Custom Protein-Bead & Particle Conjugation Services
Biodegradable and biocompatible polymers have been employed to create the nanoparticles that compose medication delivery systems. Because the production process is precisely controlled, synthetic polymers are purer than natural materials. Currently, Creative Biolabs offers several types of protein conjugation-related nanoparticles.
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of gold nanoparticles in a fluid. Vibrant hues are produced when visible light interacts with colloidal gold nanoparticles. This unique optoelectronic property has been used in several fields, including nanotechnology, materials, applied science, and biomedicine.
Magnetic nanoparticles are a class of nanoparticles that can be controlled via magnetic fields. A magnetic material and a functional chemical component are the two fundamental parts of any magnetic nanoparticle.
Small nanoparticles known as quantum dots (QDs) are composed of an alloy of semiconductor metal. Depending on their size, shape, and composition, QDs can absorb energy photons and emit distinct hues of light when exposed to light in a particular wavelength range.
Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) is synthesized through the ring-opening copolymerization of a cyclic dimer, specifically 1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione, derived from glycolic acid and lactic acid. As one of the most effective nanoparticles, PLGA has been widely used in drug delivery systems due to its characterizations of low toxicity and excellent biocompatibility.
Latex nanoparticles containing cationically charged coronas and hydrophobic cores with different glass transition temperatures (Tg) can be obtained by surfactant-free, RAFT-mediated emulsion polymerization. Using a latex conjugation kit, antibodies or proteins can be easily conjugated to latex nanoparticles.
Protein-Bead & Particle Conjugates Method
Two commonly utilized conjugation techniques are covalent binding and adsorption. Adsorption refers to the process in which proteins or antibodies bind to the surface of nanoparticles by intrinsic surface contacts. This includes both physical and ionic adsorption. Although this is an easy and moderate procedure, it frequently causes a decrease in stability. Covalent binding, including carbodiimide chemistry and maleimide chemistry, presents the advantages of high stability and excellent reproducibility. Compared with absorption, covalent binding is more strongly to ordered antibody orientations. Depending on the conjugation technique employed, proteins may immobilize to the surface of nanoparticles in a site-specific or non-site-specific manner.
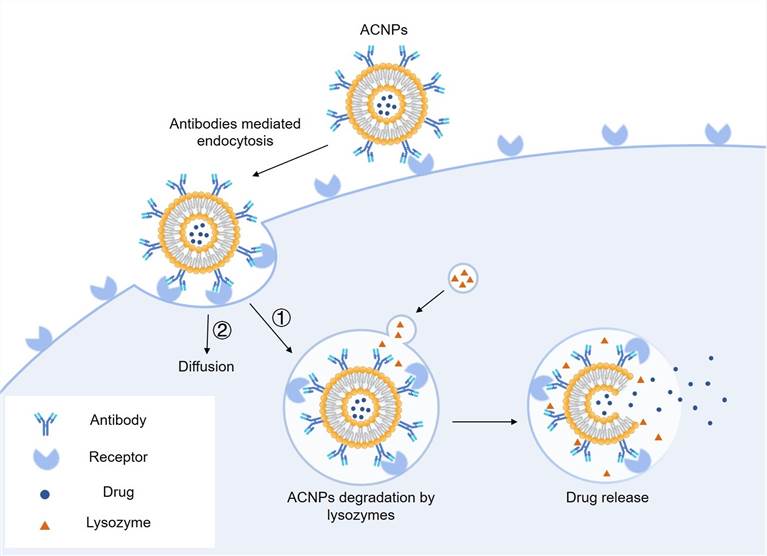 Fig. 1 Action mechanism of antibody-conjugated nanoparticles (ACNPs).
Fig. 1 Action mechanism of antibody-conjugated nanoparticles (ACNPs).
Creative Biolabs offers the most comprehensive and cutting-edge protein-bead & particle conjugation services. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to understanding your unique needs and providing you with customized services. If you are intrigued by our services, please contact us for more details.
Recommended products
Related Sections
