Celery-derived Exosome Research and Application
Celery-derived exosomes have not only been found to inhibit the inflammatory response of T-lymphocytes, showing potential for use in immunotherapy but can also be used as vehicles for effective drug delivery to improve therapeutic efficacy. Creative Biolabs can provide services to support the production and development of celery-derived exosomes, assisting in expanding the broader application of celery-derived exosomes.
Isolation of Celery-derived Exosomes
-
Grind and squeeze the cleaned celery extract parts in a blender.
-
Filter celery lysate to remove larger contaminants.
-
Differential centrifugation to remove large celery fragments.
-
Precipitate celery exosomes with polyethylene glycol ( optional step).
-
Ultracentrifugation to obtain isolated celery exosomes and resuspension with PBS.
-
Purify celery exosomes by density gradient centrifugation in sucrose.
-
Wash celery exosomes with PBS and suspend celery exosome precipitates with PBS after centrifugation.
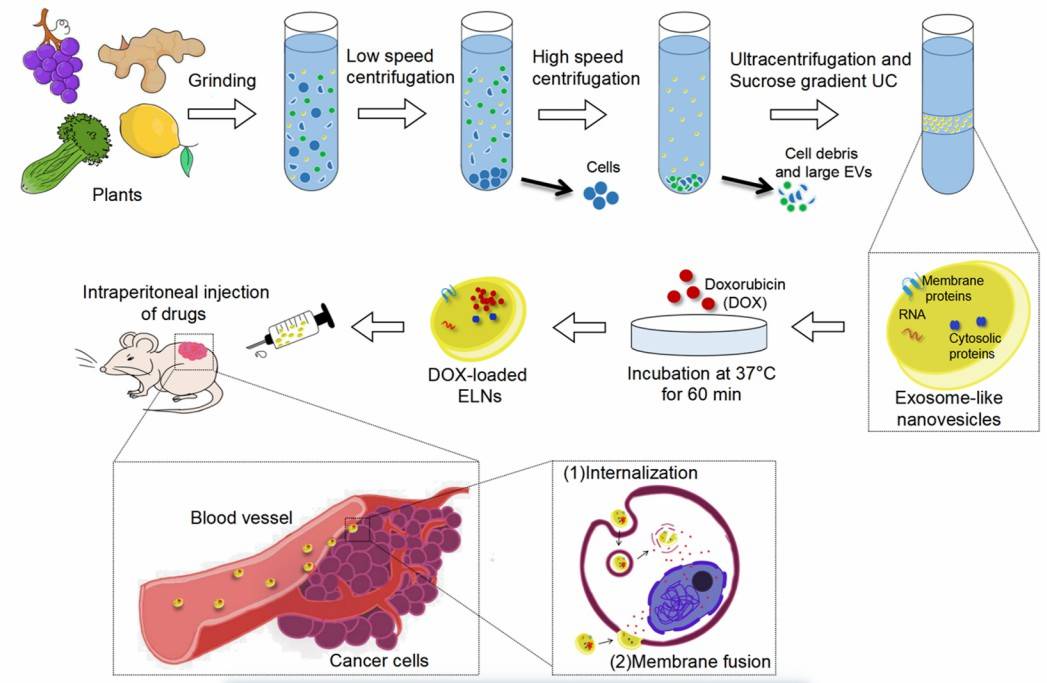 Fig. 1 Celery-derived exosomes are isolated and used for drug delivery.1
Fig. 1 Celery-derived exosomes are isolated and used for drug delivery.1
Research on Celery-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Physical properties of celery-derived exosomes.
|
The celery-derived exosomes showed round morphology with diameters in the range of 50-200 nm. The distribution of the exosome peaks measured by NTA was about 140 nm and well dispersed.
|
|
Lipid composition of celery-derived exosomes.
|
Lipidomic analysis detected the presence of lipids including diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid in celery-derived exosomes involved in membrane fusion. In addition, the results of GC-FAME revealed the presence of fatty acids with anti-inflammatory properties in celery-derived exosomes, suggesting the potential of celery-derived exosomes to modulate immunity.
|
|
Celery-derived exosomes are efficiently taken up by cells with negligible cytotoxicity.
|
Fluorescently labeled celery-derived exosomes are taken up by cells at a high uptake rate without causing a significant reduction in cell viability.
|
|
Celery-derived exosomes effectively delivered drugs.
|
In both a cellular model and a mouse subcutaneous tumor model of non-small cell lung cancer, treatment with celery-derived exosomes delivering anticancer drugs was able to reduce the proportion of Ki67+ cells and elevate the proportion of Caspase3+ cells, resulting in effective delivery of the drug's therapeutic oncological activity.
|
|
Celery exosomes inhibited T cell activation.
|
-
RT-PCR assay revealed that celery exosomes were able to reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory markers (e.g., IL-6 and IFNγ) in PMA/ionomycin-stimulated activated T cells in a dose-dependent manner.
-
Capillary immunoblotting assay detected that celery exosome treatment resulted in a reduction in the levels of p-LAT (phosphorylated T-cell activation link protein) and p-lck (phosphorylated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) proteins in activated T cells, demonstrating the effect of celery exosome on the inhibition of T-cell activation.
-
Flow cytometry analysis showed that celery exosomes inhibited Jurkat cell activation and down-regulated the proportion of CD4+CD25+ double-positive activated cells in the CD3+ cell population. And PMA/ ionomycin-induced increased pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-8 and IL12p-70) decreased after celery exosome treatment.
|
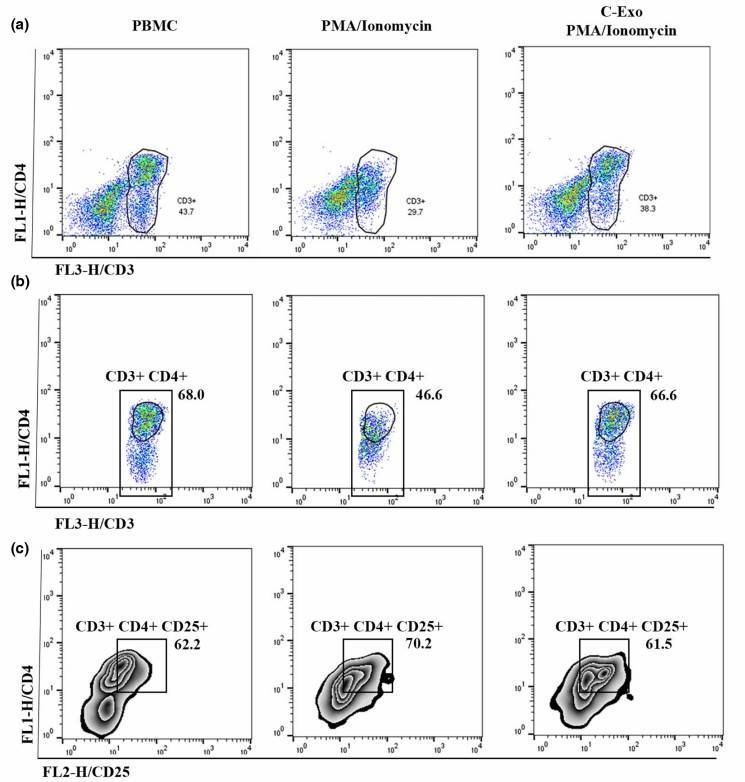 Fig. 2 Treatment with celery exosomes decreased the proportion of CD4+CD25+ double-positive activated cells in the CD3+ cell population.2
Fig. 2 Treatment with celery exosomes decreased the proportion of CD4+CD25+ double-positive activated cells in the CD3+ cell population.2
Applications of Celery-derived Exosomes
-
The active components in celery exosomes, such as polyphenols and flavonoids, are effective in scavenging free radicals in the organism, promising to aid in the development of new strategies for interventions against oxidative stress-induced cardiovascular disease and cancer.
-
Celery exosomes can effectively inhibit the expression and release of inflammatory factors, which is also highly beneficial in the treatment and prevention of many chronic diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, and diabetes.
-
Celery exosomes can act on vascular endothelial cells to improve vasoconstriction and diastole by regulating the release of vasodilatory factors, thereby promoting blood circulation and lowering blood pressure. Utilizing this action enables the development of protective strategies for blood vessels in hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
Exosomes have shown potential as novel immunomodulatory drugs. Studies have demonstrated the promise of celery-derived exosomes to be developed as immunosuppressive drugs with potential efficacy in fields such as immune disorders and antitumors. Creative Biolabs has established a comprehensive exosome research platform that can provide proficient and high-quality customized solutions for celery-derived exosomes. Please contact us to obtain support.
References
-
Lu, Xin, et al. "Celery (Apium graveolens L.) Exosome-like Nanovesicles as a New-Generation Chemotherapy Drug Delivery Platform against Tumor Proliferation." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2023).
-
Taşlı, Pakize Neslihan. "Usage of celery root exosome as an immune suppressant; Lipidomic characterization of apium graveolens originated exosomes and its suppressive effect on PMA/ionomycin mediated CD4+ T lymphocyte activation." Journal of Food Biochemistry 46.12 (2022): e14393.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Celery-derived exosomes are isolated and used for drug delivery.1
Fig. 1 Celery-derived exosomes are isolated and used for drug delivery.1
 Fig. 2 Treatment with celery exosomes decreased the proportion of CD4+CD25+ double-positive activated cells in the CD3+ cell population.2
Fig. 2 Treatment with celery exosomes decreased the proportion of CD4+CD25+ double-positive activated cells in the CD3+ cell population.2









