Custom Virus Conjugate Service
Creative Biolabs is a world-leading innovative biotechnology company that has been at the forefront of bioconjugation services. After decades of accumulation, Creative Biolabs has established an advanced platform and a professional team. We specialize in custom virus conjugate services tailored to your specific needs. Our vision is to provide reasonable solutions and one-stop services to help global customers make great breakthroughs in this field.
Background of Viruses Labeling
Viral infection in host cells is a very complicated process. The invasion mechanism of virus particles is of great significance for the prevention and treatment of viral diseases. Single virus tracking provides a powerful tool for in-depth exploration of this mechanism. A basic prerequisite for performing this technique is that the virus must be fluorescently labeled. Labeled virus facilitates visualization under fluorescence microscopy. In the past few decades, there have been tremendous advances in fluorescent labeling methods for tracking the course of viral infection. Various fluorescent labels have been used to label target viruses.
Labeling of Viruses with Quantum Dots (QDs)
QDs are fluorescent tags with many unique optical properties. The optical properties of QDs include ultrabright fluorescence, narrow emission spectrum, and excellent photostability. Viruses labeled with QDs can be quickly imaged. Compared to other fluorophores, QDs labeling provides more detailed information. A lipid-specific method has been reported to specifically and efficiently label enveloped viruses via QDs. The results demonstrate that the technique is not only applicable to normal viruses but also capable of labeling key protein mutant viruses and inactivated highly virulent viruses, providing an attractive tool for single virus tracing.
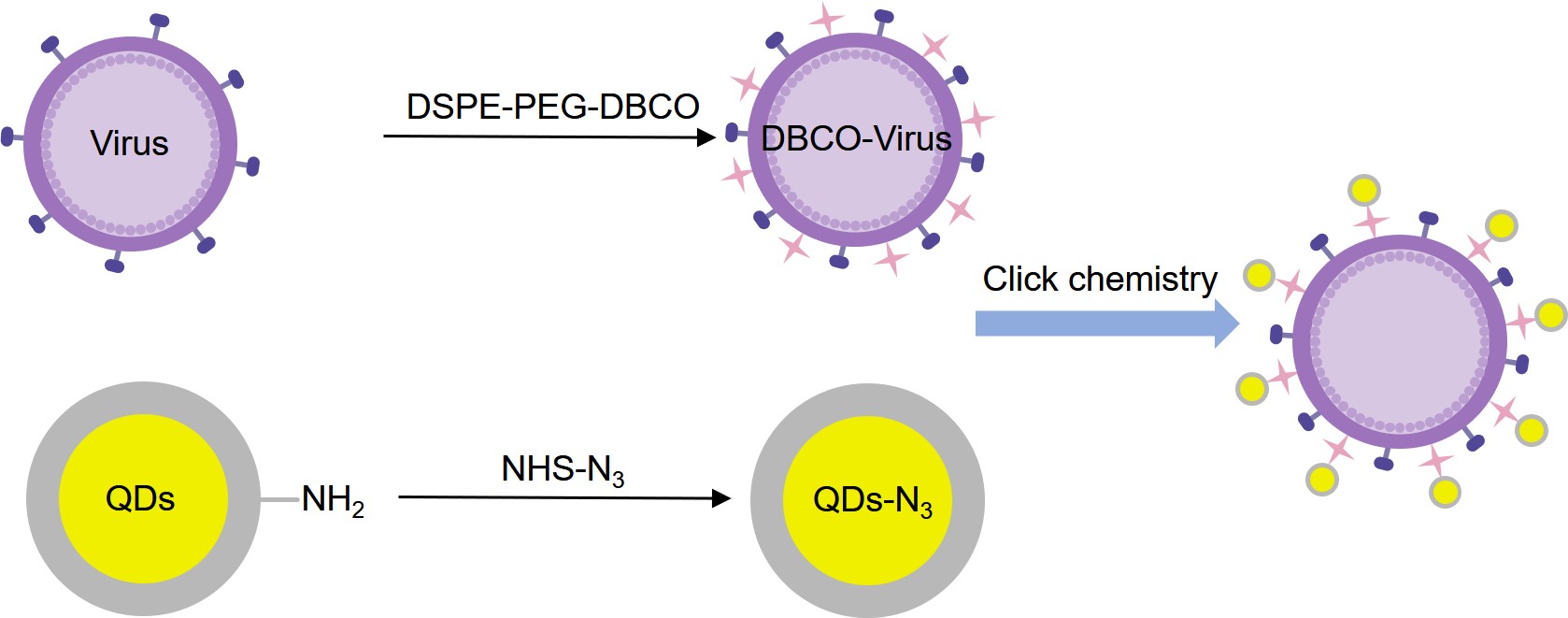 Fig.1 Lipid-specific QD labeling of enveloped virus via click chemistry.
Fig.1 Lipid-specific QD labeling of enveloped virus via click chemistry.
Labeling Viruses with Gold Nanoclusters
Fluorescent gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) are novel fluorescent materials with a long fluorescence lifetime and ultra-small size. In recent years, AuNCs have gradually become the focus in the fields of biomarkers, bioimaging, and targeted cancer therapy. The biocompatible AuNCs can be used as contrast agents in viral imaging. Labeling of viruses can be achieved in a site-specific manner by attaching clusters to the hydrophobic pockets of viruses through lipid pocket factors.
Bioconjugation of Virus-like Particles (VLPs)
VLPs, which mimic the structure of natural viruses, have gradually emerged as a widely accepted safe and effective tool. VLPs can be easily modified with genes or chemical molecules to tune their immunogenicity. N-terminal and C-terminal modifications allow alternative functional groups to be fused to the peptide. VLPs play irreplaceable functions in nanotechnology, biotechnology and medicine. For example, VLP human vaccines have made great contributions to vaccine development. In addition, VLP technology is closely linked to fields such as drug delivery, imaging, and biocatalysis.
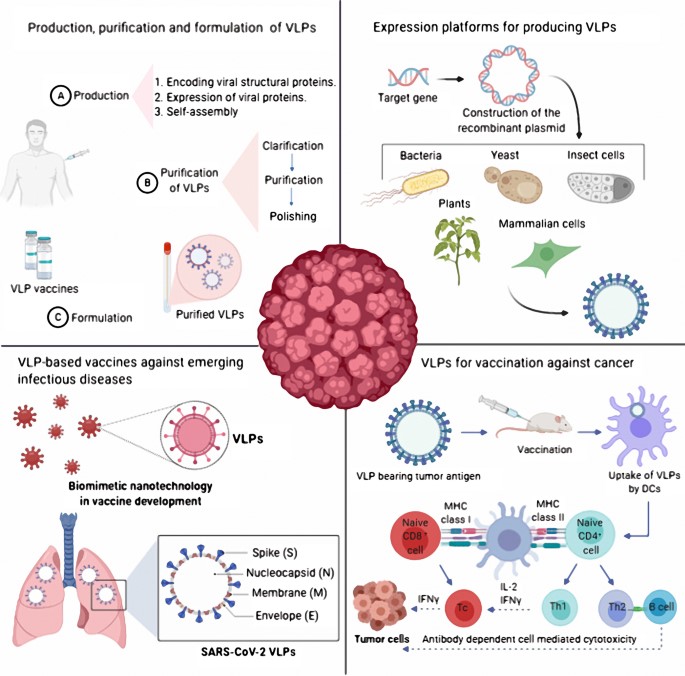 Fig.2 Virus-like particles: preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers.1
Fig.2 Virus-like particles: preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers.1
Custom Virus Conjugate Services at Creative Biolabs
The viral envelope separates from viral nucleic acid during viral infection. Therefore, rational strategies for labeling viral nucleic acids and envelopes individually should be addressed before studying viral invasion. At Creative Biolabs, the envelope can be labeled with chemical fluorophores, QDs and fluorescent proteins (FP). Furthermore, several strategies have recently been utilized to label viral genomes, such as bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and luminescent Ru (II) complexes.
With an advanced platform and strong knowledge, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive service of virus conjugate, including but not limited to organic dyes, fluorescent proteins and QDs labeling. If you are interested in our virus conjugate services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Reference
-
Nooraei, Saghi, et al. "Virus-like particles: preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers." Journal of nanobiotechnology 19 (2021): 1-27.
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Recommended products
Related Sections
