NAA and Autoimmune Disorders
The destruction or destruction of the body's own tissue by the system results from a posh complex interaction of genetic and environmental factors. When the immune system plays a role in the defense of antibiotics in the normal part of the body, such as type 1 diabetes, insulin-producing pancreatic cells, or systemic lupus erythematosus chromatin, autoimmune diseases will occur.
The Mechanisms of Autoimmune Disorders
- Genetics
- Environment
The development of autoimmune disorders depends on a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Most autoimmune diseases are considered polygenic, involving multiple genes. Human lymphocyte antigen, or HLA haplotype, is the best available predictor of developing an autoimmune disease. Genes other than MHC also increase the risk of autoimmune diseases. Common susceptibility loci have been found for a number of different autoimmune diseases, including diabetes and myocarditis, suggesting that shared genes are involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
External environmental factors, such as hormones, diet, drugs, toxins and/or infections, are important in determining whether a person will develop autoimmune diseases. Environmental factors can enhance the autoimmunity of genetically susceptible individuals, destroy the tolerance of genetically resistant individuals, and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases.
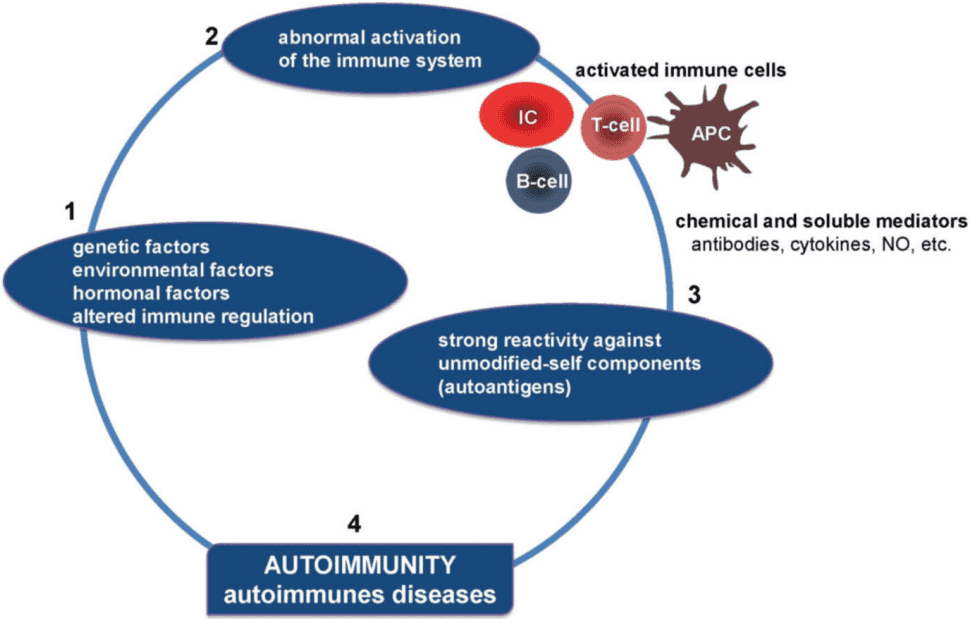 Fig.1 Pathophysiological mechanisms of autoimmune diseases.1
Fig.1 Pathophysiological mechanisms of autoimmune diseases.1
Common Autoimmune Disease
The presence of autoantibodies and inflammation is a common feature of all autoimmune diseases, including mononuclear phagocytes, autoreactive T lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Autoimmune diseases can be classified as organ-specific or non-organspecific depending on whether the autoimmune response is directed against a particular tissue.
- NAA and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- NAA and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- NAA and Celiac Disease
- Sjogren's Syndrome
- NAA and Myasthenia Gravis
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem autoimmune disease, which is characterized by the production of a large number of autoantibodies and involves the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, serosa surface, blood vessels, blood cells, lung, and heart.
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis. With the increasing understanding of the immune mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis, a large number of new therapeutic agents have been developed that can alter the natural course of the disease and reduce mortality.
Celiac disease (CD) is an immune-mediated disease caused by permanent gluten intolerance. It is the only disease with the clear origin, mainly involving the gastrointestinal tract. Its main predisposing genes are located on chromosome 6 of the HLA system, namely HLA DQ2 and DQ8 genes, which exist in at least 95% of patients.
Sjogren's syndrome is a common autoimmune disease characterized by dry symptoms and extra-glandular features. It is defined by autoantibodies to Ro and La. The current studies identified additional autoantibodies in Sjogren's syndrome to salivary gland protein 1 (SP-1), carbonic anhydrase 6 (CA6), and parotid secretory protein (PSP).
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease caused by autoantibodies against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the postsynaptic membrane at the neuromuscular junction and characterized by voluntary muscle weakness and fatigue. It can be classified according to the age of onset, presence, or absence of anti-AchR antibodies, severity, and the aetiology of the disease.
Creative Biolabs is an innovative, experienced provider of NAA services and products. We use our state-of-the-art R&D expertise to help our customers with stand-out NAA services and products that offer true value to consumers. We want to contribute to better health in the world. If you are interested in our services and products, please contact us for more detail.
Reference
- Aribi, Mourad. "Introductory Chapter: Immune system dysfunction and autoimmune diseases." Immunopathog. Immune-Based Ther. Sel. Autoimmune Disord 1 (2017).
Choosing natural autoantibody (NAA) microarray to profile autoantibody repertoire and reveal novel disease's marker.
- NAA and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- NAA and Celiac Disease
- NAA and Myasthenia Gravis
- NAA and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Related Services:
- NAA and Cancers
- NAA and Pulmonary Diseases
- NAA and Nephropathy
- NAA and Hematological Diseases
- NAA and Endocrine Diseases
- NAA and Cardiovascular Diseases
- NAA and Neurological Diseases
- NAA and Infectious Diseases

