Ginger Root-derived Exosome Research and Application
Ginger root-derived exosomes, as one of the representatives of edible plant-derived nanovesicles, have preparation advantages such as easy accessibility, low cost, and easy scale-up production, which overcomes the technical challenges of mammalian-derived exosome production. Ginger root-derived exosomes exhibit superior pharmacological activities that make them highly valuable for research and application potential. Creative Biolabs has launched vegetable-derived exosome-related research services to support customers in conducting in-depth research and promising translations of ginger root-derived exosomes.
Ginger Root-derived Exosomes Isolation
-
Pretreatment of ginger root material.
Crush and homogenize firm-textured ginger to obtain a coarse gel of ginger root.
-
Separation of ginger root exosomes.
Extract the ginger root exosomes from ginger root fragments based on differential centrifugation with different speeds and times set.
-
Purification of ginger root exosomes.
Purify ginger root exosomes by density gradient centrifugation with sucrose, where different densities of ginger root-derived vesicles are distributed in the gradient sucrose after centrifugation. There are other purification methods such as membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, and immunoaffinity separation.
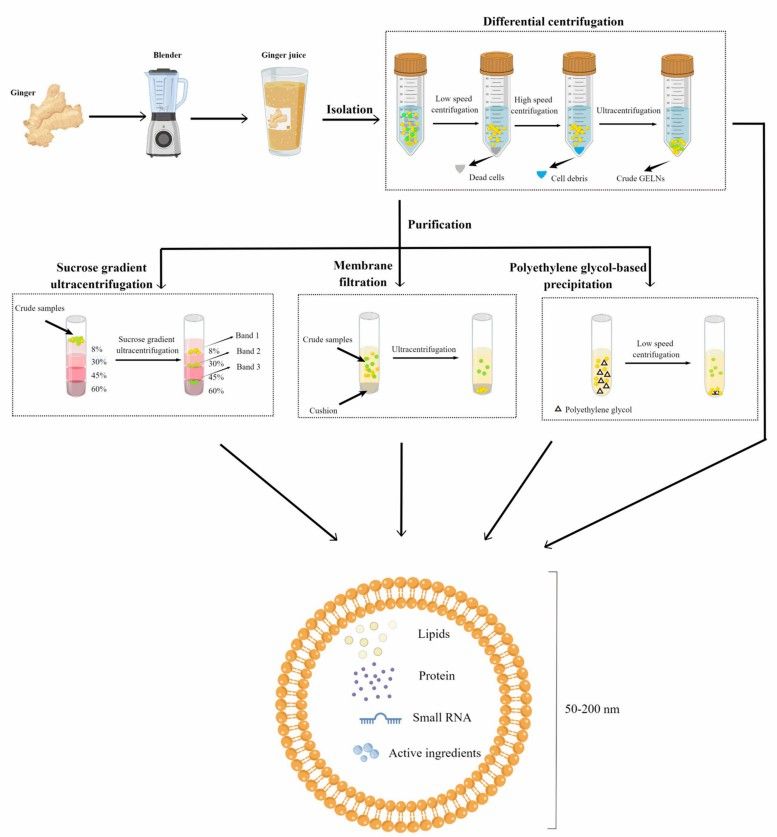 Fig. 1 Isolation and purification of ginger root-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Isolation and purification of ginger root-derived exosomes.1
Features of Ginger Root-derived Exosomes
-
Size: The size of ginger root-derived exosomes is generally between 50-200 nm, comparable to other exosomes.
-
Composition: Exosomes from ginger root are rich in bioactive molecules, including components common to plant exosomes and proprietary active components such as gingersols and shogaols. Small RNAs encapsulated in ginger root exosomes modulate the composition of gut microbes and their metabolites, inhibit colitis in mice, and create a balance between immunity and gut microbes.
-
Stability: In stability studies of ginger root exosomes, not only was it found to be stable for storage at 4°C for up to 25 days, with characteristics similar to those of freshly extracted products, but it is also suitable for presence in environments that mimic gastric and intestinal fluids.
Applications of Ginger Root-derived Exosomes
-
Drug carriers: Ginger root-derived exosomes can function as drug carriers, in which drug molecules are encapsulated and administered by injection or orally for direct action on target cells. This method of drug delivery can improve the therapeutic effect of drugs and reduce side effects because exosomes are able to target specific cells or tissues and deliver drugs precisely to the site of lesions.
-
Biomaterials: Ginger root-derived exosomes can be used as biomaterials in fields such as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. For example, they can be used as scaffolding material for cell culture. In addition, exosomes can be used to construct engineered tissues or organs to treat diseases or repair damaged organ function.
-
Immune modulation: Ginger root-derived exosomes can modulate immune responses, inhibit inflammatory responses, and have certain antioxidant effects. These properties make ginger root-derived exosomes potential drugs in the treatment of autoimmune or inflammatory diseases. Ginger root exosomes were found to selectively stimulate macrophages to release the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 and inhibit the assembly of NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles.
-
Anti-tumor effects: Studies have shown that ginger root-derived exosomes can inhibit the growth and metastasis of tumor cells and attenuate inflammatory responses, among others. Therefore, ginger root-derived exosomes may have the potential as antitumor drugs for tumor treatment and prevention.
-
Promote wound healing: Exosomes from ginger root sources also have the potential to promote wound healing. They can stimulate cell migration and proliferation and promote tissue repair. In the treatment of skin injuries or ulcers, ginger root-derived exosomes may be an effective wound-healing promoting agent.
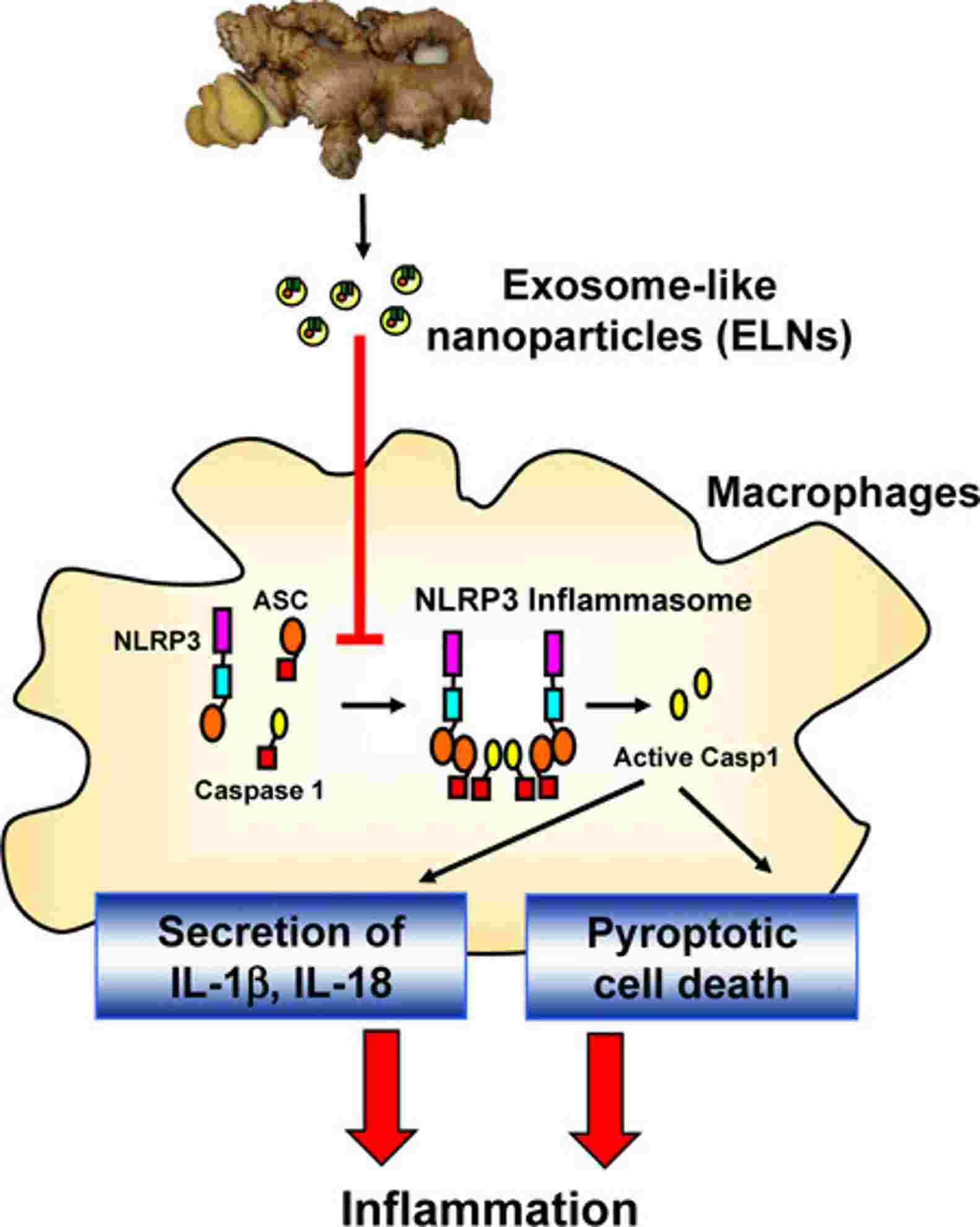 Fig. 2 Ginger root exosomes prevent NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles from becoming activated.2
Fig. 2 Ginger root exosomes prevent NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles from becoming activated.2
Ginger root-derived exosomes have potential effects such as increasing gastrointestinal tract viability, antibacterial and antiviral effects, and their abundant components and mechanisms of action deserve more in-depth study. Creative Biolabs has a professional technical team for exosome research and many years of experience in providing services to meet the demands of different projects related to ginger root-derived exosomes. Please contact us for further discussion.
References
-
Zhu, He, and Wenxi He. "Ginger: a representative material of herb-derived exosome-like nanoparticles." Frontiers in Nutrition 10 (2023): 1223349.
-
Chen, Xingyi, You Zhou, and Jiujiu Yu. "Exosome-like nanoparticles from ginger rhizomes inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation." Molecular pharmaceutics 16.6 (2019): 2690-2699.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Isolation and purification of ginger root-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Isolation and purification of ginger root-derived exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Ginger root exosomes prevent NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles from becoming activated.2
Fig. 2 Ginger root exosomes prevent NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles from becoming activated.2









