As a pivotal component of skin lipids, wax esters play a crucial role in maintaining skin health. Creative Biolabs aims to enhance understanding of wax ester synthesis pathways, their mechanisms of action, and their relevance to diseases, offering novel insights and methodologies for skin diseases and stem cell therapy.
Wax esters (WE) are esterification products of fatty acids and fatty alcohols, biodegradable in nature, and play significant roles in skin lipids.
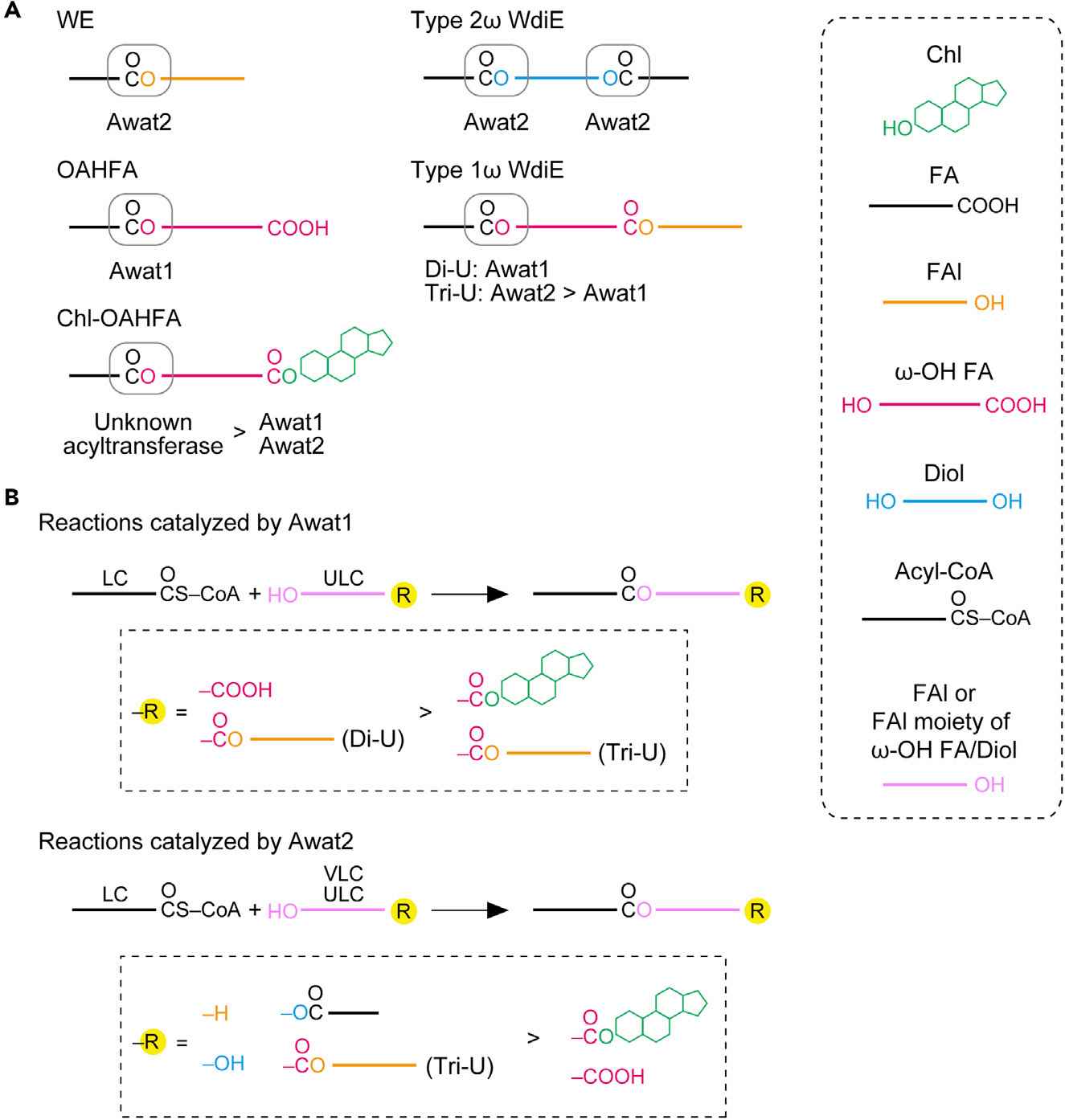 Fig.1 AWAT1 and AWAT2 in the production of diverse lipids.1
Fig.1 AWAT1 and AWAT2 in the production of diverse lipids.1
Wax esters possess a simple structure, formed by the esterification of fatty acids and fatty alcohols via ester bonds. Their synthesis initially involves the reduction of acyl-CoA by acyl-CoA reductases using the NADPH to yield fatty alcohols and coenzymes. Subsequently, wax synthases catalyze the esterification reaction between fatty acids and fatty alcohols to form wax esters.
Beyond being key components of premium lubricants and moisturizers, wax esters play significant roles in skin health:
The protein encoded by the AWAT gene belongs to the diacylglycerol acyltransferase enzyme family, serving as a key enzyme in the wax ester synthesis pathway. It catalyzes the esterification reaction between fatty acids and fatty alcohols, utilizing long-chain (wax) alcohols and acyl-CoA-derived fatty acids to produce wax esters.
Mammals possess two isoforms of AWAT enzymes (AWAT1 and AWAT2) with differing substrate affinities. Research suggests that the activity of AWAT enzymes is closely linked to the homeostasis of skin lipid metabolism, and defects in these enzymes may impair skin barrier function, leading to skin diseases.
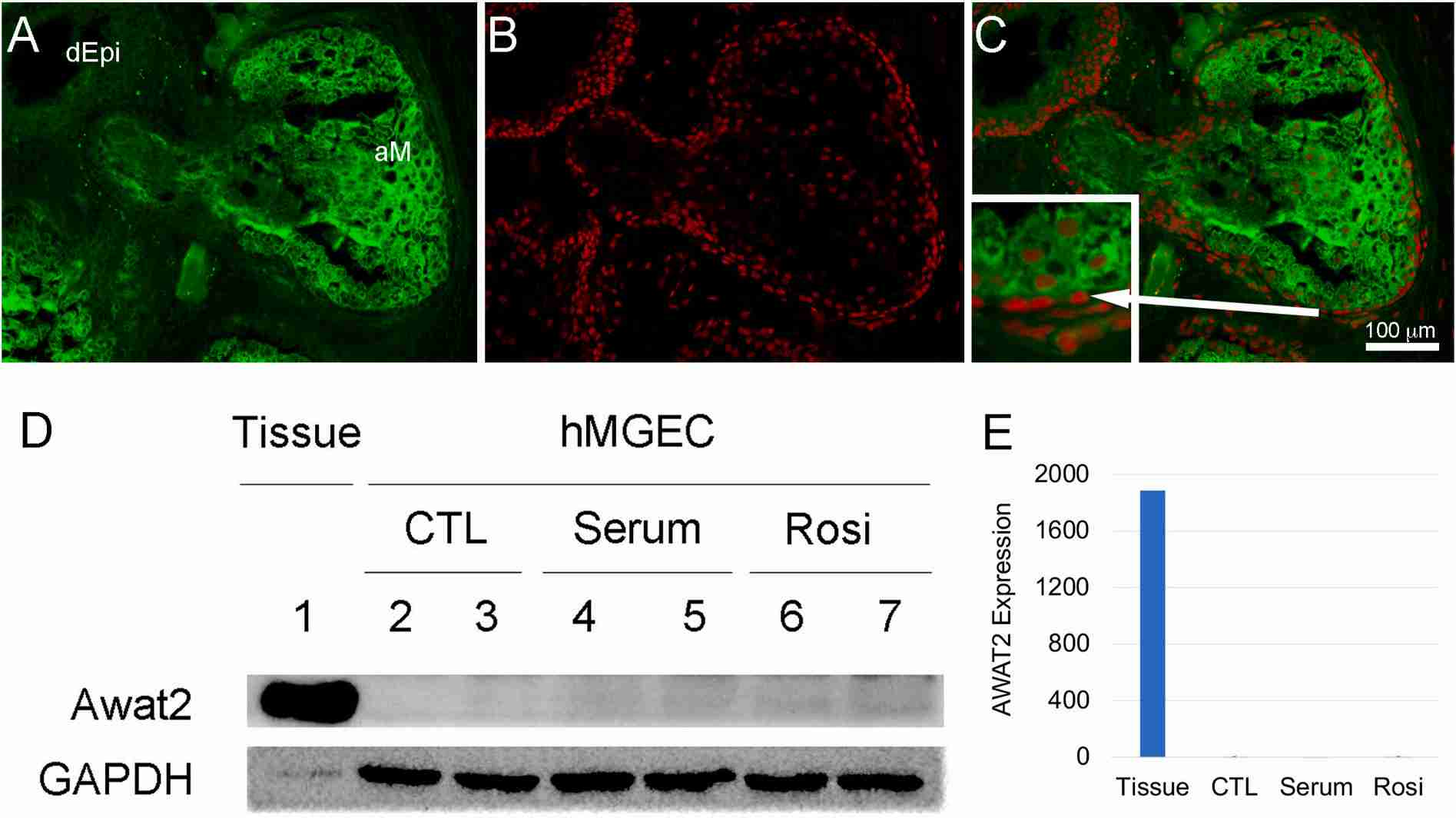 Fig.2 AWAT2 analysis.2
Fig.2 AWAT2 analysis.2
Acne involves factors such as excessive sebum secretion, follicular occlusion, and bacterial infections. Studies have found higher levels of wax esters in the skin lipids of acne patients, suggesting a potential correlation with the onset and progression of acne.
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to advancing skin health research through stem cell technology, developing intervention strategies, understanding wax ester synthesis pathways, and offering new insights and methodologies for stem cell therapy. Through our skin wax ester analysis services, you will have the opportunity to gain deeper insights into the principles of wax ester synthesis and understand their mechanisms of action in skin health. Please do not hesitate to contact us for robust support.
References
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.