A production process for tea-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 A production process for tea-derived exosomes.1
Components of Tea-derived Exosomes
-
Bioactive molecules. Includes an abundance of proteins and nucleic acids associated with catalytic activity, metabolism, cancer, and immune diseases. These molecules are known to perform important effects in intercellular communication and signal transduction.
-
Lipids. Includes amphiphilic lipid molecules such as phosphatidylcholine, triglycerides, and diacylglycerol, which are the main components of vesicles and are of great relevance in maintaining a stable structure.
-
Metabolites. Tea exosomes also contain a number of metabolites such as tea polyphenols and caffeine. These compounds exhibit several bioactive properties such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, etc.
-
Enzymes and other proteins. Tea exosomes also contain a number of enzymes and other proteins, such as antioxidant enzymes and transporter proteins. These proteins contribute significantly to cellular metabolism and signaling.
Tea-derived Exosomes Features and Functions
|
Features
|
Functions
|
-
Associated with beneficial effects of tea.
Tea-derived exosomes are closely related to the health benefits of tea. A variety of beneficial components in tea, such as tea polyphenols, caffeine, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, are contained in exosomes. These components have multiple benefits in maintaining human health.
-
Natural components derived from tea.
Tea-derived exosomes are derived from natural components in tea leaves and have the advantage of being natural and safe. It can be used as a drug carrier to deliver drugs to the target cells while utilizing the health benefits found in tea.
-
It has good biocompatibility and bioactivity.
Tea-derived exosome has good biocompatibility and bioactivity and can interact with human cells and perform its functions. It can be used as a drug carrier to improve drug efficacy and reduce toxic side effects.
|
-
Regulates metabolism.
Tea-sourced exosomes regulate the body's metabolic processes, promoting energy expenditure and lipolysis, contributing to weight loss and improved cardiovascular health.
-
Improves immunity.
Tea-derived exosomes are rich in antioxidants and antimicrobial peptides, among other components, which can boost immunity, fight infection and inflammation, and prevent disease.
-
Transmits biological signals.
Tea-derived exosomes can transmit biological signals, regulate intercellular communication and signal transduction, and maintain the normal function of body tissues and organs.
|
Application Research of Tea-derived Exosomes
-
As drug carriers.
Tea-derived exosomes have good biocompatibility and bioactivity and can be used as drug carriers to deliver drugs to target cells, improve drug efficacy, and reduce toxic side effects.
-
As nutritional supplements.
Tea-derived exosomes are rich in a variety of beneficial components and can be used as nutritional supplements to provide the nutrients needed by the body and promote health.
-
As functional food.
Tea-derived exosomes can be used in the development of functional foods, providing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other health benefits that help prevent and improve chronic diseases.
-
For cosmetic additives.
Tea-derived exosomes provide a variety of skincare benefits such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and can be used as cosmetic additives to improve the efficacy and safety of skin care products.
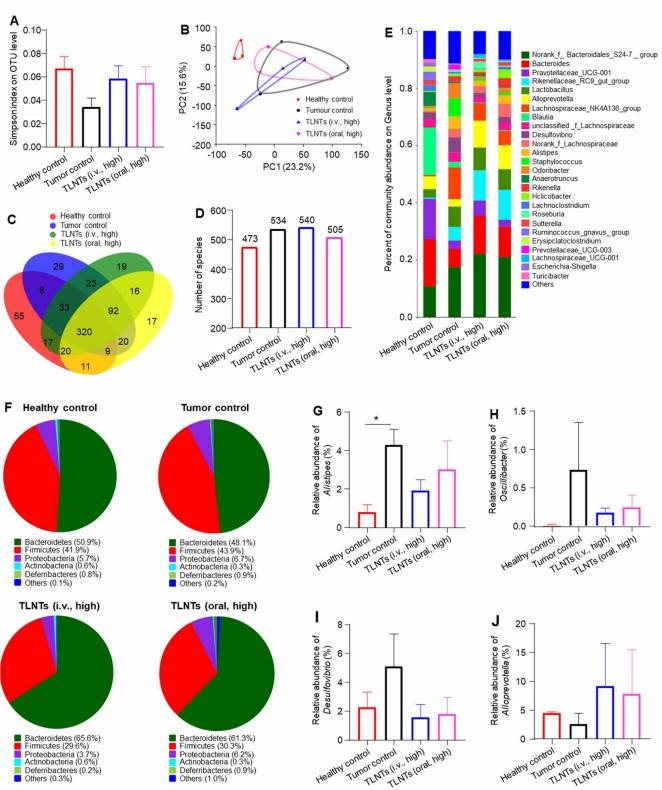 Fig. 2 Tea-derived exosomes remodel the gut microbiota.1
Fig. 2 Tea-derived exosomes remodel the gut microbiota.1
All in all, tea-derived exosomes, as a vesicle-structured bioactive substance isolated from tea, have a variety of health benefits and potential applications. Creative Biolabs has long been committed to providing customers with exosome production development and functional exploration services, including tea-derived exosomes. Please contact us to bring your interest.
Reference
-
Chen, Qiubing, et al. "Tea leaf-derived exosome-like nanotherapeutics retard breast tumor growth by pro-apoptosis and microbiota modulation." Journal of Nanobiotechnology 21.1 (2023): 1-19.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 A production process for tea-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 A production process for tea-derived exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Tea-derived exosomes remodel the gut microbiota.1
Fig. 2 Tea-derived exosomes remodel the gut microbiota.1









