NAA Services for Anti-Factor XIII Antibodies
Creative Biolabs is a pioneer company in NAA services. With our professional scientists committed to NAA research, we offer a full range of anti-Factor XIII antibodies marker services for diseases diagnosis and therapeutic. Our experienced scientists will take part in every step of your program to facilitate your project development.
Background of Anti-Factor XIII Antibodies
Factor XIII (FXIII) is a fibrin-stabilizing factor and comprises a heterotetramer formed by two catalytic A subunits (F13-A) and two non-catalytic carrier B subunits (F13-B). FXIII was initially termed as fibrin stabilizing factor participating in clot preservation. FXIII is also involved in other physiologic processes, including wound repair and healing. Although anti-FXIII autoantibodies are either oligoclonal or polyclonal, they have been sub-classified into three major types: Aa, Ab, and B. Autoantibodies of types Aa and Ab are directed against FXIII-A and FXIII-B, respectively. Type Aa autoantibodies inhibit the proteolytic cleavage of FXIII-A by thrombin for activation, while type Ab autoantibodies inhibit the enzymatic activity of activated FXIII mainly. Both of two types of autoantibodies are functionally neutralizing antibodies. These autoantibodies also can enhance the clearance of FXIII to some degree in many patients, thus, these are also hyper-clearance type autoantibodies. In contrast, type B autoantibodies mainly bind to non-catalytic FXIII-B, namely, they are not neutralizing/inhibitory antibodies. Type B antibodies interact with both FXIII-B and the A2B2 complex of FXIII molecules and remove them from the circulation, resulting in FXIII deficiency of <1-41% of the normal in the previous study.
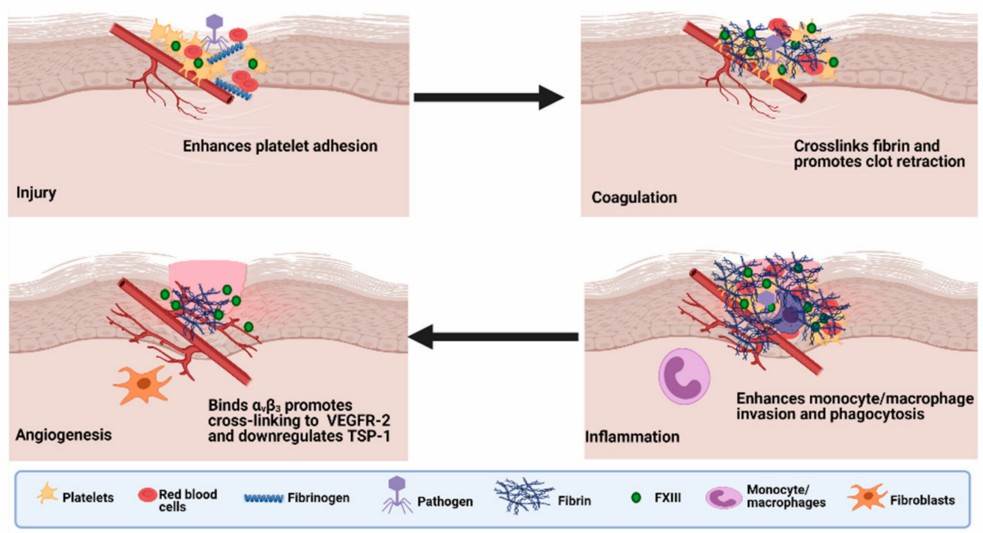 Fig.1 The roles of Factor XIII in wound healing.1
Fig.1 The roles of Factor XIII in wound healing.1
The Role of Anti-Factor XIII Antibodies in Celiac Disease
Celiac disease (CD) is an inflammatory disorder, commonly caused by an improper immune response to ingested wheat gluten (composes of gliadin and glutenin) and related cereal proteins in genetically predisposed individuals, leading to villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia and lymphocytic infiltration in the small intestine. Previous research has identified that some patients with CD have high titer autoantibodies against factor XIII. In addition, a significant increase of IgG antibody titers is noted in EMA-positive patients as well as in patients with ulcerative colitis and Morbus Crohn, as compared with plasma donors. Identification of several types of autoantibodies (IgA and IgG) directed against homologous enzymes and factor XIII helps the diagnosis of different kinds of gastrointestinal diseases.
What Can We Do about NAA?
Our NAA services can be performed with our well-established platforms and experienced scientists, include NAA detection, NAA profiling, NAA Affinity Measurement, NAA epitope mapping and paratope mapping. A wide range of NAA products is also available for your choice.
At Creative Biolabs, our seasoned scientists are confident in offering comprehensive NAA services for various biomarkers from a broad range of autoimmune diseases. Creative Biolabs has extensive expertise and experience to meet customized requirements for the detection of anti-Factor XIII antibodies in celiac disease. We also provide custom services based on the requirements of the clients to meet the specific demand. Please contact us for more information.
Reference:
- Alshehri, Fahad SM, Claire S. Whyte, and Nicola J. Mutch. "Factor XIII-A: an indispensable "factor" in haemostasis and wound healing." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.6 (2021): 3055.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-Transglutaminase 2 Antibodies (ATG2A)
- NAA Services for Anti-Transglutaminase 3 (TG3) Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Actin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Calreticulin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Gangliosides Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Collagens Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Synapsin I Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Zonulin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Cardiolipin Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain
- NAA Services for Anti-Enolase α

