Title: Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice.
Research Objectives: Investigate the impact of yam-derived exosomes on bone health and explore the potential therapeutic role in treating osteoporosis.
Research Methods:
-
Isolation and Characterization: Successful isolation, purification, and characterization of exosomes from yam, including size, morphology, and composition.
-
In Vitro Cell Experiments: Evaluation of the effects of yam-derived exosomes on osteoblast cell growth, differentiation, and mineralization, including cell proliferation, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and calcium deposition.
-
Molecular Biology Experiments: Using RT-qPCR and immunoblotting techniques to study the impact of yam-derived exosomes on osteoblast differentiation markers and signaling pathways, particularly the BMP-2/p-p38-dependent Runx2 pathway.
-
In Vivo Model Experiments: In vivo evaluation in ovariectomy-induced mouse models to assess the impact on bone regeneration, bone volume density, bone density, and regulation of bone resorption. Biodistribution analysis through in vivo imaging and safety assessment by examining organ toxicity.
Research Findings:
-
Yam-derived exosomes positively affect osteoblasts by promoting cell growth, differentiation, and mineralization, primarily through the BMP-2/p-p38-dependent Runx2 pathway.
-
In mouse models, oral administration of yam-derived exosomes significantly improves bone regeneration, bone volume density, and bone density, indicating potential for osteoporosis treatment.
-
Yam-derived exosomes demonstrate excellent biocompatibility and safety when administered orally, with no observed organ toxicity.
Conclusion: Yam-derived exosomes show promise as a potential therapeutic agent for osteoporosis treatment.
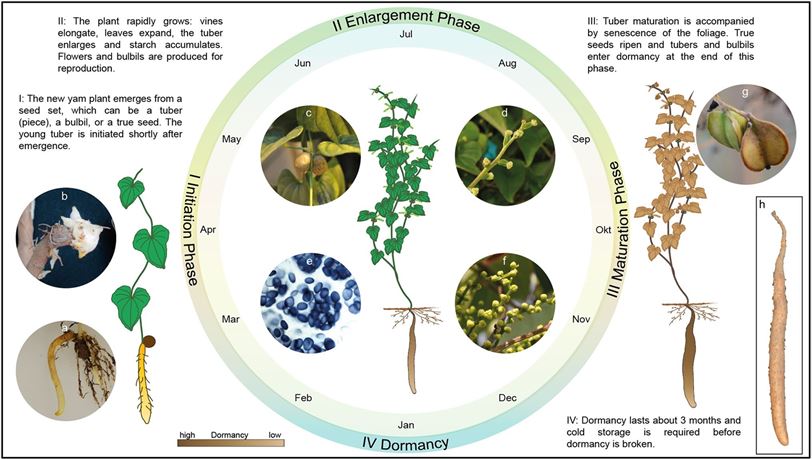 Fig.1 Growth cycle of Chinese yam.1,2
Fig.1 Growth cycle of Chinese yam.1,2
Given the beneficial bioactive components and potential medicinal value of yam, the study of yam-derived exosomes holds significance. These exosomes may carry bioactive molecules from yam, including antioxidants, polysaccharides, flavonoids, and other active ingredients, with various therapeutic potentials. However, research on yam-derived exosomes is relatively limited.
Although research in this field is in its early stages, the relative scarcity of studies highlights significant opportunities. Creative Biolabs has established a platform for plant-derived exosome research and is available to provide support to interested clients in exploring the potential of yam-derived exosomes. If you are interested in yam-derived exosome research, please feel free to contact us for more information and support.
Plant-Derived Exosome Isolation
Plant-Derived Exosome Identification
High-Throughput Screening Analysis (Proteins, RNA, Lipids and Metabolites)
Large-Scale Production of Plant-Derived Exosomes

 Fig.1 Growth cycle of Chinese yam.1,2
Fig.1 Growth cycle of Chinese yam.1,2









