Modified Oligos Synthesis Technology
As the most basic information storage unit in cells, nucleic acid polymers can convert unique information codes into proteins that control cellular processes. By modifying and designing nucleic acid fragments, applications in fluorescence detection, sequence analysis, drug delivery and other aspects can be expanded. With years of experience and advanced molecular biology technology platform, Creative Biolabs provides stable, reliable and personalized custom-modified oligos synthesis services to customers all over the world.
Oligos Synthesis and Conjugation
By cross-linking with different molecules, materials or supports, nucleic acid polymers can be used to detect hybridization signals such as conjugated enzymes, fluorophores, haptens, radiolabels, etc., or to achieve targeted delivery of proteins, small molecules, and drugs. Immobilized cDNA arrays are widely used for gene expression analysis, but synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides are also used because structure, quality, and hybridization performance are easier to control. With its wide application in molecular biology, bioconjugation technology involving nucleic acid is becoming one of the most important research/application fields in cross-linking and modification chemistry.
Custom Modified Oligos Synthesis Methods
The first difficulty in modifying and conjugating nucleic acid polymers is that common and relatively easily derivatized groups are not suitable for nucleic acid modification, and many electrophilic bioconjugation reagents do not react with nucleic acids. To modify unique chemical groups on nucleic acids, derivatization is performed at discrete sites on base, sugar, or phosphate groups. Functional groups or labels can be added to a single nucleotide or to one or more sites in a nucleic acid polymer using specific biochemical methods. There are currently two main methods for modifying DNA or RNA molecules, enzymatic and chemical, both of which can produce conjugates with high activity and are applied through the binding effect of probes and complementary strands in complex mixtures for sensitive measurement or localization.
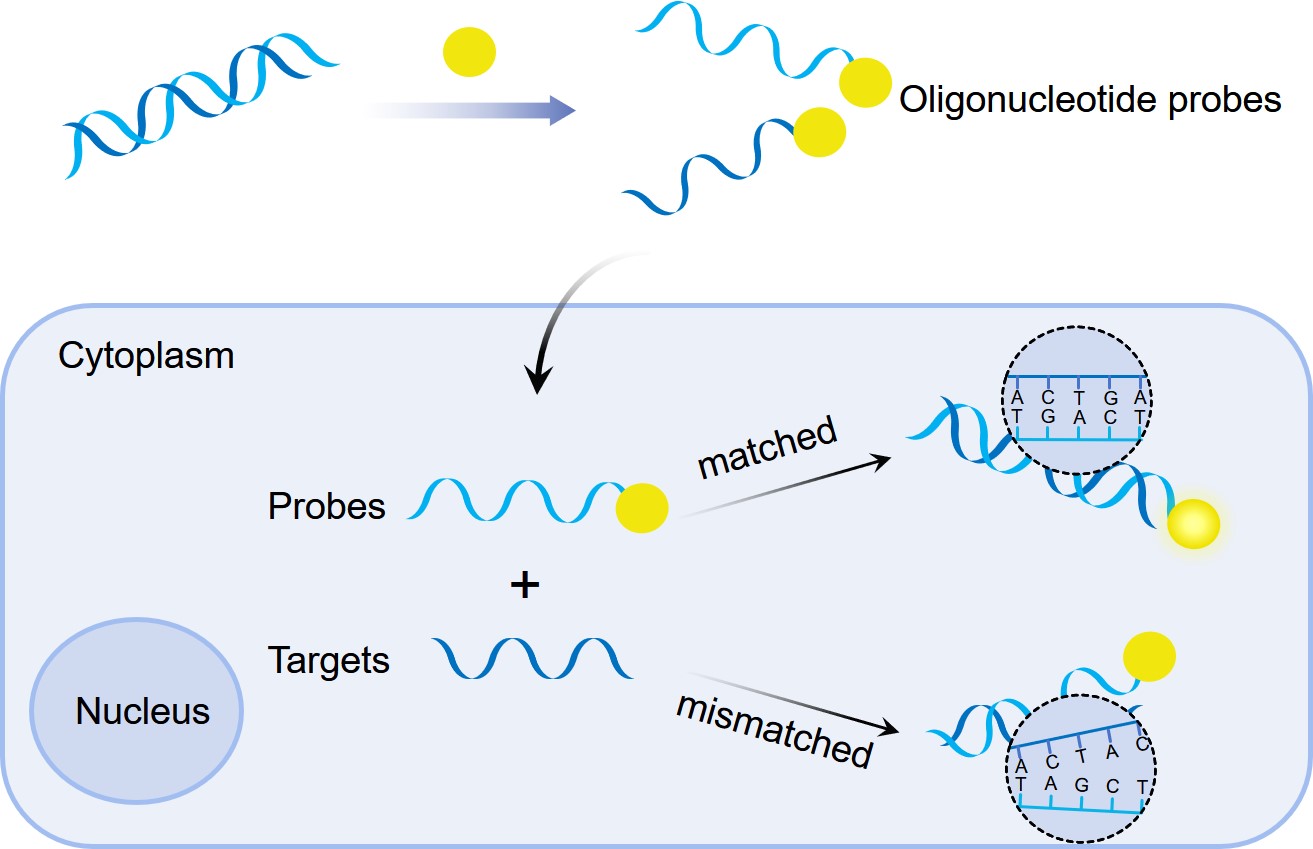 Fig.1 Construction and application of oligonucleotide probes.
Fig.1 Construction and application of oligonucleotide probes.
Enzymatic Technology
Enzymatic techniques refer to the use of a variety of DNA or RNA polymerases to add certain amounts of modified nucleotides to existing scaffolds. Polymerases can be used with templates to add modified nucleoside triphosphates to the ends of DNA molecules or to selected sites in the sequence. Terminal transferases can add modified monomers to the 3' end of the untemplated strand. Three main procedures of enzyme labeling make use of a DNA polymerase: (a) random primed labeling, (b) nick translation, and (c) polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Random primer labeling uses a random mixture of hexadeoxynucleotides to add modified nucleoside triphosphates as 3α-OH primers to the DNA template. Gap translation technology incorporates labeled nucleotides into sequences through the tandem action of a two-enzyme system. PCR technology uses the classic chain polymerization reaction to label nucleic acid polymers and generate large numbers of copies.
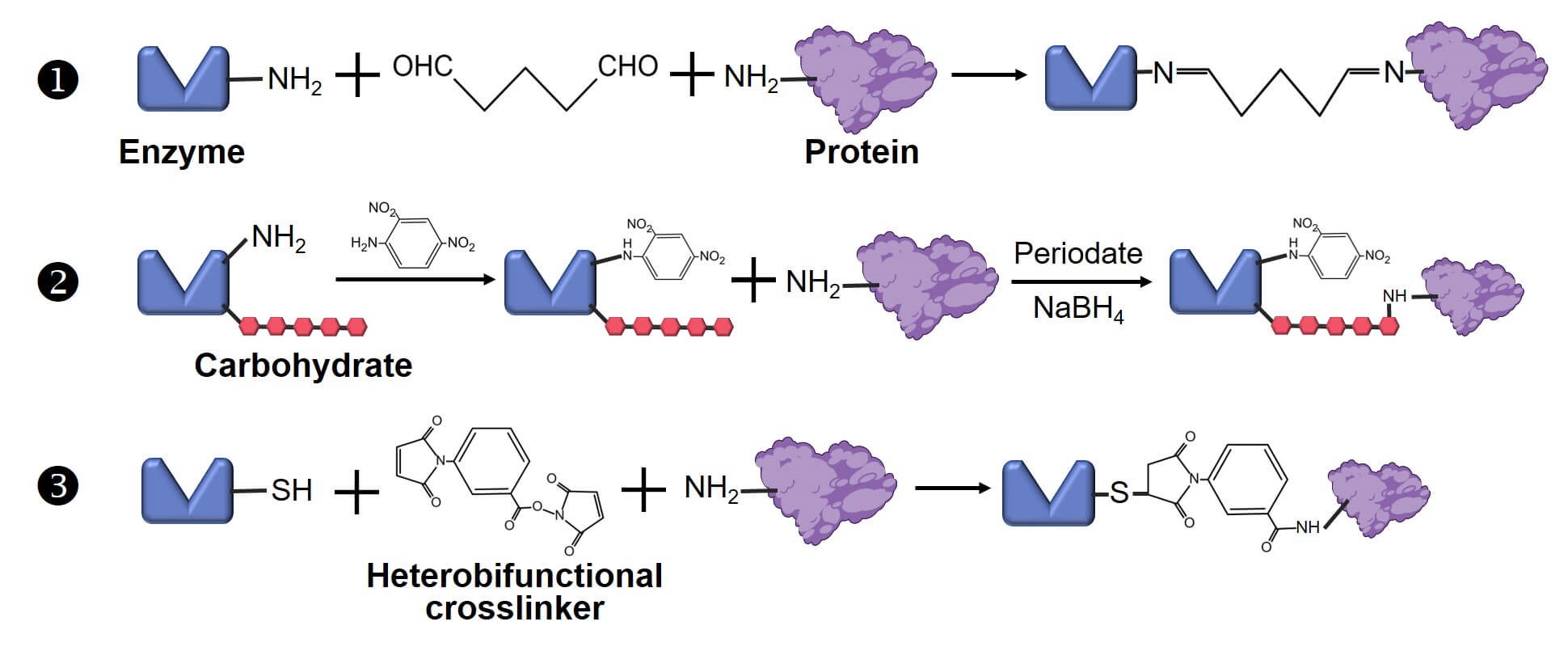 Fig.2 The methods of protein-enzyme conjugation.
Fig.2 The methods of protein-enzyme conjugation.
Chemical Modification
The chemical modification of nucleic acids at specific sites within a single nucleotide or oligonucleotide by multiple means can incorporate various labels into nucleic acid polymer probes and generate conjugates with specific properties. One of the methods for chemical modification of nucleic acids/oligonucleotides is to add amine terminal spacers through diamine compounds, and then further modify amine derivatives by means of bisulfite-activated cytosine or Carbodiimide Reaction. In addition to the amine-reactive terminus, it is also possible to create a sulfhydryl group on the nucleic acid via a reactant for conjugation reactions or to use bishydrazide for modification. Depending on the desired cross-linked conjugate, various functional groups and chemical modification methods can be selected.
Our Services
Nucleic acids/oligonucleotides have been widely used in the field of molecular biology due to their unique hybridization patterns, and after bonding with different conjugates, they also endow polymers with unique properties, structures and functions. Based on our powerful technology platform and cutting-edge technology, Creative Biolabs provides customized modification services to customers all over the world. Through a variety of modification, synthesis and bonding methods, we can provide you with other conjugation service, including but not limited to nucleic acids/oligonucleotides, proteins, antibodies, fluorescent labels, and small molecules. We can also design a customized synthesis scheme according to your experiment, providing the most stable, controllable and reproducible nucleic acid/oligonucleotide modification and conjugation for your project. In addition, we also provide synthetic nucleic acid/oligonucleotides of specified sequences, cross-linking reagents and various chemical reagents you may need. Please contact us for more information if you have any needs.
