Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive mitochondrial oxidative stress assay service tailored specifically for iPSC-facilitated drug discovery targeting Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD). Our cutting-edge assay empowers researchers with valuable insights into mitochondrial function and oxidative stress levels, crucial factors in AMD pathology, and potential therapeutic interventions.
The mitochondria play a pivotal role in cellular energy metabolism and are central to the oxidative stress response. Given that AMD is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and increased oxidative stress, assessing mitochondrial oxidative stress can provide:
| Step | Details |
| 1 Cell Culture and Maintenance |
iPSCs are cultured and maintained in appropriate culture media supplemented with growth factors and other necessary nutrients. Cells are regularly checked for their pluripotency and quality to ensure they are suitable for downstream assays. |
| 2 Differentiation of iPSCs into RPE Cells |
iPSCs are induced to differentiate into RPE cells using specific differentiation protocols. The differentiated RPE cells are characterized to confirm their identity and functionality. |
| 3 Treatment with Compounds |
Differentiated RPE cells are treated with potential drug compounds or agents known to induce oxidative stress. This step enables the evaluation of the chemicals' impact on RPE cells' mitochondrial oxidative stress. |
| 4 Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Assay |
After treatment, the cells are subjected to a mitochondrial oxidative stress assay. This assay typically involves measuring ROS levels, mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitochondrial superoxide production using fluorescent probes or other detection methods. The assay provides quantitative data on the extent of mitochondrial oxidative stress induced by the compounds. |
| Data Analysis | The data obtained from the mitochondrial oxidative stress assay are analyzed to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of the tested compounds. |
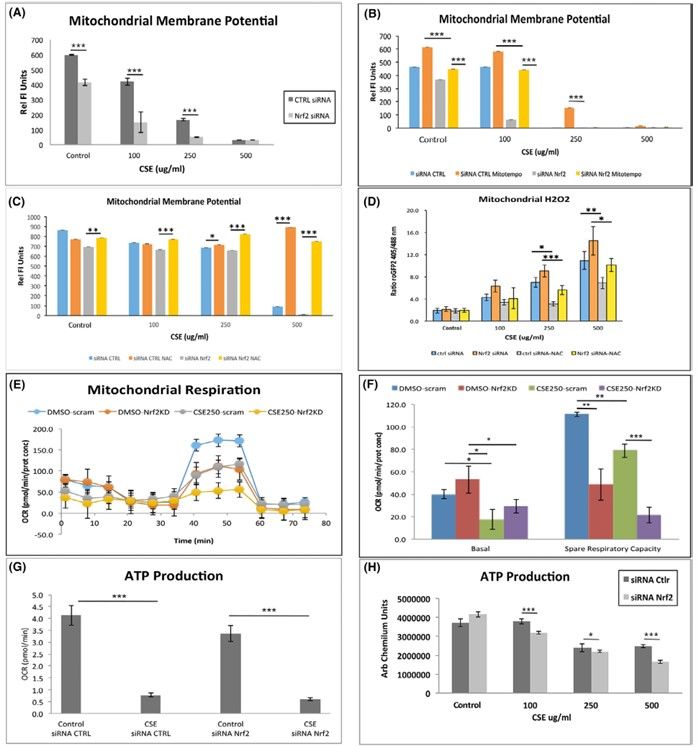 Fig.1 Mitochondrial dysfunction assay in iPSC-differentiated RPE cells.1
Fig.1 Mitochondrial dysfunction assay in iPSC-differentiated RPE cells.1
1. What is the principle behind the mitochondrial oxidative stress assay?
The assay measures the levels of mitochondrial ROS and evaluates mitochondrial membrane potential, offering a comprehensive assessment of mitochondrial oxidative stress.
The assay provides a thorough evaluation of mitochondrial oxidative stress by measuring ROS and assessing mitochondrial membrane potential.
2. How can I initiate the mitochondrial oxidative stress assay service?
To initiate the service, please contact our customer support team or submit a service inquiry through our website. In addition to assisting you with the service initiation process, our committed scientists will respond to any additional queries you might have.
Creative Biolabs offers a mitochondrial oxidative stress assay service tailored for AMD therapy development. Our comprehensive assay is designed to assess mitochondrial oxidative stress levels, providing valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions for AMD. For more information about mitochondrial oxidative stress assay service in AMD, please contact us today.
Reference
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.