Garlic-derived Exosome Research and Application
With its rich bioactive components, garlic possesses various pharmacological effects, including antioxidation, anti-inflammation, anti-tumor, lipid-lowering, and anti-diabetic properties, contributing to the maintenance of human health. Garlic-derived exosome-like nanoparticles, as a bio-product of garlic, may carry similar active ingredients and exhibit comparable pharmacological potential. Creative Biolabs fully supports research on garlic-derived exosomes and the development of new drugs or health products for disease treatment and prevention.
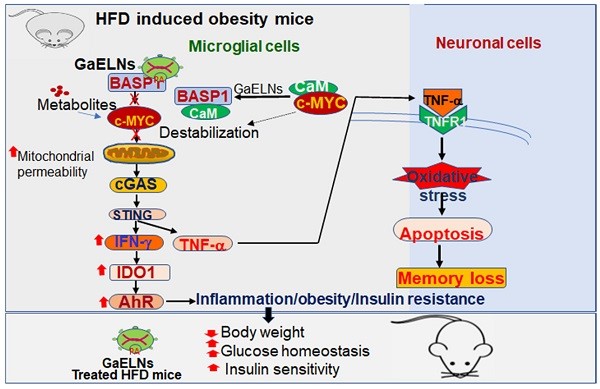 Fig.1 Garlic exosome-like nanoparticles reverse high-fat diet induced obesity via the gut/brain axis.1,2
Fig.1 Garlic exosome-like nanoparticles reverse high-fat diet induced obesity via the gut/brain axis.1,2
Main Active Components of Garlic and Their Pharmacological Effects
-
Allicin: Allicin can activate antioxidative signaling pathways, alleviate cardiovascular diseases, and potentially benefit anti-tumor and anti-diabetic treatments.
-
Alliin: Alliin, the most abundant sulfur-containing amino acid in garlic, possesses remarkable antioxidative properties, maintains mitochondrial membrane potential, inhibits lipid peroxidation, and protects liver function.
-
Other Sulfur-Containing Compounds: These compounds, including S-allylcysteine, diallyl sulfide, and more, influence various signaling pathways, including inflammatory pathways, potentially contributing to cardiovascular health and anti-cancer effects.
-
Ajoene: Ajoene inhibits platelet aggregation, helping to reduce blood clot formation and, consequently, lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
List of Garlic-Derived Exosomes Research Results
Exosomes, as tiny vesicles, can serve as drug delivery systems. If garlic-derived exosomes contain health-beneficial active ingredients, they can enhance the bioavailability and stability of these components, holding significant promise for disease treatment and health maintenance.
|
Potential Function
|
Target
|
Possible Mechanism
|
|
Anticancer
|
Cancer cells
|
Garlic-derived exosomes induce apoptosis in cancer cells by activating the caspase-mediated pathway and inhibiting angiogenesis.
|
|
Anti-inflammatory
|
Neuronal cells
|
Garlic-derived exosomes interact with BASP1 in microglia through their own phosphatidic acid to inhibit the c-Myc/STING/IFNIDO1 inflammatory signaling cascade pathway, thereby inhibiting microglial inflammation and nerve cell death.
|
|
Promoting hair growth
|
Skin hair follicles
|
Garlic-derived exosomes promote hair growth by upregulating platelet-derived growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and transforming growth factor-β1 through Wnt/β-catenin.
|
|
Alleviating colitis
|
Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells
|
Garlic-derived exosomes ameliorate colitis in mice via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway and modulation of intestinal microbiota.
|
|
Anti-inflammatory
|
Macrophages and adipocytes
|
The specific miR-396e of garlic-derived exosomes reshapes the interaction between macrophages and adipocytes by regulating the expression of glycolytic enzyme genes, ultimately reducing inflammation in adipocytes.
|
|
Improving non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
|
Macrophages and hepatic cells
|
The unique miR-396e of garlic-derived exosomes inhibits inflammation and modulates the interaction between macrophages and hepatocytes to alleviate high-fat diet-induced liver dysfunction by regulating glycolytic enzyme genes.
|
|
Alleviating acute liver failure
|
Monocytes and macrophages
|
Garlic-derived exosomes can hinder the migration of monocytes to the liver and reduce macrophage infiltration, thereby ameliorating the inflammatory outbreak. This is primarily achieved by inhibiting CCR2/CCR5 signaling.
|
Looking ahead, garlic exosomes hold potential as a novel therapeutic strategy. In future garlic-derived exosome development, Creative Biolabs offers plant exosome extraction and development services. This presents an opportunity for biomedical researchers and pharmaceutical companies. If you have related demands, please feel free to contact us.
Plant-Derived Exosome Isolation
Plant-Derived Exosome Identification
High-Throughput Screening Analysis (Proteins, RNA, Lipids and Metabolites)
Large-Scale Production of Plant-Derived Exosomes
References
-
Sundaram, K.; et al. Garlic exosome-like nanoparticles reverse high-fat diet induced obesity via the gut/brain axis. Theranostics. 2022, 12(3):1220-1246.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Garlic exosome-like nanoparticles reverse high-fat diet induced obesity via the gut/brain axis.1,2
Fig.1 Garlic exosome-like nanoparticles reverse high-fat diet induced obesity via the gut/brain axis.1,2









