Neisseria lactamica-derived Exosome Research and Application
Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes have been shown to carry abundant pathogen-associated molecular patterns that strongly stimulate the innate immune system and promote antigen presentation and T-cell activation. Presentation and delivery of exogenous antigens using fusion expression with scaffolding proteins increase the potential for Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes for ideal vaccine nanocarrier applications. Creative Biolabs can provide customized production services for bacterial-derived exosomes, supporting engineering-based modifications to expand the functionality of bacterial-derived exosomes.
Production and Engineering of Neisseria lactamica-derived Exosomes
-
Recover and culture Neisseria lactamica, then centrifuge at low speed to obtain Neisseria lactamica supernatant.
-
Ultracentrifuge the supernatant and then further recover Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes by sucrose solution.
-
To reduce the amount of LPS in Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes, mix 1 % sodium deoxycholate with exosome resuspension at 1:1, tangential flow filter the mixture, and finally wash it with sucrose solution to obtain concentrated Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.
-
Measure the endotoxin concentration of Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes to confirm meeting subsequent requirements.
-
Incubate in buffers containing PBS, NaCl, and sucrose to achieve carbodiimide-mediated conjugation of biotin and Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.
-
After removal of free biotin, incubate for binding of biotinylated Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes to fusion proteins containing rhizavidin and the target antigen.
-
Due to the high-affinity mediation between rhizavidin and biotin, specific antigens can be displayed on Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.
-
Finally, purify the antigen-modified Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes by volumetric exclusion chromatography.
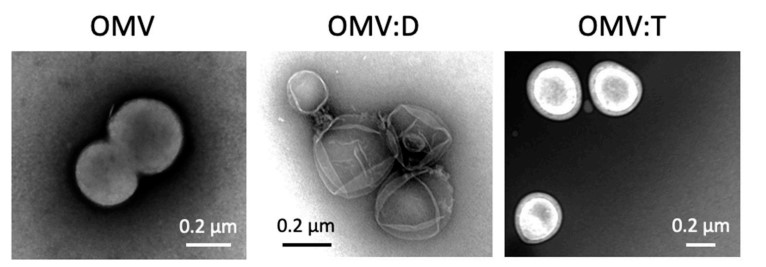 Fig. 1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1
Studies of Neisseria lactamica-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Characterization of Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes displaying target antigens.
|
Engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes containing outer membrane protein markers as well as target antigens were confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and protein blotting.
|
|
Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes were able to activate dendritic cells.
|
Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes were found to activate mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells by measuring levels of the co-stimulatory molecules CD40 and CD86 as well as immunomodulatory cytokines.
|
|
Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes presenting antigen induced specific immune responses.
|
Measurement of cytokines in the mouse splenocyte supernatants after three immunizations revealed that antigen-modified Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes induced the mouse organism to produce higher levels of IL-6, IL-17, and IL-10 cytokines. Moreover, flow cytometry detected that this immunization drove more CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes expressing TNF-α and IL-4, and CD8+ T lymphocytes expressing IFN-γ and IL-2.
|
|
Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes coupled with antigen induced significantly high levels of specific antibody production.
|
Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes with coupled antigens induced significantly higher titers of specific antibodies compared to unmodified Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes, free antigens, and co-administration of both.
|
The property combination of Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes and adjuvants was achieved through engineered modifications that enhanced the immune system's ability to recognize and respond to antigens, working synergistically to exert a potent immune response-inducing effect in mouse models. Creative Biolabs can provide research services for customized modification and high-yield production of bacterial-derived exosomes. Please contact us to discuss.
Reference
-
Barbosa, Mayra M. Ferrari, et al. "Primary and memory response of human monocytes to vaccines: role of nanoparticulate antigens in inducing innate memory." Nanomaterials 11.4 (2021): 931.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1








