Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived Exosome Research and Application
Pediococcus pentosaceus is a Gram-positive bacterium belonging to the group of lactic acid bacteria, which is one of the common beneficial bacteria in the food fermentation process. In recent years, there has been a gradual increase in exosome-like vesicles of Pediococcus pentosaceus source to regulate inflammatory functions and related studies. Creative Biolabs has accumulated insights into gram-positive bacteria, including Pediococcus pentosaceus, and can provide customized research services on bacterial-derived exosomes.
Isolation of Exosomes from Pediococcus pentosaceus
-
Culture Pediococcus pentosaceus in medium overnight at 37°C and then collect the supernatant.
-
Centrifuge at low speed and then filter the Pediococcus pentosaceus supernatant with filters.
-
After the filter, centrifuge the Pediococcus pentosaceus supernatant several times at ultra-high speed.
-
Resuspend the centrifuged Pediococcus pentosaceus exosome precipitate with sterile PBS and store frozen.
Studies on Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived Exosomes
|
Study
|
Conclusion
|
|
Characterization of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes.
|
Compared to E. coli-derived extracellular vesicles, exosomes derived from human intestinal commensals, including Pediococcus pentosaceus, had larger sizes. In addition, disposable capillary cell assay showed that Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes exhibited high negative electronegativity.
|
|
Therapeutic effects of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes in liver fibrosis models and vaccination models.
|
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes ameliorated hepatic fibrosis pathology in inflammation-induced mouse models.
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes negatively regulate vaccine-induced immune responses by inhibiting Th1 cells.
|
|
Effects of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes on immune cells.
|
-
Differentiation of myeloid derived suppressor cells from bone marrow precursors was promoted in mice injected intraperitoneally with Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes.
-
Treatment with Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes was capable of inducing myeloid-derived macrophage polarization toward an M2-like immunosuppressive phenotype, inhibiting T-cell activation, and strongly promoting the expression of IL-10, arginase-1, and PD-L1.
-
The results of neutralizing antibody blocking assays showed that this immunomodulatory activity of Pediococcus pentosaceus exosomes was mediated by TLR2.
|
|
Effects of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes on inflammation-related diseases and wound healing.
|
-
Treatment with Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes reduced the level of neutrophil accumulation in the peritoneal cavity in models of acute peritonitis in mice.
-
Assays of chemical-induced mouse colitis models also showed that Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes protected against and mitigated inflammation.
-
In mouse skin wound models, intraperitoneal injection of Pediococcus pentosaceus exosomes reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and recruited more MDSC to the wound to favor wound healing.
|
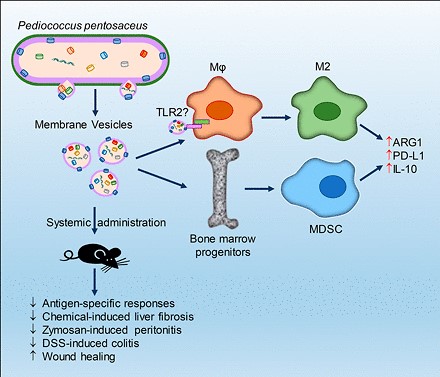 Fig. 1 Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes modulate inflammation and therapeutic potential for inflammation-related diseases.1
Fig. 1 Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes modulate inflammation and therapeutic potential for inflammation-related diseases.1
It has been shown that Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes can possess potential therapeutic effects on inflammation-related diseases by modulating inflammation-related signaling pathways, influencing immune cell activity, and improving the balance of intestinal flora, etc. Creative Biolabs has a comprehensive platform for exosome research to facilitate a deeper understanding of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes. Please contact us with your project demands.
Reference
-
Alpdundar Bulut, Esin, et al. "Human gut commensal membrane vesicles modulate inflammation by generating M2-like macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells." The Journal of Immunology 205.10 (2020): 2707-2718.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes modulate inflammation and therapeutic potential for inflammation-related diseases.1
Fig. 1 Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes modulate inflammation and therapeutic potential for inflammation-related diseases.1








