PMEL17 (Melanocyte protein PMEL) has been investigated for its possible relevance to the function of the pigment epithelium, which is necessary to maintain retinal function. Creative Biolabs provides a PMEL17 expression measurement service in iPSC-facilitated discovery for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), enabling researchers to better understand the role of PMEL17 in AMD pathogenesis.
PMEL17, also known as Melanocyte protein PMEL or GP100, plays a critical role in melanosome biogenesis and is associated with the development and progression of AMD. Detecting the expression levels of PMEL17 in iPSC-derived retinal cells can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying AMD and help identify novel biomarkers or therapeutic targets. Our PMEL17 expression assay can be utilized in:
Our streamlined workflow ensures accurate and reliable detection of PMEL17 expression in iPSC-derived cells for AMD drug discovery:
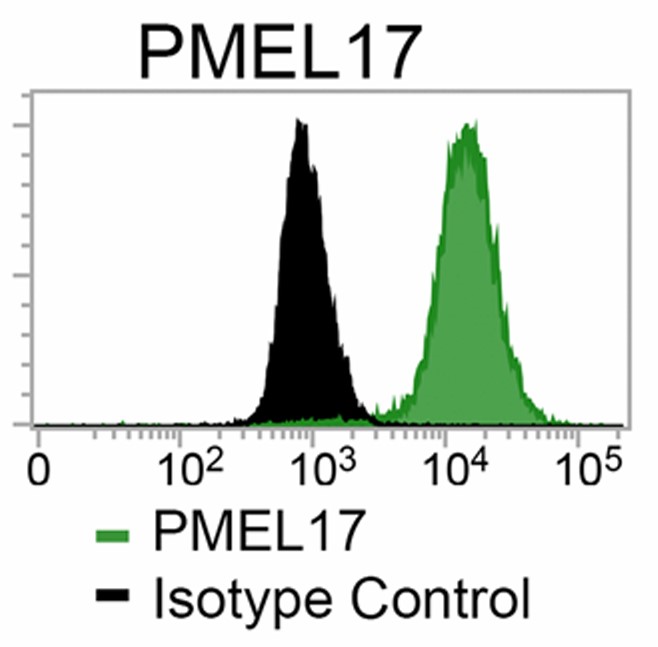 Fig.1 Flow cytometric analysis of PMEL17 expression is performed to assess the ability of PSC to maintain RPE markers after prolonged amplification.1
Fig.1 Flow cytometric analysis of PMEL17 expression is performed to assess the ability of PSC to maintain RPE markers after prolonged amplification.1
1. What is PMEL17 and why is it important in AMD research?
PMEL17 is a protein involved in the formation of melanosomes, which are pigment-producing organelles in the retinal pigment epithelium. Alterations in PMEL17 expression have been associated with AMD, making it a crucial target for research and drug discovery.
2. How do you detect PMEL17 expression?
We employ advanced molecular biology techniques, such as qRT-PCR and Western blotting, to quantify and analyze PMEL17 expression levels.
Creative Biolabs is pleased to offer a specialized PMEL17 expression assay to accelerate drug discovery for AMD. By iPSCs, our service aims to provide valuable insights into the expression levels and patterns of PMEL17, a key protein associated with AMD. Please contact us to streamline your research process.
Reference
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.