Streptococcus suis-derived Exosome Research and Application
Streptococcus suis is an important zoonotic pathogen. Vaccination and antibiotic treatment have been the main strategies to combat Streptococcus suis infections. However, with increasing antibiotic resistance in bacteria, there is a need to explore new treatment approaches. In this context, research on pathogen-derived exosomes has gradually gained attention. Studies have shown that exosomes derived from the pathogen contain a significant amount of proteins and factors related to disease pathogenicity and immunogenicity. This makes them potential vaccine candidates that can induce an immune response to counter the pathogen. Creative Biolabs' platform not only supports common cell-derived exosome research but also focuses on microbe-derived exosomes, providing a unique opportunity for researchers.
Harm of Streptococcus suis:
-
Harm to the pig farming industry: Streptococcus suis infections cause significant economic losses to the pig farming industry. It leads to various severe diseases such as pig meningitis, septicemia, and arthritis, resulting in high mortality and culling rates, especially in piglets.
-
Zoonotic disease risk: Humans can potentially become infected with Streptococcus suis when they come into contact with infected pigs or contaminated pork products. This zoonotic disease can lead to serious conditions like sepsis, meningitis, endocarditis, arthritis, and more. In recent years, the number of human cases of Streptococcus suis infection has been gradually increasing in some regions.
-
Antibiotic resistance issue: Streptococcus suis shows a high level of resistance to antibiotics, particularly sulfonamide drugs. Overuse of antibiotics can lead to more serious antibiotic resistance problems, making the treatment of this disease more complex.
Current Limitations in Streptococcus suis Prevention and Treatment
-
Vaccination: Vaccination is one of the main methods for preventing Streptococcus suis infections. However, current vaccine types have limitations, including the need for different vaccines for different serotypes of Streptococcus suis and the potential inability of vaccines to provide broad cross-protection.
-
Antibiotic treatment: In veterinary clinical practice, antibiotics are commonly used to treat Streptococcus suis infections. However, excessive and improper antibiotic use can lead to the development of bacterial resistance, limiting treatment effectiveness.
New Research Direction: Development of Exosome Vaccines Derived from Streptococcus suis
The development of exosome vaccines derived from Streptococcus suis is a promising new research direction that may offer innovative solutions for the prevention and treatment of Streptococcus suis infections. Here are some achievements related to this research direction.
1. Exosomes produced by Streptococcus suis are found contain various proteins, nine of which are considered known or suspected virulence factors. Additionally, it was discovered that these exosomes contain active proteases and nucleases. It is likely that these active substances in exosomes derived from Streptococcus suis enable them to degrade neutrophil extracellular traps, helping the pathogen evade the host's defense response.
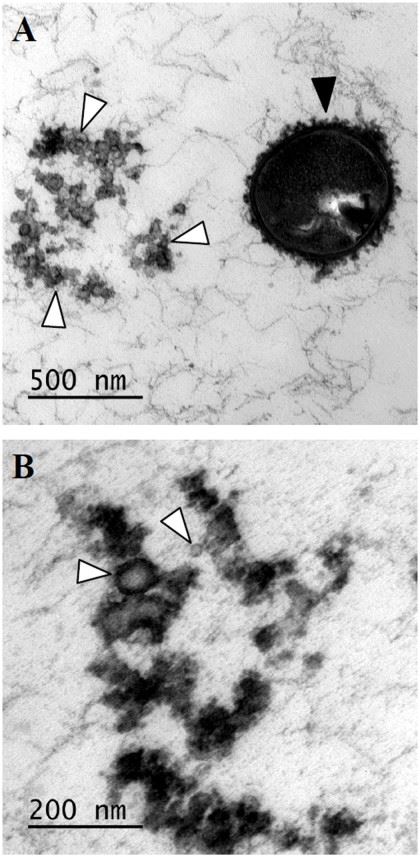 Fig. Transmission electron micrographs of an overnight culture of Streptococcus suis P1/7 and the membrane vesicle preparation.1,2
Fig. Transmission electron micrographs of an overnight culture of Streptococcus suis P1/7 and the membrane vesicle preparation.1,2
2. Due to the important role of the SaoA protein in the immune response and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis, researchers first engineered exosomes carrying the SaoA protein from Streptococcus suis. These engineered exosomes exhibited significant immunogenicity in a mouse model, inducing a strong immune response, including the production of IgG1 and IgG2a antibodies, as well as the release of cytokines IL-4 and IFN-γ.
These research outcomes highlight the potential application of exosomes derived from Streptococcus suis as vaccine candidates. They provide a new platform and strategy for the vaccine field, with the potential to improve the prevention and treatment of Streptococcus suis infections and offer new insights into vaccine development for other pathogens. Creative Biolabs, as an institution focused on biomedical research, has extensive experience in exosome development. If you are interested in or need support and collaboration for exosome development from bacterial sources, please contact us.
Bacteria-derived Exosome Isolation and Identification
In Vitro Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
In Vivo Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
References
-
Haas, B.; Grenier, D. Isolation, characterization and biological properties of membrane vesicles produced by the swine pathogen Streptococcus suis. PLoS One. 2015, 10(6):e0130528.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. Transmission electron micrographs of an overnight culture of Streptococcus suis P1/7 and the membrane vesicle preparation.1,2
Fig. Transmission electron micrographs of an overnight culture of Streptococcus suis P1/7 and the membrane vesicle preparation.1,2








