Creative Biolabs utilizes advanced methods to accurately measure the phagocytic activity of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). By evaluating the impact of drugs on this crucial cellular process, our clients can gain deep insights into the potential therapeutic benefits of their compounds in treating AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration).
RPE cells play a vital role, one of which is to clear away the remnants of photoreceptor outer segments through phagocytosis, a process essential for maintaining the health and normal function of the retina. Dysfunction and death of RPE cells can lead to damage to the retinal photoreceptor cells, becoming a key factor in the pathogenesis of AMD. Therefore, the phagocytosis assay, by assessing the ability of RPE cells to clear photoreceptor outer segment remnants, becomes a core part of developing treatments for AMD. Potential drugs that enhance the phagocytic function of RPE cells may open new avenues for treating or slowing the progression of AMD. Thus, in the drug development process for AMD, the phagocytosis assay is not only an essential step but also a critical one.
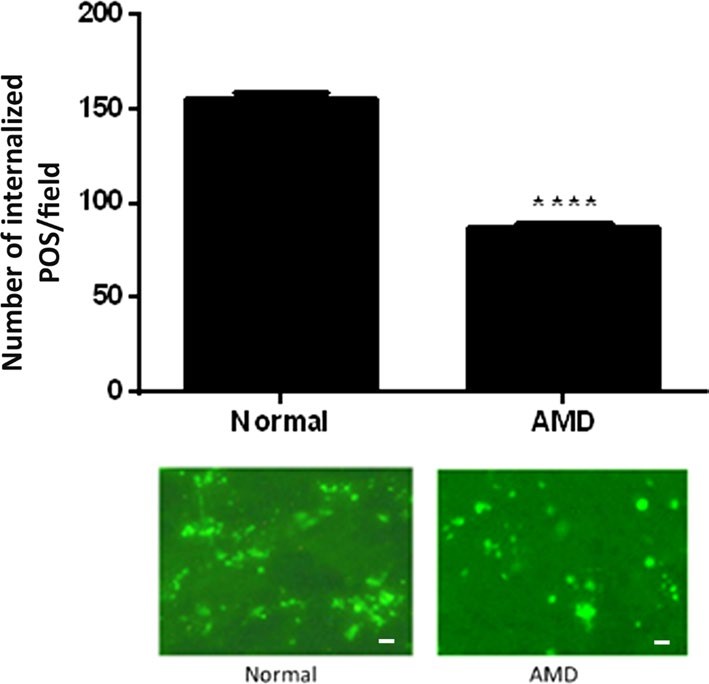 Fig.1 Phagocytosis level in RPE from eyes of AMD donors.1
Fig.1 Phagocytosis level in RPE from eyes of AMD donors.1
With technological advancements, the iPSC technology platform's application in phagocytosis assays provides a unique and powerful tool for AMD research and drug development. This technology involves reprogramming adult cells into pluripotent stem cells, which can then differentiate into various cell types, including RPE cells. By utilizing the iPSC technology platform, researchers can specifically study the functional changes of RPE cells in AMD and their response to drug treatments. Evaluating these cells' phagocytic function under the influence of different drugs can help screen and optimize potential treatment strategies.
Q1: How long is the cycle for the phagocytosis assay service?
A1: The service cycle depends on various factors, including the differentiation and maturation time of the cells, the scheduled drug treatment cycle, and subsequent analysis time. Generally, a complete assay cycle might take 12-14 weeks.
Q2: What should be done if a candidate drug performs poorly in the phagocytosis assay?
A2: If a candidate drug performs poorly in the phagocytosis assay, it may be necessary to reassess the drug's development potential, such as modifying the drug's dosage or administration method.
Research utilizing RPE cells from healthy subjects and AMD patients has assessed the effect of regulatory media from human umbilical tissue-derived cells (hUTC) on the phagocytosis function of RPE cells. The results indicate that hUTC regulatory media significantly improved the phagocytic dysfunction in RPE cells from AMD patients.
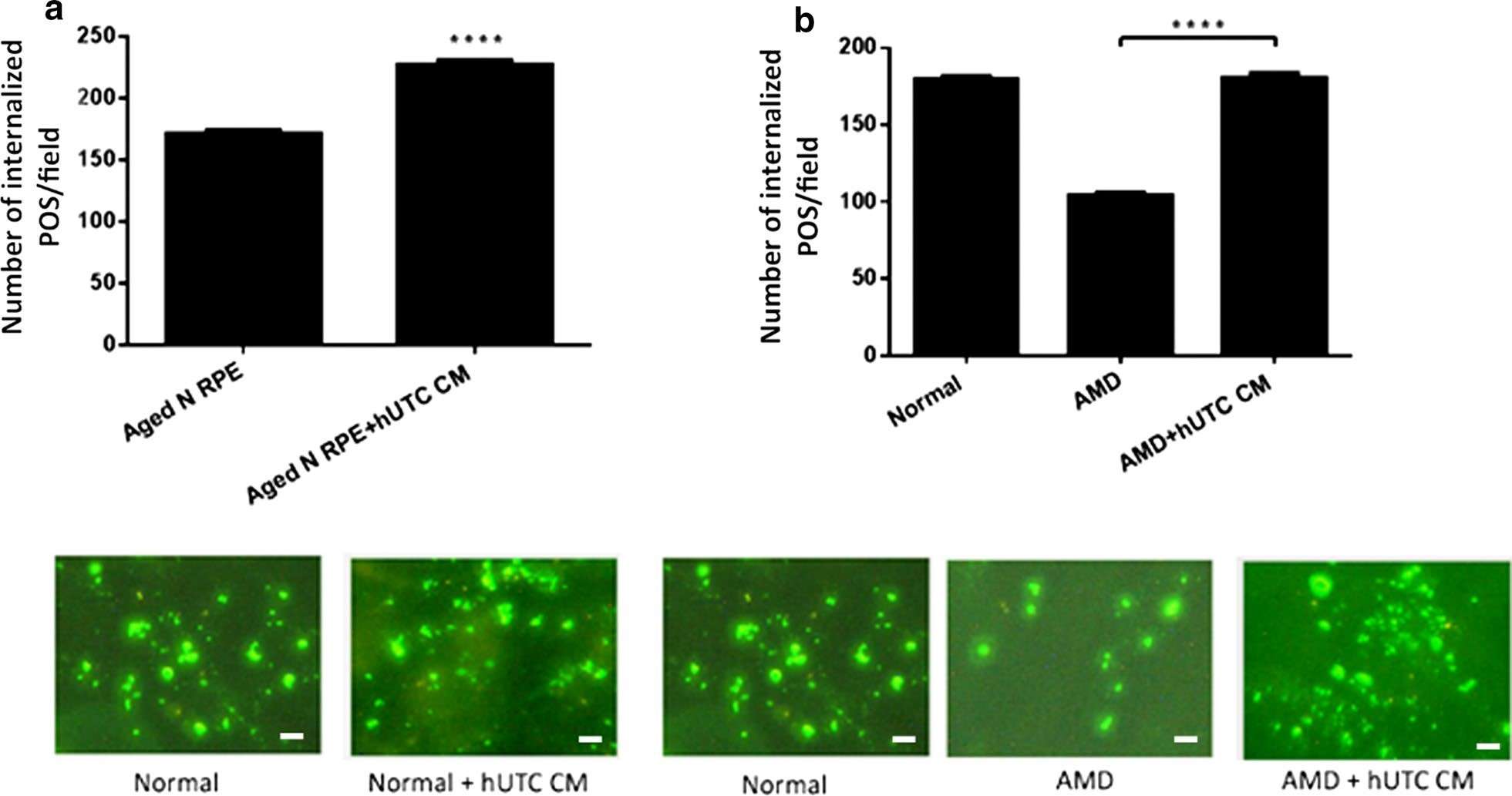 Fig.2 Effect of hUTC conditioned medium on phagocytosis in RPE from aged normal and AMD donors.1
Fig.2 Effect of hUTC conditioned medium on phagocytosis in RPE from aged normal and AMD donors.1
Creative Biolabs specializes in offering phagocytosis assay services, aimed at helping you explore the ability of candidate drugs to improve the dysfunction of RPE cell phagocytic function. If you wish to evaluate the potential improvement effects of your drugs on the phagocytic function of RPE cells, please feel free to contact us for more information and support.
Reference
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.