Bacteroides vulgatus-derived Exosome Research and Application
Exosomes from Bacteroides vulgatus are involved in the crosstalk between the gut microbiota and the host immune system through specific regulation, showing potential application in developing therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases. Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive exosome research services to assist clients around the world in studying Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes.
Isolation of Bacteroides vulgatus-derived Exosomes
-
Culture Bacteroides vulgatus in Brain-Heart-Infusion (BHI) medium, 37°C and anaerobic conditions, then collect the bacterial suspension.
-
Vortex and centrifuge the bacterial culture, then vacuum sterile filter the supernatant of Bacteroides vulgatus mpk.
-
Centrifuge again and resuspend the Bacteroides vulgatus mpk pellet with PBS.
-
Bacteroides vulgatus mpk-derived exosomes for further purification by iodixanol density gradient centrifugation.
Research on Bacteroides vulgatus-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes stimulated semimaturation of mouse CD11c bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC).
|
By comparison with PBS-stimulated negative control and pathologic E. coli mpk-stimulated positive control, flow cytometry results revealed that Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosome-stimulated BMDC moderately expressed MHC-II and T-cell co-stimulatory surface proteins. That tentatively indicated a semi-mature phenotype of Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosome-stimulated BMDC.
|
|
Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes were able to cause immune tolerance in BMDC in the anti-inflammatory sense.
|
Assays of fluorescently labeled Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes-treated BMDC revealed a direct interaction of rapid cellular uptake of exosomes. Moreover, Bacteroides vulgatus exosomes induced semimaturation of BMDC exhibiting high levels of MHC-II and IL-6, and thus were able to tolerate re-stimulation from E. coli mpk, involving both MHC-II expression and TNF secretion.
|
|
Mechanisms of immune regulation by signaling-mediated Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes.
|
Measurement of cell-released IL-8 showed that both TLR2 and CD14/TLR4/MD-2 complexes were activated by Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes.
The involvement of these two TLRs was further confirmed by comparing the immune response and tolerance of TLR2 and TLR4 single-receptor-deficient and double-receptor-deficient mouse-derived BMDC stimulated by Bacteroides vulgatus exosomes. Of these, CD14/TLR4/MD-2 is the more dominant factor, while TLR2 activation-mediated signaling is also required for the immune response silencing.
|
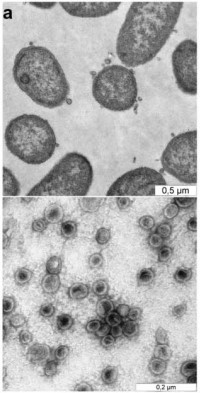 Fig. 1 Evidence for Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosome-like vesicles from bulging of the outer membrane.1
Fig. 1 Evidence for Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosome-like vesicles from bulging of the outer membrane.1
Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes can mediate Bacteroides vulgatus-host symbiosis by delivering activities that modulate the intestinal immune system. Research on Bacteroides vulgatus exosomes facilitates their application in the prevention and intervention of diseases associated with host pathologic immune responses. Creative Biolabs supports high-quality services for the study of Gram-negative bacterial vesicles including Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosomes. Please contact us with your demands.
Reference
-
Maerz, Jan Kevin, et al. "Outer membrane vesicles blebbing contributes to B. vulgatus mpk-mediated immune response silencing." Gut Microbes 9.1 (2018): 1-12.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Evidence for Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosome-like vesicles from bulging of the outer membrane.1
Fig. 1 Evidence for Bacteroides vulgatus-derived exosome-like vesicles from bulging of the outer membrane.1








