T cells have been playing a very important role in the immune response in an organism, which provides a frame of antigen-specific response for infections, diseases, and cancers. A highly selective antigen-specific cells lineage involves and activates that process. The goal of immune diagnosis is to reliably identify a little part of responders and confirm their mode of action as well as the degree of response. The individual antigen is difficult to be recognized by T cells in most cases. Hence, the techniques of measuring T cell immune responses must be sensitive, high-throughput, and widely adopted.
The Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSpot (ELISpot) assay not only measures the magnitude and quality of T cells immunity through detecting antigen-specific T cells that involve in the secretion of cytokines and other utility but also detects the protein secretion from the single cell. Compared to other assays, the ELISpot assay can be utilized to detect the population and frequency of specific proteins such as cytokines and antigen-specific antibodies. T cells ELISpot is much more reproducible and sensitive than other measurements like cytokine measurements in detecting low-frequency antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. More than that, this accurate assay can also validate new T cell epitopes.
Creative Biolabs has developed and optimized the ECIA™ T Cells ELISpot Assay platform. Relying on the excellent sensitivity and resolution, ECIA™ T cells ELISpot assay is able to provide a multidimensional, quantitative assessment of effector function at the single cell level. And it is the first choice for the development of multifunctional T cell analysis in the areas of drug research and preclinical trials.
The ELISpot assay is a kind of technique convergence based on ELISA and Western blotting. The cells are stimulated to produce local cytokines that are captured by specific monoclonal antibody coated onto a PVDF-backed microplate. After the cells are disintegrated, a biotin-labeled antibody specific for the chosen cytokine is added to bind the captured cytokines. Following a wash to remove any unbound biotinylated antibody, the detected cytokine is then visualized using streptavidin conjugated to alkaline phosphatase and a precipitating substrate (e.g., BCIP/NBT). Purple spots will emerge in the PVDF plate. Once the signal is developed, the number of spots can be calculated manually, or by using an image-based spot reader and the accompanying analysis software. By comparing the number of the control wells, the frequency and the total number of responding cells can be determined.
Other optional ECIA™ cellular analysis services:
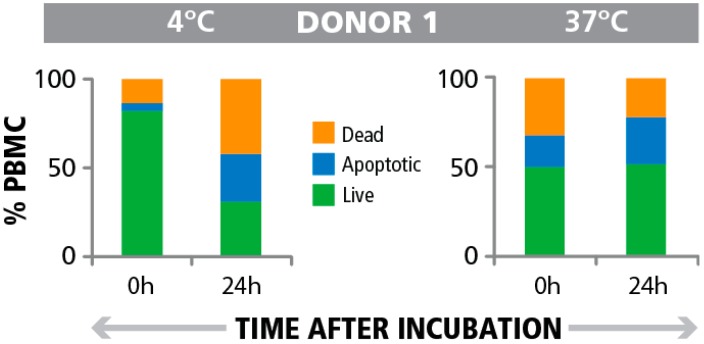 Fig. 1 Frequency of apoptotic cells pre- and post PBMC testing in the ELISPOT assay. (Marie Wunsch, 2015)
Fig. 1 Frequency of apoptotic cells pre- and post PBMC testing in the ELISPOT assay. (Marie Wunsch, 2015)
The article demonstrates the research significance of apoptotic cell numbers in improving Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) quality criteria for T cell assays. It highlights that serial measurements of apoptotic cells, both pre and post-T cell assay, provide a more accurate assessment of PBMC quality than a single pre-assay measurement. The results indicate that the presence of apoptotic bystander cells does not impair T cell functionality in the ELISPOT assay, which measures T cell response by counting spot-forming cells that secrete specific cytokines in response to antigens. This finding is critical for clinical settings, suggesting that monitoring apoptotic cells at multiple points can serve as a robust indicator of sample quality, thus ensuring the reliability of immunological assessments using T cell ELISpot assays.
The T cell ELISpot assay is utilized primarily to measure the immune response by detecting and quantifying cytokine-producing cells at the single-cell level. This assay is particularly valuable in vaccine development and immune monitoring, allowing researchers to assess the effectiveness of vaccines and immunotherapies by evaluating T cell activation.
The T cell ELISpot assay involves isolating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and stimulating them with specific antigens. Upon activation, T cells release cytokines, which are captured by cytokine-specific antibodies pre-coated on a membrane-based plate. Spots form at the site of cytokine release, each representing a single cytokine-secreting cell.
The T cell ELISpot assay can analyze any cytokine-secreting cell, but it is most commonly used to assess specific T cell responses. It can evaluate both CD4+ helper T cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, depending on the cytokine being targeted (e.g., IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-4).
The T cell ELISpot assay is highly sensitive, capable of detecting low-frequency cytokine-secreting cells. It offers quantitative results and can be used with minimal sample volumes, making it more efficient than methods like flow cytometry or cytokine bead arrays, especially in scenarios where cell numbers are limited.
The T cell ELISpot assay can detect a wide range of cytokines, including but not limited to IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-17. The choice of cytokine depends on the type of immune response being studied, such as Th1, Th2, or Th17 responses.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
