Creative Biolabs is a professional service provider delighted to present the RPE apoptosis assay service as an integral component of our extensive iPSC-enabled therapy discovery platform for AMD. This assay is essential for pinpointing and comprehending the apoptotic pathways associated with AMD, thus advancing the creation of groundbreaking therapeutic approaches utilizing iPSCs.
Research Significance
-
Understanding apoptosis pathways in iPSC models of AMD is pivotal for uncovering disease mechanisms.
-
The discovery of apoptosis regulators may result in the creation of focused AMD treatments.
-
RPE apoptosis assay enables precise evaluation of therapeutic candidates, expediting drug discovery processes.
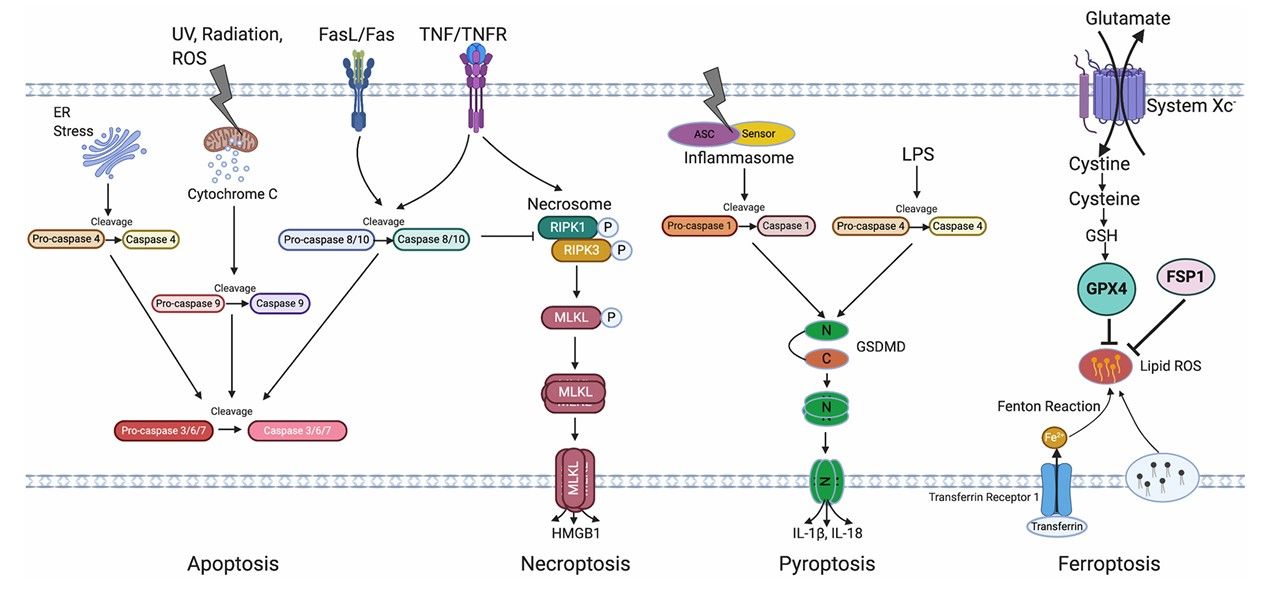 Fig.1 Overview of RPE cell death pathways in AMD.1
Fig.1 Overview of RPE cell death pathways in AMD.1
Workflow
-
iPSC-RPE cell differentiation: The first step is to differentiate iPSCs into RPE cells. Once the iPSC-RPE cells have been differentiated, they are typically subjected to quality control measures to ensure their purity, multi-laminar alignment, and functionality.
-
Induction of oxidative stress: To mimic the AMD conditions, oxidative stress is generated in the iPSC-RPE cell culture. This can be achieved by treatment with a ROS-generating agent such as hydroquinone or hydrogen peroxide.
-
Anti-apoptotic compounds treatment: The cells are treated with drug candidates and ROS-inducing agents simultaneously. Any protection offered by the drug candidates against ROS-induced apoptosis will then be measured.
-
Measuring cell viability: Cell viability is assessed using a colorimetric assay like the MTT or viability dye staining which turns the live cells into a specific color. The protectiveness of a compound is determined by comparing the climber of live cells in the compound and ROS-induced wells with the ROS-only cells.
-
Further mechanism of action study: Once the active compounds have been identified and their anti-apoptotic activity confirmed, it is necessary to understand the mechanism through which they operate. This involves further experiments that may include gene expression studies, protein assays, or mass spectrometry analysis.
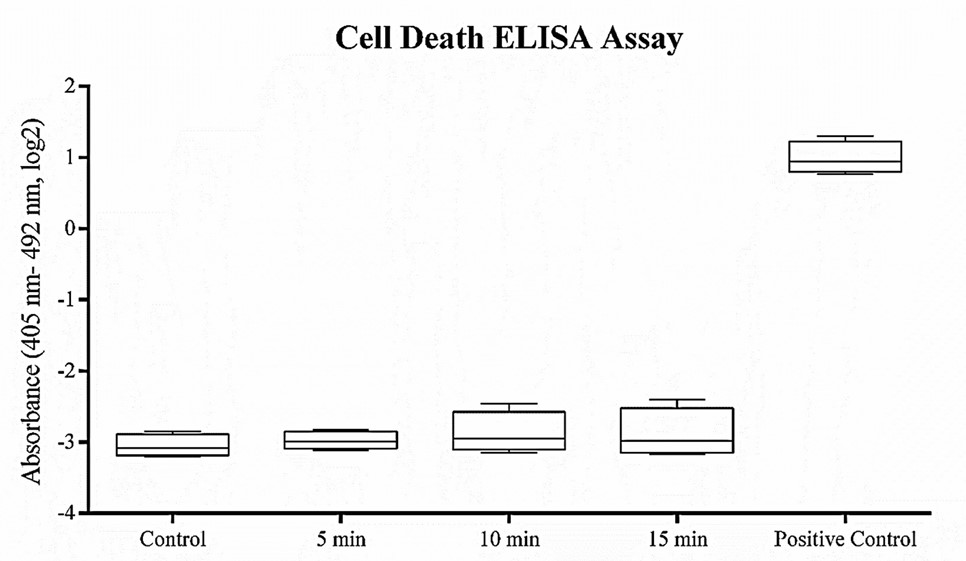 Fig.2 Cell death ELISA assay for RPE death detection.2
Fig.2 Cell death ELISA assay for RPE death detection.2
Deliverables
-
Detailed RPE apoptosis assay protocols and experimental procedures.
-
Comprehensive data analysis report of RPE apoptosis, including graphs and statistical analysis.
-
Expert consultation and support throughout the RPE apoptosis assay project duration.
FAQs
1. What is the principle of the RPE apoptosis assay?
The RPE apoptosis assay is based on the principle that apoptotic cells undergo changes in their plasma membrane integrity, which can be detected using specific dyes that can penetrate these altered membranes. The RPE apoptosis assay is relatively simple and rapid compared to other apoptosis detection methods.
2. What information on AMD can be obtained from the RPE apoptosis assay?
This assay can quantify the rate of cell death or apoptosis induced by AMD, which helps researchers and clinicians understand the severity and progression of the disease at a cellular level. Additionally, it can assist in evaluating the efficacy of potential treatments or interventions aimed at reducing apoptosis and preserving retinal function in AMD patients.
Creative Biolabs provides an RPE apoptosis assay service in the domain of iPSC-facilitated therapy development for AMD. Please contact us to experience the power of our well-established techniques and innovative tools to further your research and development endeavors.
References
-
Tong, Yao, and Shusheng Wang. "Not all stressors are equal: Mechanism of stressors on RPE cell degeneration." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 8 (2020): 591067.
-
Oladnabi, Morteza, et al. "Correlation between ELF–PEMF exposure and Human RPE Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Gene Expression." Journal of Ophthalmic & Vision Research 16.2 (2021): 202.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
 Fig.1 Overview of RPE cell death pathways in AMD.1
Fig.1 Overview of RPE cell death pathways in AMD.1
 Fig.2 Cell death ELISA assay for RPE death detection.2
Fig.2 Cell death ELISA assay for RPE death detection.2