CD24-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
The cluster of differentiation 24 (CD24) is a glycoprotein that releases antiphagocytic signals. Previous studies have shown that many tumors, especially ovarian cancer and breast cancer, specifically highly express CD24, which is related to the immune escape of tumor cells. Thinking about this in reverse, CD24 can be used for drugs that are not intended to be cleared by the body. As nanovesicles of natural origin, exosomes have been described as efficient delivery vehicles for many drugs. Although exosomes have brought promise in the field of novel medicine, exosomes are easily taken up by the mononuclear-phagocyte system in vivo, limiting their accumulation at the lesion site. Some researchers have proposed that CD24 may be modified on exosomes to inhibit the uptake of exosomes by phagocytes and improve the efficiency of exosomes reaching target organs. This can improve the utilization of exosomes as drug-delivery vehicles. Creative Biolabs can design CD24-expressed exosomes for customers to greatly enhance their therapeutic potential.
CD24 Overview
CD24 is a highly glycosylated adhesion protein without a transmembrane domain and is anchored to the cell membrane through glycosyl-phosphatidyl-inositol. In this physiological state, CD24 acts as a brake on the human immune system, suppressing excessive immune responses. In recent years, a large amount of literature have shown that CD24 is overexpressed in various human malignant tumors, such as breast cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, etc., which can promote cancer cell adhesion, growth, proliferation, invasion, and metastasis while inhibiting cancer cell apoptosis. CD24 is known to be the natural ligand for the inhibitory receptor Siglect-10 expressed on tumor-associated macrophages. The combination of CD24 and Siglect-10 can inhibit the phagocytic signaling cascade reaction and cytoskeleton rearrangement in macrophages, so that the tumor cannot be cleared by phagocytosis, thereby promoting the immune escape of the tumor. Further experiments proved that blocking CD24/Siglec-10 signaling can restore phagocytosis of macrophages, and then re-attack tumor cells. Therefore, CD24 is considered to be a potential target for future tumor immunotherapy, as well as a functional protein that can endow exosomes with anti-phagocytic properties.
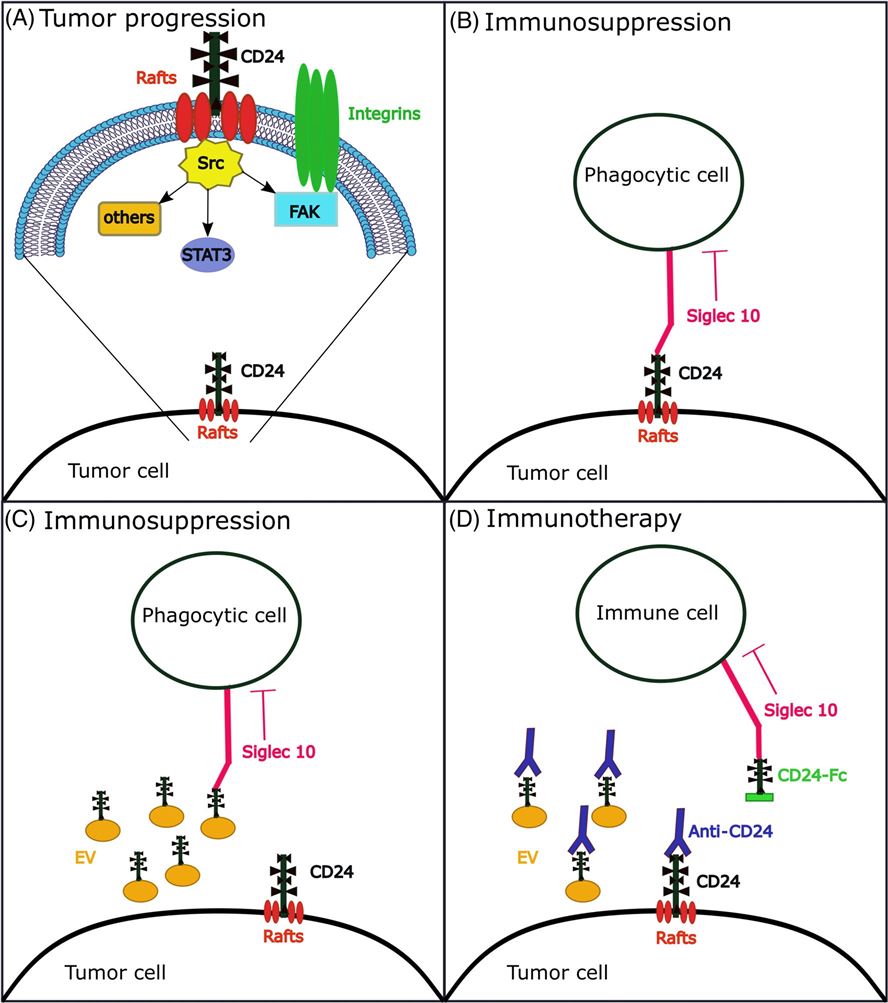 Fig.1 The functional role of CD24 in oncoimmunology.1,2
Fig.1 The functional role of CD24 in oncoimmunology.1,2
Strategy for Modifying Exosome with CD24
Currently, a variety of exosome surface engineering strategies have been developed and can be used for the design of CD24-expressed exosomes.
-
Fusion expression with exosome membrane-localized protein. The strategy is to fuse CD24 with proteins abundant on the surface of exosome membranes, such as Lamp2b, CD63, or PDGFR, to achieve overexpression of CD24 on the surface of exosomes.
-
Post-isolation modification of exosomes. This strategy includes a variety of combined approaches. The first approach is to insert lipid-conjugated CD24 onto phospholipids in exosomes. The second method is to combine CD24 and exosomes with different linker molecules that can bind to each other, and then connect CD24 to the surface of exosomes by chemical conjugation methods such as click chemistry. The third approach is to conjugate biotin on the surface of exosomes. Due to the high binding affinity between streptomycin (SA) and biotin, SA-coupled CD24 can bind to the surface of exosomes.
Creative Biolabs is the world's leading technical service provider in the field of exosomes and has always been committed to continuously launching new technologies around customer needs. We have established a stable and mature exosome engineering transformation platform, which can construct innovative CD24-expressed exosomes for customers through endogenous modification or exogenous modification and verify its anti-phagocytosis ability in vivo and in vitro. In addition, we can also provide customers with a full range of engineered exosome solutions through leading exosome isolation and identification tools and innovative high-throughput multi-omics solutions. If you are interested in CD24-expressed exosomes, please contact us to put forward your specific needs so that our team can develop an experimental plan for you more quickly.
References
-
Altevogt, P.; et al. Novel insights into the function of CD24: A driving force in cancer. International Journal of Cancer. 2021, 148(3):546-559.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The functional role of CD24 in oncoimmunology.1,2
Fig.1 The functional role of CD24 in oncoimmunology.1,2








