With extensive experiences in the field of epitope mapping, Creative Biolabs offers a unique CreMap™ peptide/protein microarrays service for our clients to screen and detect the potent epitopes of a target protein. A peptide library is constructed by synthesizing the oligopeptide sequences from overlapping and non-overlapping segments of a target protein. And the ability to bind the corresponding antibody of interest is tested. This method is especially suited to profiling epitopes of a defined protein for candidate antibodies in a high-throughput way. It is quick, cost-effective and will be an excellent option for the case of small amounts of your precious samples.
A peptide/protein microarray, also commonly known as peptide/protein chip, goes by displaying the target peptides on a solid surface (often a glass or plastic chip). This platform delivers a full compatibility of the chips based on overlapping peptide libraries (or non-overlapping peptide libraries) of your target protein or your target proteins by utilizing a flexible peptide synthesis technology. There is a variety of peptide libraries for a target protein and the construction of a peptide library could be obtained by different approaches. The overlapping peptide library is the most commonly used and other libraries are also available at Creative Biolabs, including truncation library, alanine scan library, random library, positional scan library and scrambled library. Basically, the microarrays epitope mapping analysis involves the following major steps, which are the synthesis of a peptide library, then binding analysis, followed by bioinformatics-based data analysis, and constructing initial results. In addition, our unique technology ensures greater reproducibility of this assay, and reduces background signal and improves assay performance in sensitivity, dynamic range, and variance.
Compared with ELISA or other ligand binding assays, our CreMap™ peptide/protein microarray platform features a competitive price and high-throughput assays. It can detect thousands of interactions in a single run and enables higher sensitivity with lower cost and allows customized plate chips by providing different forms and shapes (e.g. direct assays, sandwich assays, bridging assays). Furthermore, your established assay protocols can be easily transferred to our service platform by supplying microliter amounts sample of your protein/antibodies/sera.

Based on our CreMap™ technical platform, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing high-class epitope mapping service by using peptide microarray. If you are now trying to figure out epitopes on an antigen, or if you are interested in our platform, please contact us. A formal feedback will be sent back as soon as possible
Other optional CreMap™ B cell epitope mapping services:
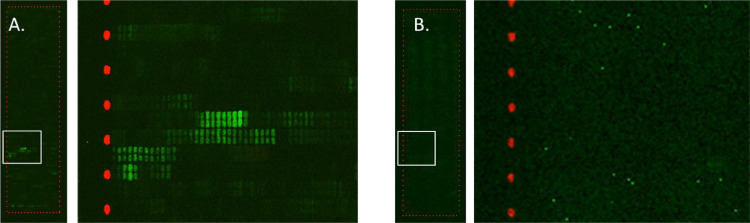 Fig. 1 Fluorescent image of peptide array chips after reaction with A) ASF positive pig serum sample (S31), and B) ASF negative pig serum sample. (Cloé Desmet, 2024)
Fig. 1 Fluorescent image of peptide array chips after reaction with A) ASF positive pig serum sample (S31), and B) ASF negative pig serum sample. (Cloé Desmet, 2024)
The article addresses the critical need for an effective vaccine against African swine fever virus (ASFV) by applying high-density peptide microarrays for epitope mapping. This method enabled the identification of protective antigens that are recognized by antibodies from infected animals, which is pivotal for vaccine development. Results indicated specific ASFV proteins like p54 that are already targets for vaccine development, and new epitopes were identified that could potentially improve vaccine designs. This epitope mapping by peptide microarrays provided a detailed and high-throughput analysis of antibody interactions at the amino acid level, which is crucial for tailoring vaccines that elicit strong protective immune responses in pigs against various ASFV strains.
Epitope mapping by peptide/protein microarrays involves the use of microarray technology to identify the specific parts of antigens recognized by antibodies. This technique allows for the simultaneous screening of thousands of peptides or proteins, helping to pinpoint which sequences within a protein are involved in immune recognition.
In peptide/protein microarrays, synthetic peptides or proteins are printed in a dense array on a solid surface. These arrays are then exposed to sera or antibodies, and interactions are detected using labeled secondary antibodies that fluoresce under specific conditions. The fluorescence intensity at each spot indicates the strength of antibody binding, identifying potential epitopes.
Microarrays allow for high-throughput screening, meaning many peptides can be tested simultaneously, which accelerates the discovery process. This method is also highly sensitive and can detect even weak interactions between antibodies and antigens. It requires only small amounts of antibodies and antigens, making it resource-efficient.
While peptide microarrays are excellent for identifying linear epitopes, they are less effective for conformational epitopes, which depend on the three-dimensional folding of proteins. Protein microarrays that preserve the native structure of proteins are more suitable for identifying conformational epitopes.
Epitope mapping by microarrays is invaluable in vaccine development, diagnostic research, allergy research, and autoimmunity studies. It helps in identifying which parts of a pathogen or allergen elicit an immune response, guiding the development of targeted therapies and vaccines.
Peptide/protein microarrays are designed based on the sequence of the target protein. Peptides—usually 15 to 20 amino acids long—are synthesized to cover the entire length of the protein, often with overlapping sequences to ensure complete coverage. These peptides are then chemically bonded to a solid surface, like glass or plastic.
Sample preparation for microarray epitope mapping typically involves purifying antibodies or sera to remove components that might cause non-specific binding. Samples may also need to be diluted to optimal concentrations to balance sensitivity and specificity.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
