Neisseria meningitidis-derived Exosome Research and Application
Numerous studies have demonstrated the possibility that Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes can be used as an effective tool in applications against Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections. Creative Biolabs can provide comprehensive research services for the Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosome project, supporting the exploration of the potential applications of bacterium-derived vesicles.
Overview of Neisseria meningitidis Infectious Disease and Neisseria meningitidis Exosome-based Vaccine
|
Neisseria meningitidis infectious disease
|
Neisseria meningitidis exosome-based vaccine
|
-
Neisseria meningitidis is classified into 13 serogroups depending on the characterization of podoplanar polysaccharides.
-
Neisseria meningitidis infections are mainly caused by strains of groups A, B, C, W135, and Y.
-
Group B strains have a low immunogenicity of the podoplanar polysaccharide, which is susceptible to autoimmunity due to the homology of the polysaccharide's salivary acid structure with human nervous tissue. This made it more difficult to study vaccines against group B strains compared to other serogroups.
-
Group B strains share a wider variety of phenotypic and genotypic characteristics, yet tend to cause epidemics in a dominant clonal group.
|
-
Protein vaccines against group B strains were developed based on Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes.
-
Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes target outer membrane proteins (OMPs) of group B strains mainly including Por A, Por B2, and Por B3.
-
It is necessary to fully characterize the OMP phenotype of the prevalent serogroup strains for developing Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes as vaccine candidates with respect to the immunogenicity of the OMP, the ability to induce bactericidal antibodies, the conservation of the proteins, and the amount of protein expression.
-
Monovalent Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosome vaccines are weakly cross-protective against other strains with different phenotypes.
|
Research on Neisseria meningitidis-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Cross-reaction of Neisseria meningitidis-derived detoxified exosomes treated against gonococcal.
|
Exosomes derived from strains of wild Neisseria meningitidis, with PorA deletion, and with deletions of PorA, PorB, and RmpM were compared by antigen-binding patterns and bactericidal activity assays for varying degrees of resistance to Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection.
|
|
OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes attenuated gonococcal infection in mice.
|
OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes showed higher gonococcal clearance in mouse lower genital tract infection models compared to wild and PorA-deficient sources.
|
|
Characterization of mouse-specific antibodies immunized by Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes.
|
Characterization of Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes-induced cross-reactivity of serum IgG antibodies to gonococcal lysates by protein blotting showed that in the first challenge study, OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes-induced antibodies were able to bind high molecular weight antigens, but wild ones were not.
|
|
Identification of antigens that elicit the production of cross-reactive antibodies after immunization with Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes.
|
The gonococcal antigens screened by immunoprecipitation included the multidrug efflux protein MtrE, antibodies generally recognized the pilocarpon protein PilQ, as well as the specific peptides AceF and GuaB.This facilitated the identification of more targets for vaccine development.
|
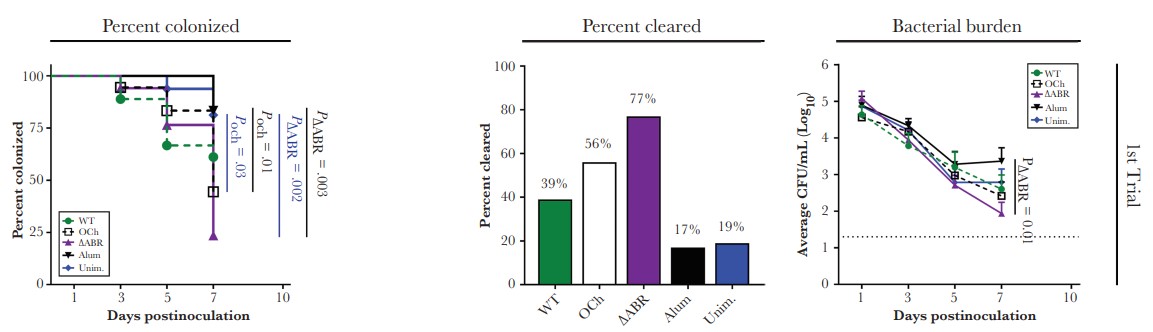 Fig. 1 OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes resulted in faster and higher gonococcal clearance.1
Fig. 1 OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes resulted in faster and higher gonococcal clearance.1
Exosomes isolated from Neisseria meningitidis exhibited enhanced resistance to gonococcal infection in diseased mice when administered intranasally and intravaginally. Meanwhile, OMP-deleted Neisseria meningitidis-derived detoxified exosomes were found to exhibit further enhanced ability to clear gonococcal. Creative Biolabs provides services including, but not limited to, bacterial vesicle characterization and profiling to assist in bacterial-derived exosomes/outer membrane vesicle research. Please contact us with your needs.
Reference
-
Matthias, Kathryn A., et al. "Meningococcal detoxified outer membrane vesicle vaccines enhance gonococcal clearance in a murine infection model." The Journal of Infectious Diseases 225.4 (2022): 650-660.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes resulted in faster and higher gonococcal clearance.1
Fig. 1 OMP-deficient Neisseria meningitidis-derived exosomes resulted in faster and higher gonococcal clearance.1








