CD44-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
The enormous uptake and quick clearance mediated by the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) pose a long-term and significant barrier to exosomes as delivery vehicles, which significantly impedes the development of exosome delivery platforms. Investigating potential phagocytosis-evading molecules is beneficial for achieving exosome evasion of MPS regulation and improving cargo delivery. Creative Biolabs offers CD44-related exosome engineering services to assist clients in researching the function of CD44-expressed exosomes.
Overview of Exosomal Evasion of Phagocytosis
Recognition and phagocytic destruction of exosomes by phagocytes is the main reason for the short half-life of exosomes circulating in vivo after systemic injection, which greatly diminishes the therapeutic effect of the drug. These macrophages recognize multiple factors including antibodies, complement, and fibronectin through surface receptors to achieve wrapping and phagocytosis of foreign objects. Therefore, understanding and controlling the granular phagocytosis of exosomes evading macrophages is extremely critical to improving exosome delivery performance.
Different strategies have been proposed to generate "stealth" exosomes for the immune system by modifying exosomes to express different anti-phagocytic molecules on their surface. This increases the bioavailability and circulating half-life of therapeutic exosomes, allowing the delivery of exosomes to target tissues, transferring their therapeutic molecular cargo, and improving their efficacy. Therefore, it is promising to explore the effect of exosome modification by molecules associated with the phagocytosis machinery on their evasion of phagocytosis for strategies to inhibit exosome clearance and increase targeting effects.
 Fig.1 The modification methods of engineered exosomes.1
Fig.1 The modification methods of engineered exosomes.1
CD44-Expressed Exosome Modification Strategies at Creative Biolabs
A well-known marker of tumor stem cells, CD44 plays a crucial role in regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is implicated in the development, spread, and metastasis of tumors. Different selective splicing during transcription gives rise to two CD44 isoforms, including the standard isoform (CD44s) and the CD44 variant isoform (CD44v).
-
CD44 is involved in regulating the expression of MMPs (Matrix metalloproteinases), especially MMP2 and MMP9, in a HA (hyaluronic acid)-dependent or HA-independent manner, degrading the extracellular matrix and promoting tumor invasion and metastasis.
-
CD44 also promotes the separation of E-cadherin and β-catenin at the cytoplasmic membrane and promotes translocation of released β-catenin, which in turn activates genes that drive cell migration and invasion.
Blocking CD44 using monoclonal antibodies inhibited macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, allowing the particles to remain in the bloodstream for longer periods. This suggests the biological relevance of studying the transport function of CD44-expressing exosomes. CD44 expression on the surface of exosomal membranes can be achieved through pre- and post-isolation approaches of exosome engineering while being compatible with the loading of therapeutic cargoes.
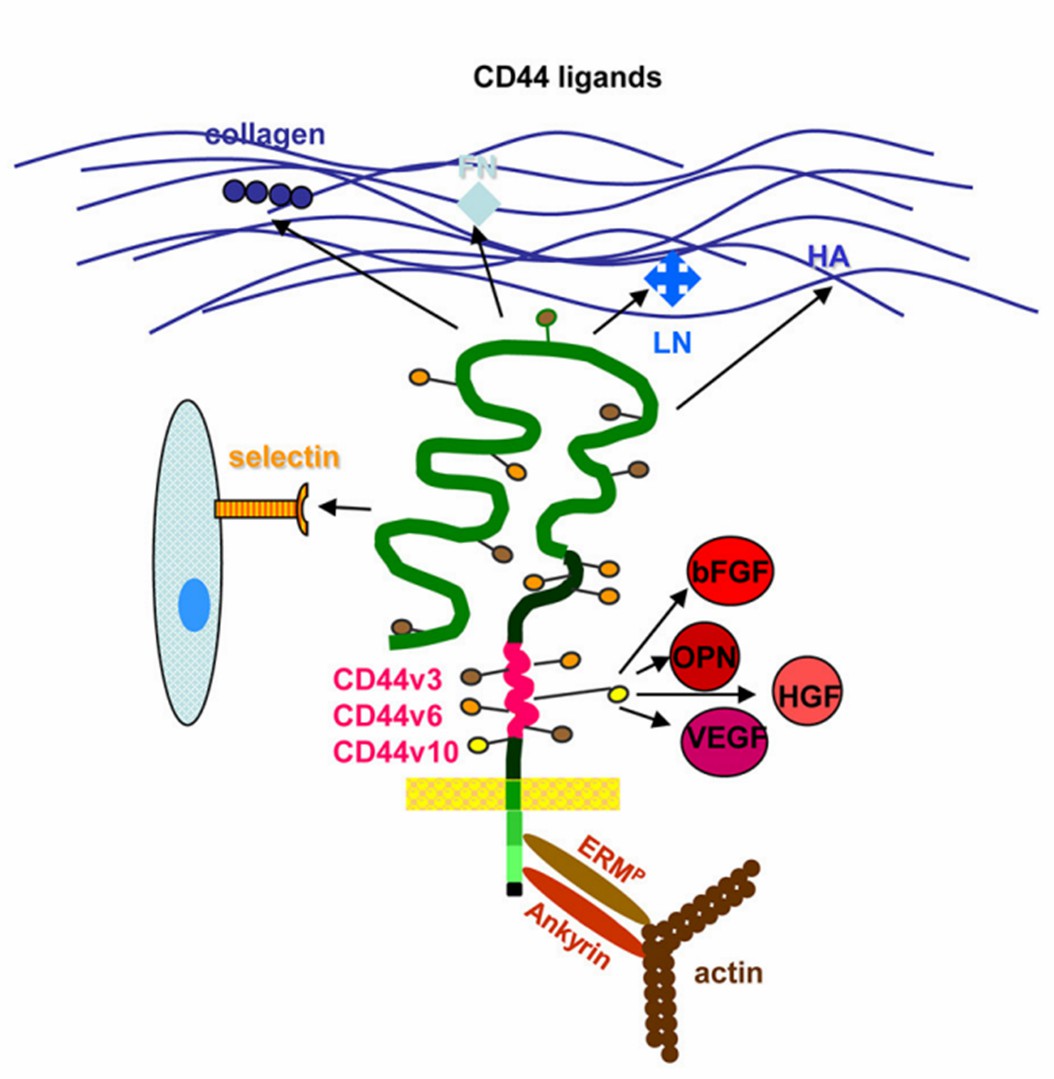 Fig.2 CD44 molecules, prominent ligands and associated molecules.2
Fig.2 CD44 molecules, prominent ligands and associated molecules.2
CD44-Expressed Exosome Modification Features
-
Increased Circulation Time: CD44-modified exosomes are expected to remain in the bloodstream longer, enhancing drug availability and efficacy.
-
Targeted administration: By enabling targeted administration to particular tissues or cells, the modification may lessen the likelihood of off-target effects.
-
Reduced Dosage Frequency: Longer circulation time could lead to less frequent dosing, improving patient compliance and convenience.
-
Improved Safety Profile: Enhanced targeting and reduced systemic exposure may lower the risk of adverse effects.
Creative Biolabs has established multiple cargo loading modification strategies to provide CD44-expressed exosome modification service. Please contact us to discuss your project.
FAQs
Q: What is CD44, and why modify exosomes with it?
A: CD44 is a glycoprotein found on the cell surface that regulates cell adhesion and migration. Modifying exosomes with CD44 can enhance their stability, prolong their circulation time in the bloodstream, and potentially evade phagocyte clearance of drugs.
Q: How does this technology improve drug delivery?
A: By increasing the circulation time of drugs encapsulated in CD44-modified exosomes, the technology ensures that a higher drug concentration remains in the bloodstream for a longer period. This can improve the therapeutic efficacy and reduce the frequency of administration.
Q: How are CD44-expressed exosomes modified?
A: Exosomes are modified through various techniques such as genetic engineering, protein conjugation, or lipid modification to incorporate CD44 onto their surface while preserving their biological integrity.
References
-
Xiao, Guixiu, Zihan Xu, and Feng Luo. "Combinational antitumor strategies of exosomes as drug carriers: Mini review." Frontiers in pharmacology 13 (2023): 1107329. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
-
Wang, Zhe, et al. "CD44/CD44v6 a reliable companion in cancer-initiating cell maintenance and tumor progression." Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 6 (2018): 97. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part B of the original image, and by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The modification methods of engineered exosomes.1
Fig.1 The modification methods of engineered exosomes.1
 Fig.2 CD44 molecules, prominent ligands and associated molecules.2
Fig.2 CD44 molecules, prominent ligands and associated molecules.2








