Overview Workflows Case study Related Products Featured Services Protocols Q&A Resources
With extensive expertise in immunology and complement biology, Creative Biolabs offers precise complement C1 complex functional tests, enabling researchers to explore complement deficiencies, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic efficacy with reliable, high-quality results.
Overview of Complement C1 Complex Functional Test
Complement C1 Complex
The complement C1 complex is the initiating component of the classical complement pathway, a key part of the immune response. It consists of three distinct three protein components: C1q, C1r, and C1s. C1q interacts with antibodies (IgG or IgM) that are bound to the surface of pathogens, triggering a conformational change in C1r and C1s. This activates the C1 complex, leading to the cleavage of C4 and C2, which in turn form the C3 convertase (C4b2a). This initiates the cascade of complement activation, enhancing pathogen clearance, promoting inflammation, and facilitating immune responses through opsonization and cell lysis.
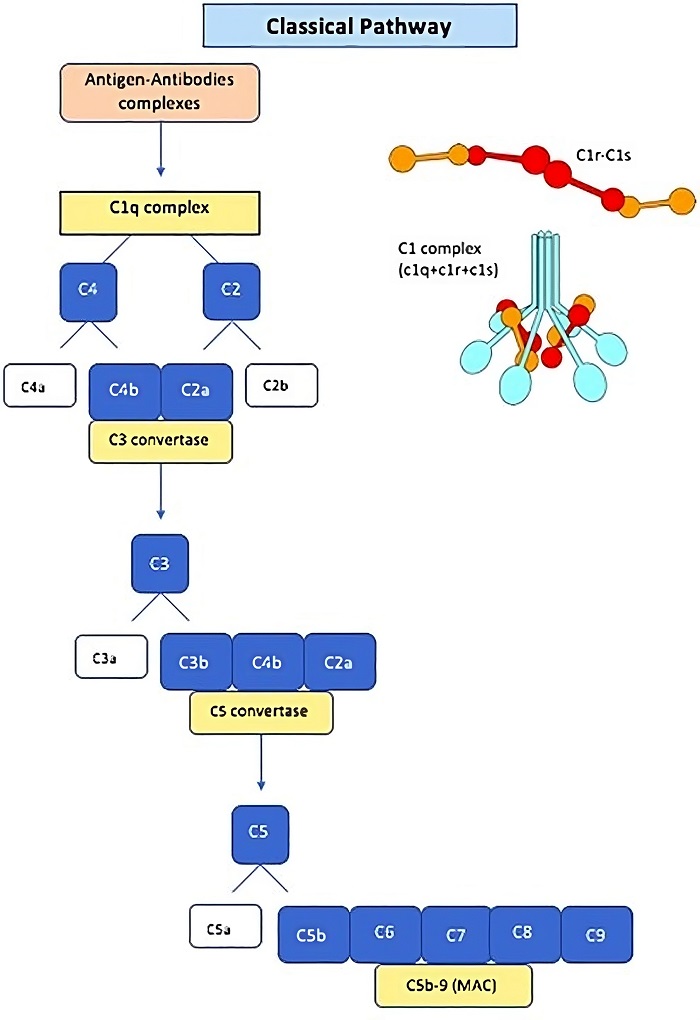 Fig.1 The classical pathway of the complement system and structure of the C1 complex.1
Fig.1 The classical pathway of the complement system and structure of the C1 complex.1
Complement C1 Complex Functional Test
Method
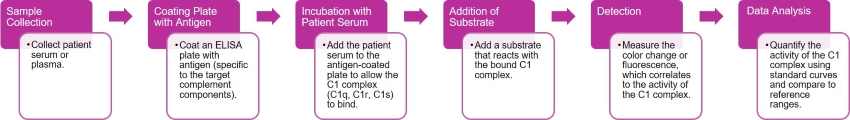
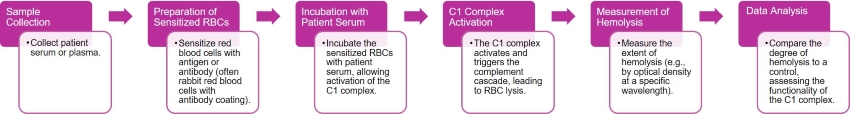
The C1 complex functional test evaluates the activity of the C1 complex within the classical complement pathway. The test involves mixing patient serum with a specific substrate or antigen-antibody complex that activates C1. C1 activation is then measured by the resulting breakdown of complement components, often monitored through hemolysis or other specific assays.
Analysis
The C1 complex functional test is crucial for diagnosing complement deficiencies, particularly in conditions like hereditary C1q deficiency or autoimmune disorders. It helps assess immune response efficiency and complement-mediated inflammation, guiding treatment decisions for complement-related diseases or immune system dysfunctions.
Workflow of C1 Complex Functional Test
C1 Complex ELISA
Hemolytic assay
Case Study
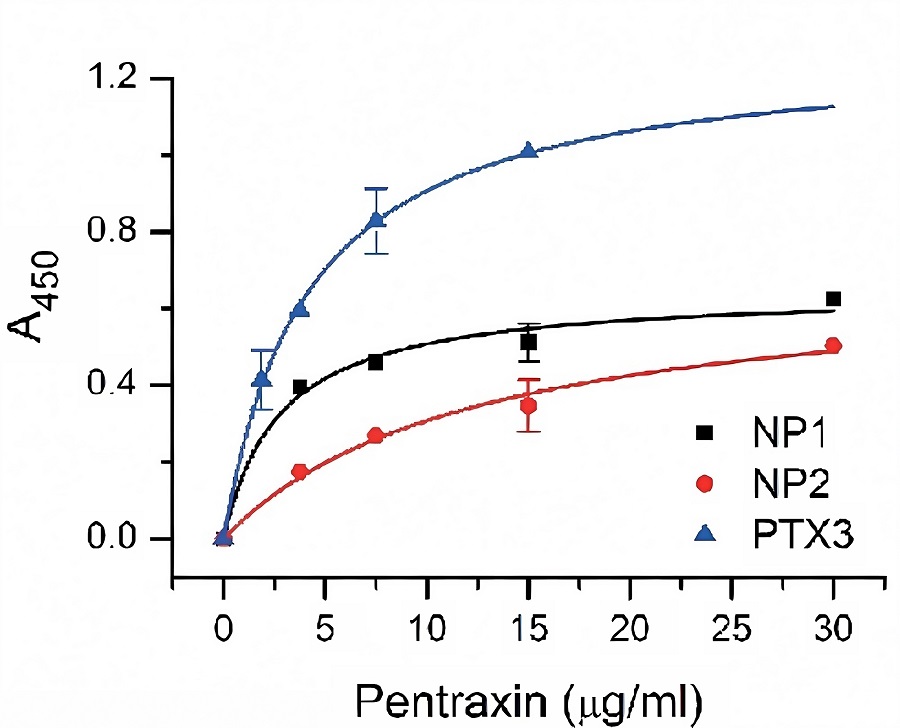
Fig.2 Interaction of neuronal pentraxins with C1
in vitro with an ELISA assay.
2,4
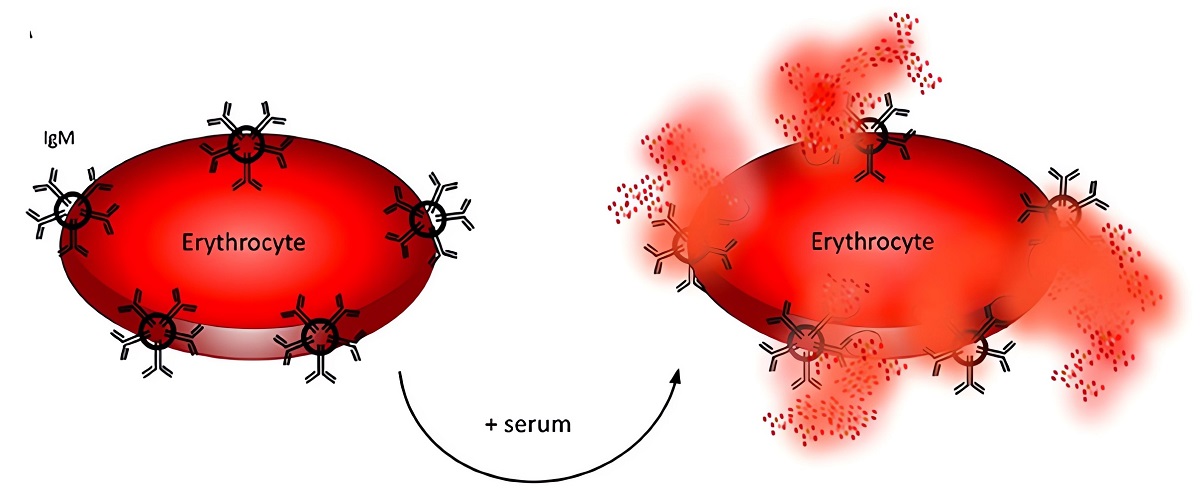
Fig.3 Hemolytic assay for detection of complement classical pathway and C1 complex function.
3,4
Related Products
Featured Services

|

|
|
Total Complement Activity Test
|
C1q-Binding Assays
|
|
Creative Biolabs offers total complement activity test services for our clients. Total complement activity tests include CH50, AH50, and LP50.
|
Creative Biolabs offers high-quality C1q-binding assays for the characterization of therapeutic mAbs.
|
|
Learn more
|
Learn more
|
Protocols
Questions & Answer
A: Absolutely. The test can monitor the impact of complement-targeted therapies, such as C1 inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies, by evaluating changes in C1 complex activity. This helps researchers assess the effectiveness of therapies in modulating the complement system and offers real-time data on treatment efficacy during clinical trials.
A: The complement C1 complex functional test typically requires serum or plasma samples from patients or research subjects. These samples are processed to evaluate the functionality of the C1 complex components, and the test can be performed on both human and animal models, providing flexibility for various research applications.
A: The results can be integrated by correlating C1 complex activity with disease phenotypes, complement deficiencies, or therapeutic responses, aiding in the identification of biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for complement-mediated diseases.
A: Factors such as sample handling, storage conditions, complement inhibitor presence, genetic variations, and the health status of the subject can influence test outcomes, requiring careful control and standardization in research settings.
A: C1 complex deficiency can lead to recurrent infections, autoimmune diseases, and an increased risk of developing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Patients may also experience angioedema and chronic inflammation.
A: C1 complex deficiency is typically caused by genetic mutations, leading to impaired synthesis or function of the C1 components (C1q, C1r, C1s), disrupting the complement system’s immune response.
Resources
Creative Biolabs has an impeccable complement detection platform supported by a team of highly trained scientists. We provide in-depth functional tests of the C1 complex using a range of advanced methods, ensuring customized solutions for every client's unique requirements. Contact us today for tailored service and expert guidance.
References
-
Calatroni, Marta, et al. "Anti-C1q antibodies: a biomarker for diagnosis and management of lupus nephritis. A narrative review." Frontiers in Immunology 15 (2024): 1410032. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
-
Kovács, Réka Á., et al. "Identification of neuronal pentraxins as synaptic binding partners of C1q and the involvement of NP1 in synaptic pruning in adult mice." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2021): 599771.
-
Ekdahl, Kristina N., et al. "Interpretation of serological complement biomarkers in disease." Frontiers in Immunology 9 (2018): 2237.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 The classical pathway of the complement system and structure of the C1 complex.1
Fig.1 The classical pathway of the complement system and structure of the C1 complex.1