PD-L1-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
PD-L1 (Programmed death-ligand 1) is an essential immunomodulatory molecule, and its high expression is frequently a survival strategy to evade phagocytosis in conditions such as tumors and inflammation. The biological role played by PD-L1 in exosomes remains to be explored in depth, with the potential to prolong the circulation of exosomes by evading phagocytosis. Creative Biolabs offers PD-L1-expressed exosome modification services to explore the potential for improving the performance of exosome delivery platforms.
PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway Mediates Evasion of Phagocytosis
PD-L1 is a regulatory molecule of the body's immune function and is one of the immune regulatory ligands of PD-1. The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway is involved in regulating the regular immune system as well as an important mechanism of immune escape states such as tumor and inflammation.
-
PD-L1 regulates adaptive immune responses by binding PD-1 on the surface of T lymphocytes, including inhibiting the activation of T cells and inducing their apoptosis so that immune cells lose the ability to attack tumor cells or inflammatory cells.
-
It has been found that the level of expressed PD-1 on TAMs (tumor-associated macrophages) is also negatively correlated with their phagocytosis. And blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 increased phagocytosis of TAMs and induced an antitumor effect of innate immunity, showing TAM-dependent prolongation of survival in mice with disease models.
The above evidence suggests that PD-L1 could be an exciting candidate molecule to confer the ability of exosomes to evade cytophagy.
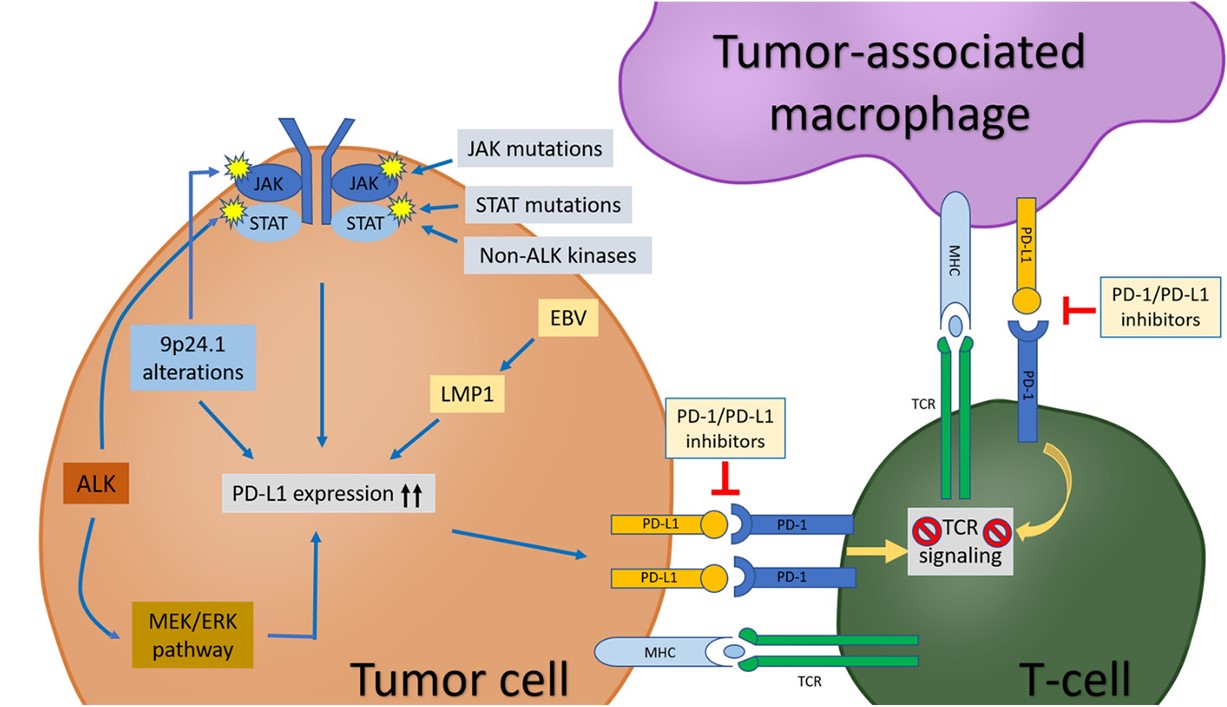 Fig.1 The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor cells, TAMs, and T-cells in tumor microenvironment.1, 3
Fig.1 The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor cells, TAMs, and T-cells in tumor microenvironment.1, 3
Insights on PD-L1-Expressed Exosomes at Creative Biolabs
It has been demonstrated that the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway mediates the inhibition of TAMs and T-cell immunity against tumor cells. Therefore, modification of PD-L1 on the surface of exosomes by engineering modifications is a promising strategy to inhibit phagocytosis of exosomes by macrophages.
-
PD-L1-expressing exosomes are potentially generated in tumor cells, immune cells, MSCs, and tumor microenvironments with specific signaling roles that distinguish them from exosomes of other cellular origins.
-
PD-L1-expressing exosomes can also be generated by transfection of PD-L1-containing expression plasmids to modify specific donor cells or surface-modified PD-L1 ligands.
-
Based on previous evidence that PD-L1 inhibits phagocytosis of TAMs and to some extent can also interact to enhance immunosuppressive effects, the alteration of phagocyte recognition and catabolism by PD-L1-expressing exosomes can be monitored by cellular uptake assays and intratumoral targeted retention assays, thus explore whether this modification strategy contributes to prolonged exosome recycling.
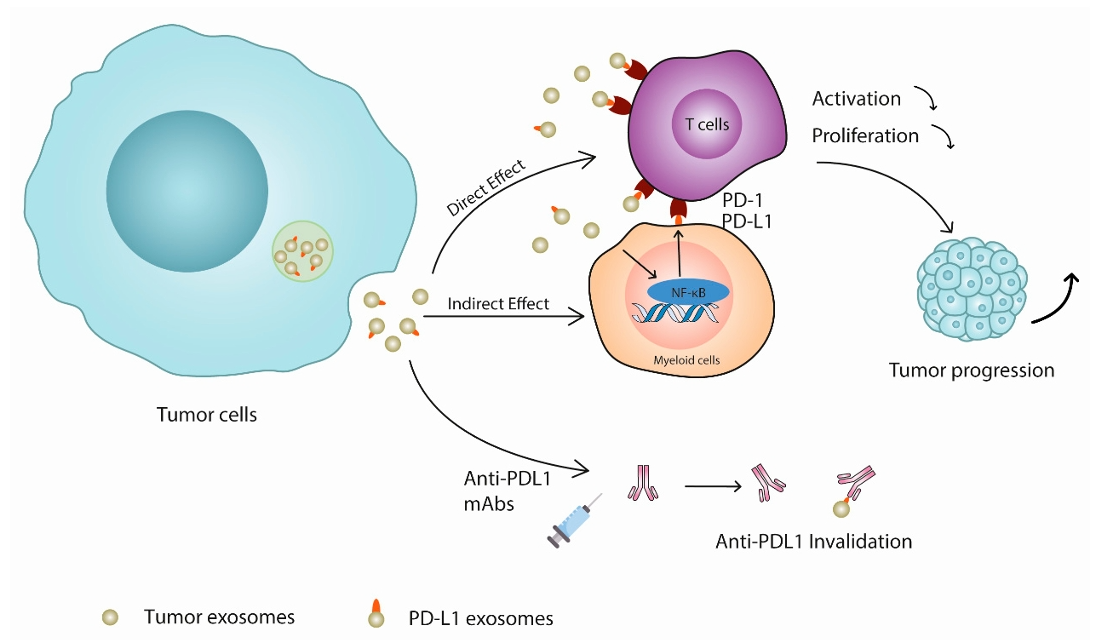 Fig. 2 Mechanisms of exosomal PD-L1 mediated tumor cell immune escape.2, 3
Fig. 2 Mechanisms of exosomal PD-L1 mediated tumor cell immune escape.2, 3
Features
-
Advanced Molecular Techniques: Utilization of cutting-edge molecular biology techniques for precise and efficient PD-L1 integration into exosomes.
-
High Purity and Yield: Production of exosomes with high purity and yield, ensuring optimal performance in subsequent experiments or therapeutic uses.
-
Comprehensive Characterization: Detailed analysis and characterization of modified exosomes, including PD-L1 expression levels, size distribution, and functional assays.
-
Scalability: Services available from small-scale research-grade preparations to large-scale production suitable for trials.
PD-L1 signaling inhibits the innate immune response through a negative effect on the phagocytosis of TAMs opening new directions for improving the potential of exosome-targeted delivery. Moreover, the mechanisms related to the anti-phagocytosis effect of exosomes need to be further investigated. At Creative Biolabs, we have developed a variety of exosome engineering strategies that can provide services for the modification of PD-L1-expressed exosomes and the research of their phagocytosis-evading related mechanisms, thus helping our customers to advance the research of exosome vector-based therapeutic systems. Please contact us to discuss your project.
FAQs
Q: What are PD-L1-expressed exosomes?
A: PD-L1-expressed exosomes are extracellular vesicles engineered to display the PD-L1 protein on their surface. These exosomes can be used to study immune evasion mechanisms and for therapeutic purposes, such as cancer immunotherapy.
Q: What applications can benefit from PD-L1-expressed exosome modification?
A: Applications include cancer immunotherapy research, immune evasion mechanism studies, biomarker discovery, and the development of novel therapeutic approaches targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway.
Q: How do PD-L1-expressed exosomes contribute to immune evasion?
A: PD-L1 on the exosome surface can bind to the PD-1 receptors on T-cells, inhibiting their activation and allowing cancer cells or other target cells to evade the immune response.
Q: Can you customize the level of PD-L1 expression on exosomes?
A: Yes, we offer customization of PD-L1 expression levels based on the specific needs of your research or therapeutic application.
Q: What validation methods are used to ensure the functionality of PD-L1 on exosomes?
A: We perform various validation assays, including flow cytometry, western blotting, and functional T-cell inhibition assays to confirm PD-L1 expression and functionality.
References
-
Xie, Wei, et al. "PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: A Therapeutic Target in CD30+ Large Cell Lymphomas." Biomedicines 10.7 (2022): 1587.
-
Ye, Lingxiao, et al. "The importance of exosomal PD-L1 in cancer progression and its potential as a therapeutic target." Cells 10.11 (2021): 3247.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor cells, TAMs, and T-cells in tumor microenvironment.1, 3
Fig.1 The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor cells, TAMs, and T-cells in tumor microenvironment.1, 3
 Fig. 2 Mechanisms of exosomal PD-L1 mediated tumor cell immune escape.2, 3
Fig. 2 Mechanisms of exosomal PD-L1 mediated tumor cell immune escape.2, 3








