Creative Biolabs offers the unparalleled mass sequencing service to analyze the B cell receptors (BCR) repertoires. Our scientists adopt hierarchical clustering algorithm using single linkage with Hamming distance to identify clones with high confidence. We can provide a fully automated method for clonal grouping. We are proud to introduce this high-quality service to our global customers.
Adaptive immunity is motivated by somatic hypermutation, expansion, and selection of B cell clones. Each clone is the progeny of a single B cell responding to an antigen (Ag), with diverse Ig receptors. Our ability to profile this adaptive immune response has dramatically improved through the application of next-generation sequencing (NGS). Such data provides a window into the microevolutionary dynamics which drives successful immune responses and the dysregulation that occurs with aging or disease. This microevolutionary process known as affinity maturation results in B cells with diverse immunoglobulin (Ig) receptors. Clonal partitioning of adaptive immune receptor repertoire sequencing data is central to a wide range of applications. For example, clone size distributions are the basis for several diversity measures, such as species richness, Shannon entropy, and the Gini-Simpson index. Diseases such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia are characterized by low diversity, which is driven by the dominance of a small number of clones. Identifying clones that include sequences with known Ag specificities has also been used to reveal novel Ag-specific sequences. However, despite its importance, the identification of sequences that belong to the same B cell clone in these data remains a significant challenge. Although several hierarchical clustering-based methods have been proposed, they always result in a significant loss of sensitivity. There is no consensus on the best method for grouping Ig sequences into B cell clones. Most current approaches leverage the high diversity of the junction region as a “fingerprint” to identify each B cell clone. However, these algorithms are time consuming, which is computationally intractable for large sequencing datasets.
Creative Biolabs has developed an effective strategy to identify B cell clones by BCR repertoire data analysis based on hierarchical clustering. This strategy consists of (1) library preparation, (2) BCR sequencing on our Magic™ platform, and (3) data processing, including distance metrics, analysis of specificity and sensitivity, and Shannon entropy calculation. The results show that single-linkage hierarchical clustering with nucleotide Hamming distance has excellent performance, with high specificity and sensitivity.
With years of research and development experience in the field of immunology, Creative Biolabs has owned a group of scientists who have the distinguished skills in BCR repertoires sequencing. We are proficient in BCR repertoire analysis for B cell clones identification based on hierarchical clustering. We are pleased to offer the best service with the most accurate results for our global customers.
Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Diverse Species of Our Unbiased BCR Repertoire Profiling
Applications of Our Unbiased BCR Repertoire Profiling
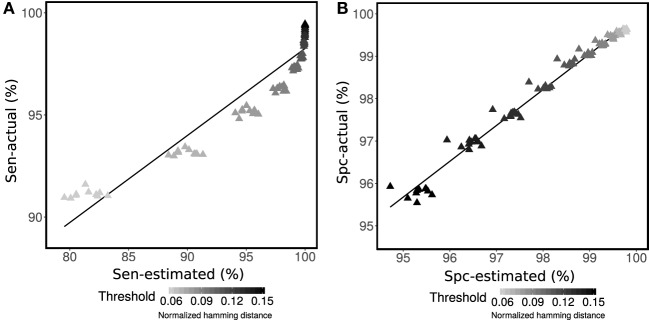 Fig. 1 Determining membership in multi-sequence clone.1
Fig. 1 Determining membership in multi-sequence clone.1
The study focuses on improving computational methods for identifying B cell clones from Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire sequencing (AIRR-seq) data. The research addresses the computational challenges of setting thresholds for clone identification and introduces a new algorithm that optimizes both sensitivity and specificity. By using a finite mixture model, the method achieves high accuracy in partitioning B cell sequences into clonal groups. The BCR Repertoire Profiling Service plays a critical role in this study by enabling precise identification of B cell clones, which is essential for applications such as diversity analysis, lineage reconstruction, and antigen-specific sequence detection. This approach enhances the understanding of immune responses, with potential applications in cancer, infectious diseases, and vaccine research.
BCR repertoire profiling is essential for identifying specific B cell clones that contribute to immune responses. This profiling helps researchers understand how the immune system reacts to infections, vaccines, and malignancies. By identifying B cell clones, researchers can explore how the immune system recognizes pathogens and cancer cells, potentially leading to more effective treatments.
BCR repertoire profiling helps identify specific B cell clones involved in the immune response to tumors or infections. Understanding these clones allows for the development of targeted immunotherapies, such as monoclonal antibodies or vaccines, by focusing on B cell populations that effectively combat diseases. This precision aids in developing therapies that are more efficient and less toxic.
BCR repertoire profiling employs high-throughput sequencing technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) to capture the diversity of B cell receptors. Advanced bioinformatics tools are then used to analyze the data, grouping similar BCR sequences into clones. This combination of sequencing and computational analysis enables precise identification of B cell clones within complex immune repertoires.
BCR repertoire profiling can identify B cell clones that are specific to particular antigens, such as viruses, bacteria, or cancer cells. This capability is critical for studying immune responses to infections or tumors and for developing vaccines or therapies that target these antigen-specific clones. It helps researchers track immune responses more accurately over time.
B cell clone identification through BCR repertoire profiling has several applications, including understanding immune responses to infections, cancer, and vaccines. It is also used in studying autoimmune diseases, tracking disease progression, and evaluating treatment efficacy. Additionally, B cell clone identification is critical for developing personalized immunotherapies based on individual immune profiles.
BCR repertoire profiling is an effective tool for monitoring immune responses following vaccination. By analyzing B cell clone expansion and diversity before and after vaccination, researchers can assess the strength and specificity of the immune response. This data helps in the evaluation of vaccine efficacy and in the improvement of vaccine design for various diseases.
In cancer research, identifying B cell clones through BCR repertoire profiling helps understand how the immune system recognizes and fights tumor cells. It enables researchers to detect clonal B cells that may be involved in tumor suppression or progression. This knowledge is vital for developing targeted cancer immunotherapies and improving treatments like CAR-T cell therapy or monoclonal antibodies.
BCR repertoire profiling provides a comprehensive view of the diversity within the B cell population, allowing for detailed analysis of the various B cell clones present in an individual's immune system. This understanding of immune diversity is critical for identifying how different B cell clones respond to pathogens or tumors, leading to more effective treatments and vaccines tailored to individual immune responses.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
