App1-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
Cryptococcal meningoencephalitis is an important cause of more than 15% of deaths in HIV patients worldwide and is currently the most common cause of nonviral meningitis in the United States. Cryptococcus can survive and replicate within macrophages by evading surveillance by the immune system or regulating host cells. Part of the reason is that Cryptococcus can secrete antiphagocytic protein 1 (App1) to inhibit macrophage-driven fungal phagocytosis to evade phagocytosis and increase infection capacity. However, App1 holds great promise in exosome drug delivery. Exosomes have been developed into a new generation of drug delivery vehicles due to their good stability, biocompatibility, permeability, and low immunogenicity. However, engineered exosomes are exogenous after all, and a part of engineered exosomes entering the body's circulation will be cleared by the body's immune system. What's more, phagocytes play a key role in this process. In order to strengthen the ability of engineered exosomes to stay in the body so that they can better reach target tissues and release drugs, it is especially important to modify proteins that can inhibit phagocytosis of phagocytic cells on the surface of exosomes. Therefore, researchers have proposed to modify App1 on the surface of exosomes to increase the ability of exosomes to escape phagocytosis. Creative Biolabs can construct App1-expressed exosomes through exosome membrane protein modification or exosome membrane surface modification, helping customers to further develop the therapeutic potential of exosome carriers.
App1 Overview
Cryptococcus is a yeast-like fungus that can cause an infection of lung tissue. After Cryptococcus infects the human body, its outcome in macrophages at least includes phagocytosis, replication, non-lytic exocytosis, and lateral transfer. As the first line of immune defense, macrophages can quickly identify, phagocytize and destroy pathogens. But avoiding phagocytosis to escape oxidative stress and nutrient deficiency is central to the pathogenesis of Cryptococcus. Studies have found that App1 secreted by Cryptococcus plays a key role in the survival of Cryptococcus. During phagocytosis, App1 can bind to Complement Receptor 2 / Complement Receptor 3 (CR2/CR3), thereby inhibiting the phagocytosis of cryptococcus by macrophages. More seriously, escaped Cryptococcus can spread from the lungs to the brain, causing fatal cryptococcal meningitis. The virulence factor App1 of Cryptococcus can be applied to exosome drugs to exert their anti-phagocytic ability, which can increase the half-life of exosome drugs.
 Fig.1 Increased expression of virulence genes in old cells.1,3
Fig.1 Increased expression of virulence genes in old cells.1,3
Exosome Modification Method with App1
Currently, exogenous or endogenous exosome modifications have been widely used to endow exosomes with targeting properties. Furthermore, modifying the anti-phagocytic protein App1 on the surface of exosomes can endow the exosomes with anti-phagocytic ability, thereby improving the therapeutic effect of exosome drugs in the body. One method is to construct a fusion expression plasmid of the App1 gene and exosome membrane surface marker protein (such as CD9, CD63, or Lamp2b). This plasmid is then transfected into parental cells. The surface of exosomes secreted by the parental cells bears App1 protein so that these exosomes acquire anti-phagocytic ability. Another method is to construct the App1 protein with polyethylene glycol as a lipid assembly. The assembly can be attached to the surface of exosomes by interacting with phospholipid molecules on the exosome membrane.
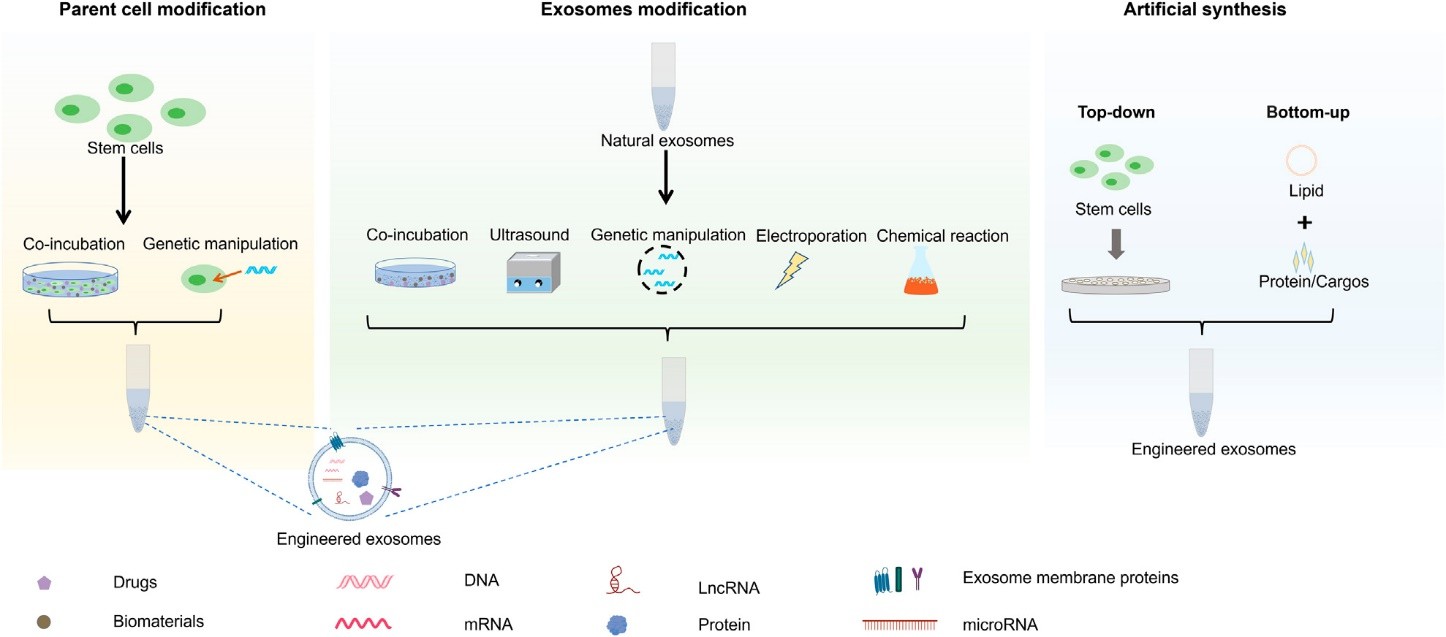 Fig.2 Illustration of the synthesis of engineered stem cell exosomes.2,3
Fig.2 Illustration of the synthesis of engineered stem cell exosomes.2,3
Creative Biolabs is a biomedical service company that provides experimental services in the biomedical field. We have virus platform, cell platform, exosome platform, molecular platform, pathology platform, and bioinformatics platform, and are committed to providing global customers with one-stop experimental outsourcing services, including exosome isolation, identification, content analysis, engineering, exosome next-generation sequencing, and in vivo and in vitro functional research. If you want to increase the half-life of exosomes in the body, you can contact us. Our professional team can construct App1-expressed exosomes to maximize the efficacy of exosome drugs.
References
-
Orner, EP.; et al. Cell wall-associated virulence factors contribute to increased resilience of old cryptococcus neoformans cells. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2019, 10:2513.
-
Hao, M; et al. Engineered stem cell exosomes for oral and maxillofacial wound healing. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 2022, 10:1038261.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Increased expression of virulence genes in old cells.1,3
Fig.1 Increased expression of virulence genes in old cells.1,3
 Fig.2 Illustration of the synthesis of engineered stem cell exosomes.2,3
Fig.2 Illustration of the synthesis of engineered stem cell exosomes.2,3








