Exosomal LncRNA Microarray Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
More and more reports have shown the variety of roles LncRNA plays in exosome research. Creative Biolabs can provide clients with convenient one-stop services. To help with the dilemma researchers encountered in this field, we launch an exosomal lncRNA microarray service with lower sample amount requirements and higher efficiency.
Exosomal LncRNA Microarray
lncRNAs within exosomes can be transferred between cells, regulating the gene expression and functions of recipient cells. For example, cancer cells can transmit specific lncRNAs to surrounding normal cells via exosomes, altering their behavior to promote tumor growth and metastasis. Moreover, lncRNAs in exosomes can serve as potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and disease progression prediction.
The capacity to simultaneously test a huge number of immobilized ligands—often over 10,000—with the target biomolecule is a key advantage of microarray-based ligand screening, which offers far higher throughput than conventional RNA binding assays. Moreover, the microarray method is very effective for researching RNA that is challenging to generate in big amounts because it only needs a small amount of RNA to be employed. In conclusion, microarray screens can be run in multiplex or parallel configurations to provide selectivity data that is not achievable with conventional biochemical experiments. Given that exosomes typically contain very little lncRNA, these benefits are essential for exosome lncRNA study.
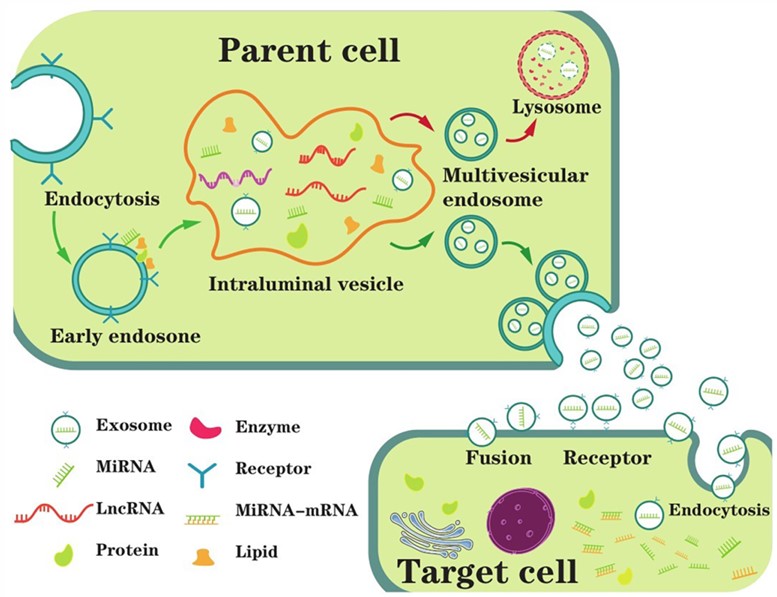 Fig. 1 The main process of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and ingestion.1
Fig. 1 The main process of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and ingestion.1
LncRNA Microarray Service at Creative Biolabs
-
Sample Collection and Processing
-
Collect exosomes from biological samples (e.g., serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants).
-
Isolate exosomal RNA using specialized techniques.
-
Quality Control and RNA Quantification
-
Assess RNA quality and quantity using advanced analytical tools.
-
Ensure high-quality RNA for downstream applications.
-
Microarray Hybridization
-
Label exosomal RNA and hybridize to the microarray platform.
-
Capture hybridized signals using state-of-the-art scanning technology.
-
Data Analysis and Interpretation
-
Analyze microarray data to identify differential expression profiles.
-
Employ bioinformatics tools for in-depth analysis and visualization.
-
Report Generation
-
Compile results into a comprehensive report.
-
Provide insights and interpretations relevant to the study objectives.
Features
-
High Sensitivity and Specificity: Detects low-abundance LncRNAs with high accuracy.
-
Comprehensive Analysis: Provides detailed expression profiles of exosomal LncRNAs.
-
Customizable Solutions: Tailored workflows to suit specific research needs.
-
Expert Support: Access to experienced scientists for technical guidance and data interpretation.
-
Robust Quality Control: Ensures reliable and reproducible results.
Please feel free to contact Creative Biolabs for expert assistance if you need a partner in exosome research or if you have any concerns regarding our services.
FAQs
Q: How is RNA quality assessed during the service?
A: To determine the content and integrity of RNA, we employ bioanalyzer methods and spectrophotometry.
Q: Can you perform custom data analysis beyond standard protocols?
A: Yes, we offer customized bioinformatics analysis to meet specific research requirements.
Q: Regarding the microarray analysis, what is the estimated duration of delivery of the results?
A: Turnaround times vary depending on project scope and sample size, typically ranging from 8-12 weeks.
Q: Comparing exosomal LncRNA research to cellular LncRNA research, what are the benefits?
A: Exosomal LncRNAs can serve as potential biomarkers and mediators of intercellular communication, offering insights into disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Reference
-
Wang, Zhong-Yu, et al. "Exosomal noncoding RNAs in central nervous system diseases: biological functions and potential clinical applications." Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 15 (2022): 1004221. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 The main process of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and ingestion.1
Fig. 1 The main process of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and ingestion.1









