Therapeutic Exosomes for Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal Cancer (CRC) is subject to a malignant tumor in the gastrointestinal tract. The intercommunication of CRC cells with the surrounding and distant environments is critical for CRC proliferation and metastasis. Numerous studies have shown that exosomes are an intercellular communication tool between CRC cells and other cells in the microenvironment. Similarly, exosomes can also be engineered and loaded with drugs for targeted therapy of CRC. Creative Biolabs has established a complete one-stop exosome drug research platform. Our services cover every step of exploration, including extraction, loading, and subsequent in vivo and in vitro functional studies of exosomal drugs.
Colorectal Cancer (CRC) and Exosome
Symptoms of CRC include blood in the stool, changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain and bloating, fatigue, anemia, and unexplained weight loss. The pathophysiological mechanism of CRC is mainly the alteration of gene expression, resulting in the dysregulation of multiple signaling pathways and cytokine expression. Combination therapy in advanced CRC is prone to drug resistance, making metastasis the leading cause of death, with a five-year survival rate of about 60%. Exosomes released by CRC cells (CRC-Exo) are key tumorigenic agents that can mediate the tumor microenvironment, promote angiogenesis, and regulate the proliferation of CRC cells. CRC-Exo also promotes CRC by promoting metastasis to the lung, liver, and lymphatic system. Furthermore, CRC-Exo modulates immune cell responses and promotes resistance to therapy. Studies have shown that miRNAs in CRC-Exo, such as miRNA-21, miRNA-181a, miRNA-23a, etc., can promote CDC cell proliferation and migration, as well as CDC liver metastasis. Proteomic analysis of serum exosomes from CRC patients showed that proteins such as Hsp60, Glypican-1 (GPC1), collapse protein-responsive mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2), Copine 3 (CPNE3), interferon regulatory factor 2 (IRF-2), and S100A9 were significantly increased. Therefore, through a simple liquid biopsy, the cargo of CRC-Exo has great application prospects in the diagnosis of CRC. On the other hand, exosomes, as natural lipid vesicles, are expected to be used to deliver drugs for the treatment of CRC.
Exosomes and the Therapy of CRC
MSC-derived exosomes (MSC-Exo) have been found to have beneficial effects on CRC by inducing antitumor responses. miR-3940-5p in exosomes from human ulcerative colitis-MSCs (hUC-MSC-Exo) can inhibit CRC growth and metastasis by downregulating the expression of ITGA6. In addition, antitumor miRNAs in exosomes from human bone marrow-MSCs (BM-MSC-Exo), including miR-22-3p and miR-16-5p, inhibited CRC cell proliferation by modulating the RAP2B/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. proliferation and migration. Therefore, the treatment of CRC with MSC-Exo has great prospects.
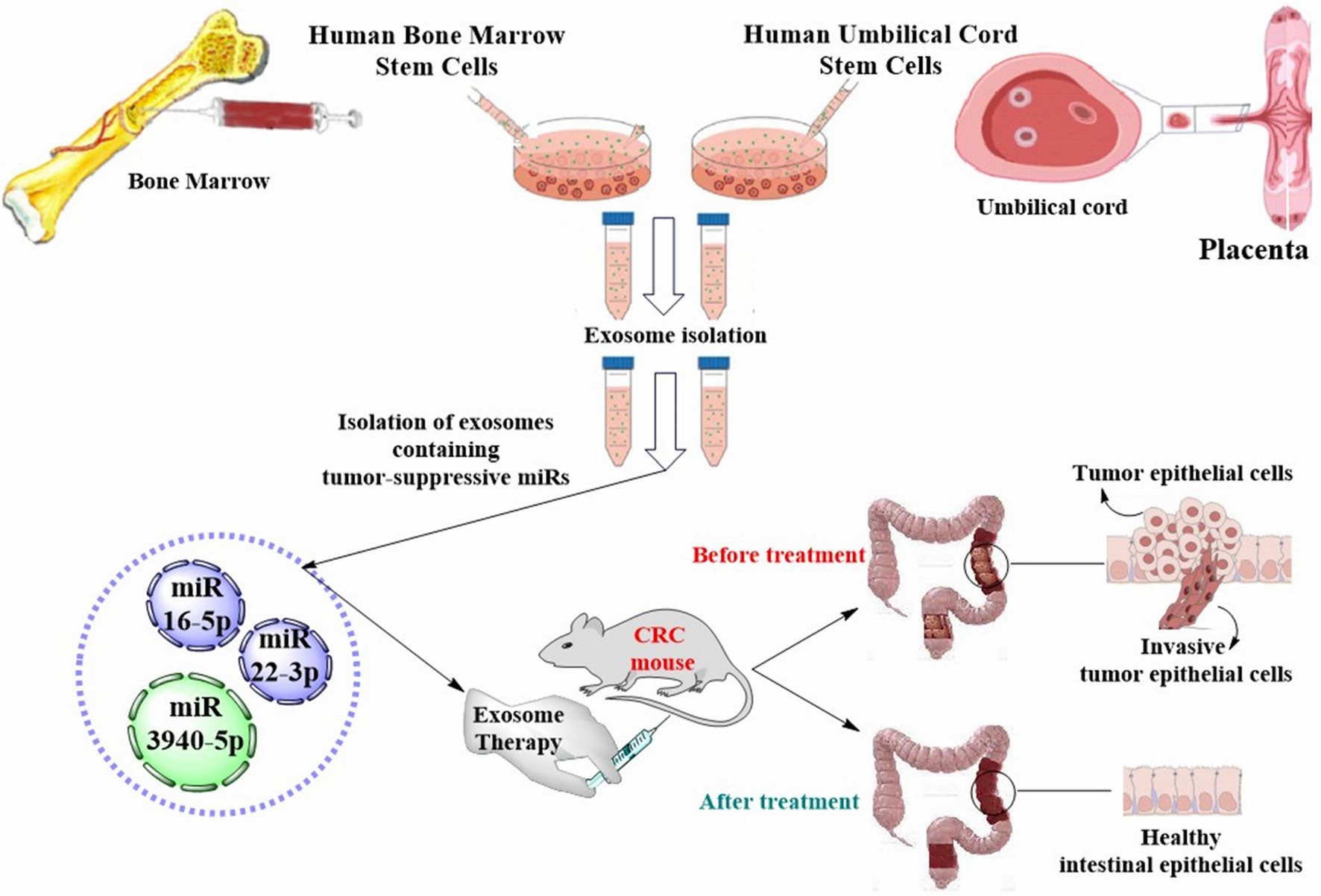 Fig.1 A schematic view of the exosome therapy for CRC treatment using MSC-derived exosomes containing tumor-suppressive miRs.1,2
Fig.1 A schematic view of the exosome therapy for CRC treatment using MSC-derived exosomes containing tumor-suppressive miRs.1,2
Curcumin can exert anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects through a variety of targets, has a strong inhibitory effect on the growth of CRC cell lines, and has been shown to inhibit colon cancer progression. However, in the reported clinical trials of curcumin, the delivery of curcumin has been a challenge to effectively treat CRC. Emerging data suggest that plant-derived exosomes can be used as vehicles for the treatment of intestinal diseases. Because such exosomes can bind strongly to many hydrophobic drugs, including curcumin, and are taken up by intestinal cells and immune cells in the gut. An exosome drug that has entered clinical phase I is the use of plant-derived exosomes to deliver curcumin to CRC cells for the treatment of CRC.
Creative Biolabs has rich experience in exosome loading and has established a comprehensive technology platform covering the whole process of exosome drug research. We also believe that our services will accelerate the progress of your project. If you have any needs for exosome drug research, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
-
Guo, G.; et al. The therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived exosomes in ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Research and Therapy. 2022, 13(1):138.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 A schematic view of the exosome therapy for CRC treatment using MSC-derived exosomes containing tumor-suppressive miRs.1,2
Fig.1 A schematic view of the exosome therapy for CRC treatment using MSC-derived exosomes containing tumor-suppressive miRs.1,2








