Overview Service Features Published Data FAQs Scientific Resources Related Services
Creative Biolabs has extensive experience to offer various characterization services of iPSC pluripotency. Now our team of developers and technical support specialists work together to bring our customers the most high-efficient embryoid body (EB) formation and characterization service.
Introduction to Embryoid Body (EB) Formation and Characterization for iPSC
Background of iPSC Pluripotency
Based on the core properties of unlimited self-renewal and differentiation potentiality, human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) has been served as the exciting cell source for various applications such as drug discovery, regenerative medicine, and investigation of disease etiology and pathogenesis. It has been proved that the strategy of inducing pluripotency is valid in reprogramming adult somatic cells to be the embryonic-like state. However, the pluripotent Capability and differentiation potential of the hiPSCs should be evaluated before their downstream regulation applications. Now Creative Biolabs provides the embryoid body (EB) formation and characterization assay to characterize pluripotency and differentiation potential for iPSC.
Embryoid Bodies for Pluripotency Assessment
The generation of embryoid bodies from iPSCs is an in vitro approach for the pluripotency evaluation. EBs are three-dimensional aggregates of cells which contain the amalgam of the three developmental germ layers. In our method, the undifferentiated hiPSCs are placed in a suspension that promotes random differentiation of cells into all three germ layers. The formation of EBs is a common approach to differentiate iPSCs into different cell types. The advantage of this approach is that the regulatory issues and extensive expenses associated with maintaining immune-deficient mice can be avoided in in vitro culture with standard tissue culture methods and materials. Our service portfolio includes various methods for the generation of EBs and subsequent analysis in biochemistry and histology, the details can be read as follow.
Methods for Embryoid Bodies Formation
-
Heterogeneous methods: Stirred flask culture; Liquid suspension culture.
-
Homogeneous methods: Low adhesion U-bottom multiwell plates; Hanging drop culture.
-
Other methods: Hydrogels (e.g., methylcellulose, agarose, alginate).
Analysis of Germ Layer Formation in Embryoid Bodies
To assess the pluripotency of hiPSCs by in vitro methods to derive EBs, it is necessary to carry out a definitive downstream assay that demonstrates the ability to form a representative of three developmental germ layers, thereby demonstrating their increased differentiation capacity upon reprogramming.
-
Expression of germ layer-specific genes. (To identify the presence of germ layer-specific gene markers and the concomitant loss of pluripotent gene markers.)
-
Histological analysis of embryoid bodies. (Tissue differentiation assessment based on the histological evaluation of EBs by investigating tissue organization, cellular morphology, and localized protein expression.)
 Fig.1 Histological evidence of germ layer differentiation in embryoid bodies.1
Fig.1 Histological evidence of germ layer differentiation in embryoid bodies.1
Based on our extensive experience and advanced platform, Creative Biolabs offers a series of characterization services of iPSC pluripotency. In addition, other services regarding iPSC generation and iPSC applications can also be found on our web pages. If you are interested in them, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Services at Creative Biolabs
Our EB formation and characterization service is designed to provide researchers with high-quality, reproducible EBs derived from iPSCs. These EBs are crucial for studying early differentiation events and developing various cell lineages for downstream applications. This service encompasses the formation, maintenance, and thorough characterization of EBs to ensure they meet your experimental needs.
Here's how our process would potentially look:
-
iPSC Culturing and Preparation
-
iPSC Maintenance - We begin by culturing your provided iPSC lines or using our well-characterized in-house iPSC lines. Cells are maintained in feeder-free conditions to ensure high purity and quality.
-
Quality Control - Prior to EB formation, we assess iPSC quality through morphological evaluation, pluripotency marker expression (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG), and karyotyping to ensure genetic stability.
-
EB Formation
-
Aggregation Methods - We employ hanging drop, low-adhesion plate, or micro-well plate techniques to promote uniform EB formation. The choice of method depends on the specific requirements of your research.
-
Standardized Protocols - Our protocols ensure consistent EB size and shape, critical for reproducible differentiation outcomes.
-
Culture Conditions - EBs are cultured in optimized media that support initial pluripotency and subsequent lineage specification.
-
Differentiation Induction
-
Spontaneous Differentiation - EBs are maintained in differentiation media to allow spontaneous differentiation into three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm).
-
Directed Differentiation - If specific lineage differentiation is required, we provide directed differentiation protocols using specialized media and growth factors.
-
Characterization of EBs
-
Morphological Assessment - Regular monitoring and imaging of EBs to assess growth and morphology.
-
Molecular Analysis - RT-PCR, qPCR, and RNA-seq to evaluate the expression of germ layer-specific markers (e.g., SOX1 for ectoderm, Brachyury for mesoderm, GATA4 for endoderm).
-
Immunocytochemistry - Staining for key markers of the three germ layers, such as NESTIN (ectoderm), BMP4 (mesoderm), and SOX17 (endoderm).
-
Flow Cytometry - Quantitative analysis of pluripotency and differentiation markers.
-
Functional Assays - Optional functional assays to assess lineage-specific functionalities, such as contractility assays for cardiomyocyte differentiation or glucose-responsive insulin secretion for pancreatic differentiation.
Our service adheres to stringent quality control measures to ensure the reliability and reproducibility of your EBs. Each step is performed by experienced stem cell scientists using state-of-the-art equipment and techniques. We are committed to advancing your research through high-quality EB formation and characterization services, ensuring reliable and reproducible results for your scientific endeavors.
Features of Our Services
-
High-quality iPSC lines
-
Standardized protocols
-
High-quality, reliable, and reproducible tools
-
Customization and flexibility
-
Rigorous quality control
Published Data
Below are the findings presented in the article related to EB formation and characterization for iPSC.
Katherine Rhodes, et al. generated EBs from iPSCs using a robust mixed-pool study design and performed scRNA-seq analysis. Based on these data, they identified dozens of cell types and inferred differentiation trajectories that were highly compatible with known developmental gene expression dynamics. This emphasizes the utility of EB as a new model system for mapping dynamic inter-individual regulatory differences in various cell types.
To explore the utility of EB, they systematically explored cellular and gene expression heterogeneity in EB from multiple individuals, describing the various cell types generated by EB, and the extent to which they recapitulate gene expression in vivo.
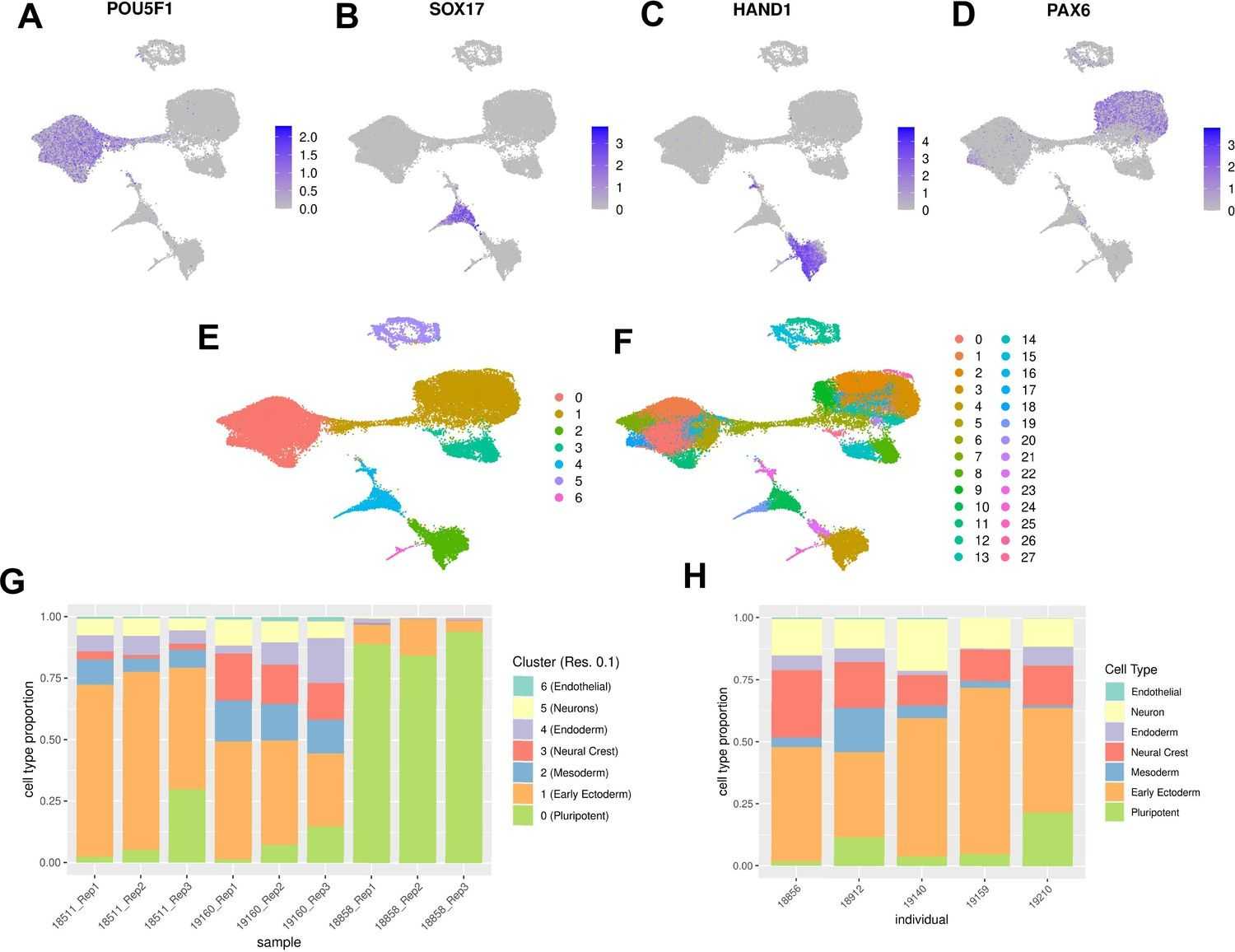 Fig.2 Characterization of EB cell type composition using marker gene expression and clustering.2
Fig.2 Characterization of EB cell type composition using marker gene expression and clustering.2
FAQs
-
Q: What information do I need to provide when submitting my iPSC lines for EB formation and characterization?
A: When submitting your iPSC lines, please provide detailed information about the origin and background of the cells, including the reprogramming method used, passage number, and any known genetic modifications. Additionally, any previous characterization data, culture conditions, and specific requests for differentiation or analysis should be included to tailor the service to your research needs.
-
Q: What kind of data and reports will I receive at the end of the service?
A: At the end of the service, you will receive a comprehensive report that includes detailed results from all characterization assays. This report will contain quantitative data, images from immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry, gene expression profiles, and an analysis summary. The report is designed to provide you with clear insights into the pluripotency and differentiation potential of your iPSC lines.
-
Q: How do I ship my iPSC lines to your facility for EB formation and characterization, and what are the best practices for ensuring their viability during transit?
A: To ship your iPSC lines to our facility, we recommend using a reliable courier service with experience in handling biological samples. Cells should be shipped in a cryopreserved state using dry ice or a liquid nitrogen dry shipper to ensure their viability. It is essential to include proper labeling, documentation, and detailed instructions for cell recovery upon arrival. We can provide specific shipping guidelines and support to help you with this process.
-
Q: Are there any additional services you offer that complement EB formation and characterization?
A: Yes, we offer a range of complementary services including iPSC reprogramming, genome editing, and specific lineage differentiation. We also provide advanced genomic and proteomic analyses, as well as custom assay development. These additional services can be integrated with EB formation and characterization to provide a comprehensive evaluation of your iPSCs and support your research goals.
-
Q: What happens if the iPSC lines I send do not meet your quality criteria for EB formation?
A: If the iPSC lines you send do not meet our quality criteria, we will notify you immediately and provide detailed feedback on the issues identified. We may suggest corrective actions or improvements in cell culture practices to enhance the quality of your iPSCs. Our goal is to work collaboratively with you to achieve the best possible results, and we can offer additional support and guidance as needed.
Scientific Resources
References
-
Sheridan, Steven D., Vasudha Surampudi, and Raj R. Rao. "Analysis of embryoid bodies derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells as a means to assess pluripotency." Stem cells international 2012.1 (2012): 738910. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only parts of the original image.
-
Rhodes, Katherine, et al. "Human embryoid bodies as a novel system for genomic studies of functionally diverse cell types." Elife 11 (2022): e71361. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For
Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
 Fig.1 Histological evidence of germ layer differentiation in embryoid bodies.1
Fig.1 Histological evidence of germ layer differentiation in embryoid bodies.1
 Fig.2 Characterization of EB cell type composition using marker gene expression and clustering.2
Fig.2 Characterization of EB cell type composition using marker gene expression and clustering.2