Bifidobacterium longum-derived Exosome Research and Application
Bifidobacterium longum is an important probiotic widely found in the human gut microbiota. This strain possesses various physiological functions and potential health benefits, which have garnered significant attention in biomedical research. Based on the intrinsic properties of Bifidobacterium longum, the exosomes produced by Bifidobacterium longum have been identified as having potential medical applications due to their cargo of various bioactive substances. Creative Biolabs is actively exploring this field to understand the potential of exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum in improving health and treating diseases.
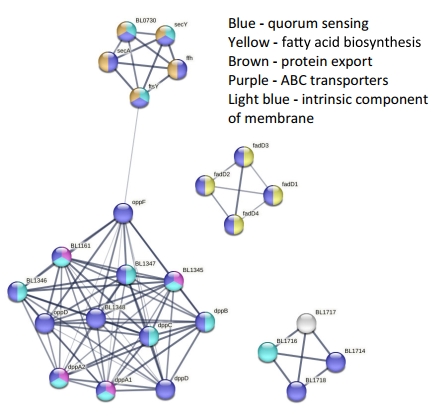 Fig.1 STRING analysis and interaction plot of quorum sensing proteins from Bifidobacterium longum-derived exosomes.1,2
Fig.1 STRING analysis and interaction plot of quorum sensing proteins from Bifidobacterium longum-derived exosomes.1,2
One of the Beneficial Bacteria in Human Gut: Bifidobacterium longum
The presence of Bifidobacterium longum in the gut is closely related to human health, and it performs several key functions:
1. Facilitating food digestion and the absorption of nutrients.
2. Inhibiting the growth and invasion of pathogens, helping maintain microbial balance in the gut.
3. Regulating intestinal function, improving bowel movements, and alleviating constipation.
4. Potentially lowering cholesterol levels, benefiting cardiovascular health.
5. Modulating the immune system, enhancing immune responses, and helping prevent inflammation and allergic reactions.
Multiple Potential Values of Exosomes Derived from Bifidobacterium longum
In addition to its essential functions, Bifidobacterium longum has recently piqued the interest of the biomedical community because it has been found to have the potential to generate exosomes. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles containing a rich variety of bioactive molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Several studies have investigated exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum, providing valuable insights into their characteristics and potential applications.
|
No.
|
Bifidobacterium longum Subtype
|
Research Findings
|
|
1
|
Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563
|
Exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum bind specifically to mast cells and induce mast cell apoptosis, thereby alleviating food allergy symptoms. This improvement is mainly associated with a specific set of proteins in the exosomes from Bifidobacterium longum.
|
|
2
|
Bifidobacterium longum NCC2705
|
Exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum contain various mucin-binding proteins with a high affinity for mucosal surfaces in the intestine, promoting the colonization of Bifidobacterium longum in the gut.
|
|
3
|
Bifidobacterium longum
|
Exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum stimulate macrophages and dendritic cells to produce inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, suggesting their potential as a novel adjuvant for immunotherapy.
|
|
4
|
Bifidobacterium longum JCM1222T
|
Exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum contain specific extracellular solute-binding proteins (ESBPs) that induce macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory interleukin-6 and induce Peyer's lymphoid follicle cells to produce immunoglobulin A (IgA).
|
|
|
Bifidobacterium longum AO44
|
Exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum AO44 are rich in ABC transport proteins, quorum-sensing proteins, and extracellular solute-binding proteins, which can induce various immune cells to produce anti-inflammatory cytokines.
|
Based on the research on exosomes derived from Bifidobacterium longum, we firmly believe in their vast potential for future applications. Creative Biolabs is a professional exosome technology service provider that has established a dedicated platform for microbiota-derived exosome development. If you have any related needs or questions, please feel free to contact us.
Bacteria-derived Exosome Isolation and Identification
In Vitro Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
In Vivo Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
References
-
Mandelbaum, N.; et al. Extracellular vesicles of the gram-positive gut symbiont Bifidobacterium longum induce immune-modulatory, anti-inflammatory effects. npj Biofilms and Microbiomes. 2023, 9(1):30.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 STRING analysis and interaction plot of quorum sensing proteins from Bifidobacterium longum-derived exosomes.1,2
Fig.1 STRING analysis and interaction plot of quorum sensing proteins from Bifidobacterium longum-derived exosomes.1,2









