Centella-derived Exosome Research and Application
Various plants give rise to different biologically active secondary metabolites, which are widely used in various skin care directions such as anti-aging and anti-inflammatory soothing. Exosomes have been found to have similar regulatory effects, and it is hypothesized that secondary metabolites from plants may be encapsulated in their secretion process. The active ingredients of Centella asiatica origin may be loaded in its exosomes, showing potential applications in skin care. Creative Biolabs is pleased to provide production pilot tests and functional investigation services related to Centella-derived exosomes to advance the understanding of Centella-derived exosomes.
Overview of Centella asiatica and Its Extracts
-
The main constituents of Centella asiatica are pentacyclic triterpenoids, of which the most abundant bioactive substances include Centella asiatica glycosides, hydroxy Centella asiatica glycosides, and their glycosides, Centella asiatica acid and hydroxy Centella asiatica acid.
-
Centella and its extracts have been found to promote wound healing, reduce hyperpigmentation, treat scarring, antimicrobial, and endocrine regulation in pharmacological tests.
-
Centella and its related components are useful in the treatment of acne, vitiligo, diabetes-related dermatological disorders, and psoriasis, as well as in the postoperative repair of skin phototherapy.
Isolation of Centella Exosomes
-
Mixing sterilized PBS with Centella asiatica
-
Breaking into Centella juice using a crusher
-
Centrifuge Centella juice at low speed and filter to remove large residue.
-
Centrifuge at high speed and take the supernatant
-
Multiple ultra-high speed centrifugations to obtain Centella exosome precipitates.
-
Resuspend Centella-derived exosomes in sterile PBS.
Centella Derived Exosomes Features
-
Centella asiatica-derived exosomes are internally encapsulated with a variety of active secondary metabolites as well as nucleic acid components with regulatory roles.
-
The phospholipid bilayer of Centella exosomes not only helps to protect the internal active components but also passes through the interstitial space of the skin's stratum corneum to make it easier for the active components it contains to be taken up by the cells and to exert their efficacy.
-
The application of Centella exosomes for skin scar prevention and relief is possible, and they can be further mixed with components such as moisturizers and stabilizers to promote their scar-improving effects in wound healing.
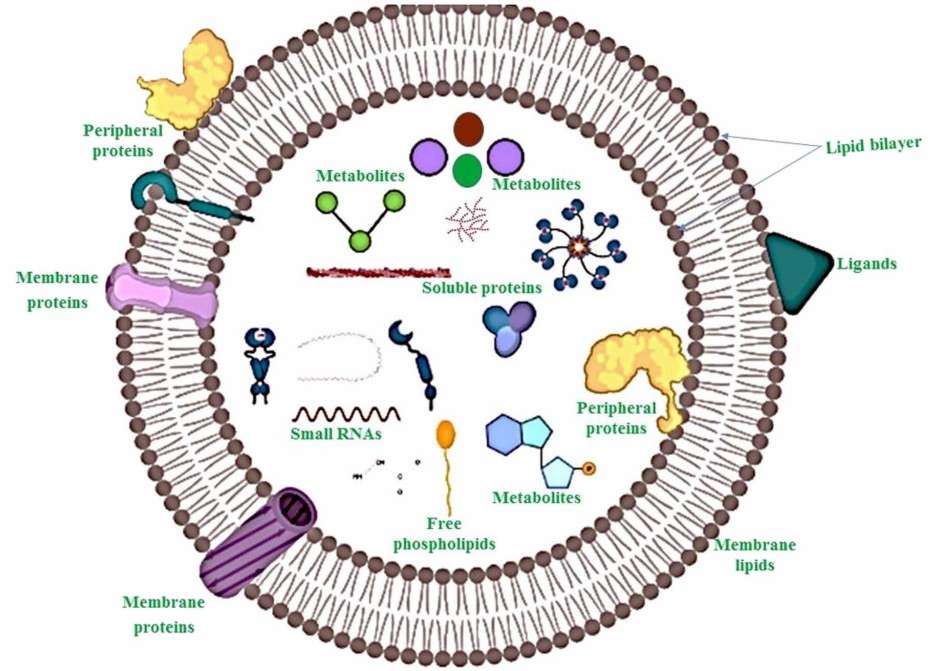 Fig. 1 Structure of Plant-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Structure of Plant-derived exosomes.1
Research Progress of Centella asiatica-derived Agents
|
Functions
|
Studies
|
|
Anti-inflammatory
|
Centella asiatica phospholipid complexes showed significant anti-inflammatory effects in a mouse model of phthalic anhydride-induced atopic dermatitis. Hydroxy Centella asiatica phospholipids significantly inhibited the nuclear translocation of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-2β, Toll-like receptor 1, and NF-κB in THP-1 human monocytes stimulated by Propionibacterium acnes and inhibited acne formation.
|
|
Promoting skin damage repair
|
Centella extract enhances the migratory activity of human keratinocytes in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. They also promoted wound repair by promoting fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis during the early stages of repair and exhibited some antimicrobial activity.
|
|
Antioxidant and anti-aging
|
Phenolics contained in Centella extract preparations have been associated with slowing down skin photoaging effects by scavenging ROS. Plant compositions containing Centella extract reduced oxidative stress-induced telomere shortening in fibroblasts and inhibited the accumulation of glycated substances.
|
|
Ameliorating skin barrier hydration
|
Centella asiatica glycosides acted to enhance skin hydration by increasing water channel protein 3 expression, promoting hyaluronic acid secretion in human dermal fibroblasts, and decreasing transepidermal water loss in a methyl nicotinate model.
|
|
Anti-scarring
|
In a rabbit ear scar model, oral administration of Centella asiatica glucoside was able to inhibit keloid formation by inhibiting the expression of collagen I and III and TGF-β and promoting the expression of Smad7 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Gel preparations of Centella extracts show better efficacy.
|
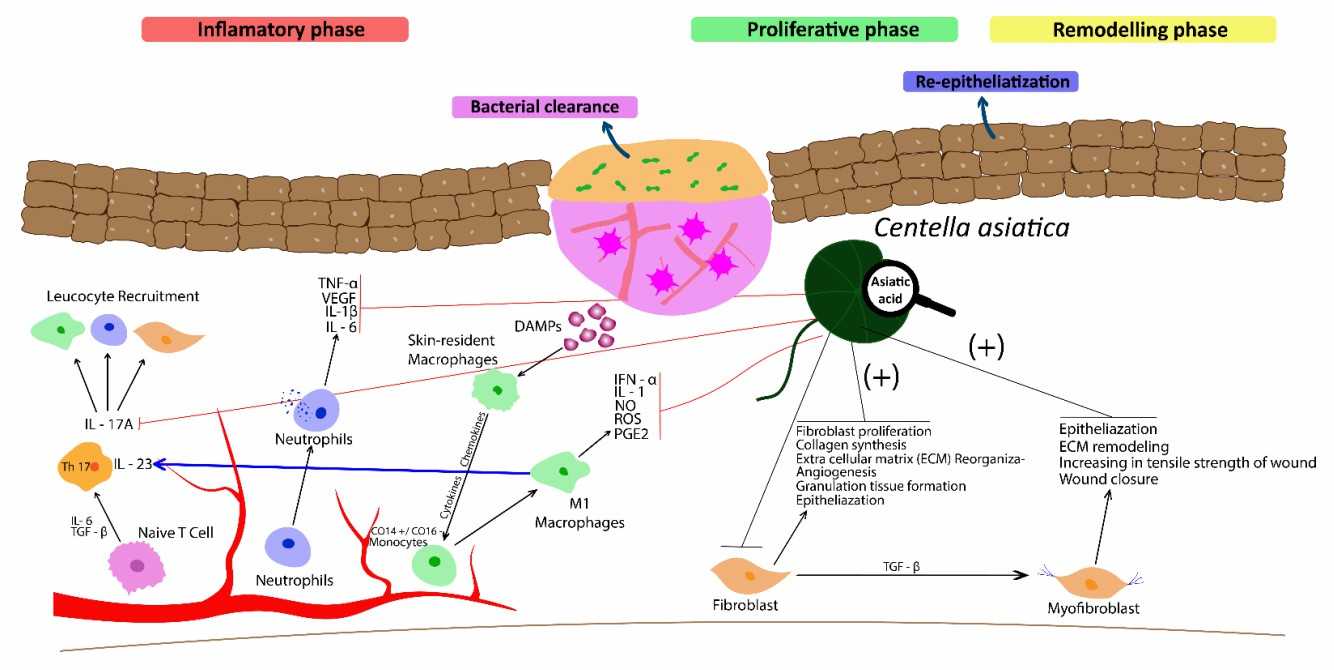 Fig. 2 Efficacy of Centella asiatica and its biological components in wound healing.2
Fig. 2 Efficacy of Centella asiatica and its biological components in wound healing.2
Centella-derived exosomes may possibly encapsulate a variety of active ingredients from Centella asiatica within their generation process, making Centella-derived preparations more valuable to utilize in cosmetic dermatology. Creative Biolabs focuses on continuously innovating the development and research platforms of flower-derived exosomes including Centella asiatica exosomes, providing customized services to clients for relevant projects. Please contact us to advance your project.
References
-
Nemati, Mohadeseh, et al. "Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel nanomedicine approach with advantages and challenges." Cell Communication and Signaling 20.1 (2022): 69.
-
Diniz, Lúcio Ricardo Leite, et al. "Centella asiatica and Its Metabolite Asiatic Acid: Wound Healing Effects and Therapeutic Potential." Metabolites 13.2 (2023): 276.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Structure of Plant-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Structure of Plant-derived exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Efficacy of Centella asiatica and its biological components in wound healing.2
Fig. 2 Efficacy of Centella asiatica and its biological components in wound healing.2









