Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived Exosome Research and Application
The probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects in several studies, and further exosomes isolated from it have been shown to contain a wide range of immunomodulatory proteins capable of interacting with the host's immunomodulatory factors and thus exporting inflammation-regulating functions. Creative Biolabs has knowledge of the Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes and is capable of providing reliable services to aid in the study of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.
Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived Exosome Isolation
-
Culture Propionibacterium freudenreichii under suitable liquid conditions to stationary phase.
-
Collect and centrifuge the bacteria-free culture of the solid phase culture strain to precipitate residual bacteria and collect the supernatant of Propionibacterium freudenreichii.
-
Filter the strain supernatant fraction to further remove Propionibacterium freudenreichii cells.
-
Concentrate the supernatant by ultrafiltration followed by serial centrifugation and recover the concentrated exosomes with TBS buffer.
-
Purifying Propionibacterium freudenreichii exosomes further by size-exclusion chromatography.
-
Discard protein-contaminated and ineffective fractions and finally pool fractions containing Propionibacterium freudenreichii exosomes.
Research on Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Protein analysis of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.
|
The cargo proteins of exosomes were analyzed by nanoLC-ESI-MS/MS, and it was found that Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes carry functionally diverse proteins. Among them, immunomodulatory proteins such as Surface layer protein SlpB, enolase 1, iron/manganese superoxide dismutase, and malate dehydrogenase showed high abundance.
|
|
Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes regulated the NF-κB pathway and pro-inflammatory factor release.
|
-
In vitro experiments demonstrated that Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes were able to dose-dependently reduce the amount of NF-κB activator in lipopolysaccharide-induced human intestinal epithelial cells, thereby exerting an attenuating effect on the inflammatory response.
-
In the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation model of human intestinal epithelial cells, it was observed that treatment of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes reduced the pro-inflammatory factor IL-8 to non-inflammatory control levels.
-
Cell proliferation assays showed that these changes were caused by Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes exerting regulatory activity rather than producing cytotoxicity.
|
|
Surface layer proteins are involved in the anti-inflammatory properties of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.
|
Comparing the effects of exosomes derived from genetic mutant strains revealed that SlpB is one of the effectors involved in the regulation of the NF-κB pathway by the Propionibacterium freudenreichii exosomes, whereas there may be other effectors involved as well.
|
Applications of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived Exosomes
-
Propionibacterium freudenreichii exosomes can be the research subject to help explain the molecular mechanisms underlying the probiotic properties of the organism from which they are derived.
-
Propionibacterium freudenreichii exosomes can be used as bioactive agents to advance the development of therapeutic products for inflammation-related diseases.
-
Propionibacterium freudenreichii exosomes are one of the commensal bacteria in the human gastrointestinal tract and can be developed as agents that modulate the ecology of the digestive flora.
-
Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes can also be involved in the processing and flavor modulation of food products such as cheese, as can their strains.
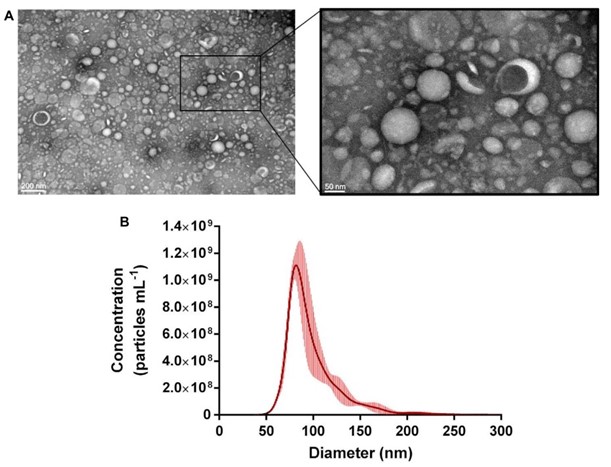 Fig. 1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1
The understanding of the characterization and function of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes facilitates further research and understanding of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosome activities and mechanisms. Creative Biolabs has a professional exosome research platform to promote the application and development of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes. Please contact us to discuss.
Reference
-
Rodovalho, Vinícius de Rezende, et al. "Extracellular vesicles produced by the probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii CIRM-BIA 129 mitigate inflammation by modulating the NF-κB pathway." Frontiers in microbiology 11 (2020): 1544.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1








