Carrot-derived Exosome Research and Application
Studies have found that carrot-derived exosomes exhibit the ability to mitigate cellular damage caused by oxidative stress, with the potential for the treatment of myocardial infarction and Parkinson's Disease. Creative Biolabs provides high-quality services to assist in the study of carrot-derived exosome production and functional development, contributing to the exploration of carrot-derived exosomes as drug candidates.
Features of Carrot-derived Exosomes
-
Carrots as exosome donors are easy to culture and take.
-
Carrots are rich in nutrients, especially recognized carotenoids, as well as high levels of vitamins, minerals such as calcium and iron, and fiber.
-
Carrot-derived exosomes have the potential to package active nutrients from carrots during formation.
-
The high yield and high purity of carrot-derived exosomes compared to other plant sources have also been found in studies.
-
Carrot-derived exosomes are known to carry excellent antioxidant activity.
Isolation of Carrot-derived Exosomes
-
Wash carrots in distilled water to remove surface dirt and pesticides.
-
Extraction of carrot juice by blender.
-
Centrifugation at low and high speeds to remove large carrot fragments.
-
Concentration of carrot juice by ultrafiltration.
-
Separation of carrot-derived exosomes from carrot juice by size exclusion chromatography.
-
Elution of carrot exosomes from size exclusion chromatography with PBS.
Research on Carrot-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Characterization of carrot-derived exosomes.
|
The results show that their size is about 140 nm, with negative electronegativity, sharing the recognized exosome characteristics.
|
|
Effect of carrot-derived exosomes on cardiomyocytes.
|
Carrot-derived exosomes did not cause damage to mouse-derived cardiomyocytes. Tracer assay of fluorescent dye-labeled exosomes demonstrated that carrot-derived exosomes can be transferred to target cells for their active potency.
|
|
Antioxidant effects of carrot-derived exosomes in cardiomyocytes.
|
Carrot-derived exosomes were able to down-regulate abnormally high levels of ROS in H2O2-induced cardiomyocytes, dose-dependently rescuing apoptosis and thus inhibiting the reduction of cell viability due to oxidative stress.
|
|
Antioxidant mechanisms of carrot exosomes in cardiomyocytes.
|
RT-PCR and protein blotting analyses demonstrated that the antioxidant potency of carrot exosomes in cardiomyocytes was achieved by inhibiting the reduction in the expression of antioxidant proteins (HO-1 and NQO-1) and their transcription factor (Nrf-2).
|
|
Effects of carrot-derived exosomes on neuroblastoma cells.
|
Similar to the effects on cardiomyocytes, treatment with carrot-derived exosomes in a neurotoxin-induced neuroblastoma model also resulted in SH-SY5Y cells being resistant to oxidative stress, indicating the potential development of carrot-derived exosomes as drug candidates against Parkinson's disease.
|
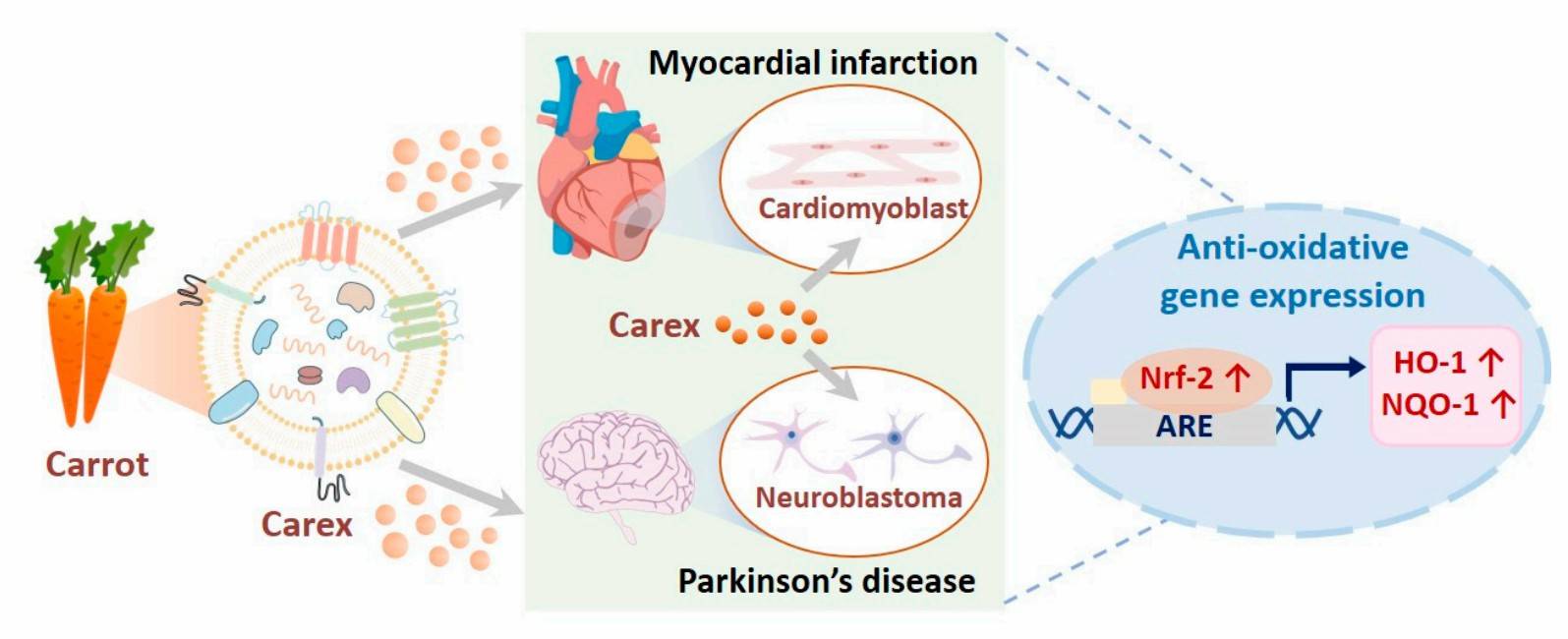 Fig. 1 Carrot-derived exosomes exert antioxidant effects and their molecular mechanisms.1
Fig. 1 Carrot-derived exosomes exert antioxidant effects and their molecular mechanisms.1
As carrots are known to exhibit a variety of healthful components including carotenoids and vitamins, carrot-derived exosomes have been viewed as promising drugs that serve a broad range of roles including, but not limited to, antioxidant activity and mitigation of cellular damage. Creative Biolabs is committed to the advancement of vegetable exosomes, including carrot-derived exosomes, and can provide customized solutions. Please contact us with your research requirements for carrot-derived exosomes.
Reference
-
Kim, Do Kyung, and Won Jong Rhee. "Antioxidative effects of carrot-derived nanovesicles in cardiomyoblast and neuroblastoma cells." Pharmaceutics 13.8 (2021): 1203.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Carrot-derived exosomes exert antioxidant effects and their molecular mechanisms.1
Fig. 1 Carrot-derived exosomes exert antioxidant effects and their molecular mechanisms.1









