Lactobacillus paracasei-derived Exosome Research and Application
Extracellular vesicles isolated from Lactobacillus paracasei are characterized as exosomes and show potential for amelioration in the pathogenesis of colitis and colorectal cancer. Creative Biolabs has a longstanding focus on research and translational advances in bacterial-derived exosomes and can provide reliable research services for projects related to Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes.
Isolation of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived Exosomes
-
Culture Lactobacillus paracasei at 37°C overnight with shaking.
-
Centrifuge the cultured medium, and collect the supernatant, and filter out any residual Lactobacillus paracasei.
-
Concentrate the filtered Lactobacillus paracasei supernatant by passing it through filter membranes and subsequently filtering it again.
-
Ultracentrifuge the supernatant to obtain Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosome precipitates.
-
Resuspend Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes and store frozen.
Research on Lactobacillus paracasei-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes regulated inflammatory responses in macrophages and colon cancer cells.
|
-
NO and TNF-α levels in macrophages were assessed, revealing that pretreatment with Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes reduced lipopolysaccharide-induced NO with accompanying TNF-α production in macrophages.
-
Similarly, in lipopolysaccharide-induced colon cancer cells, pretreatment with Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes exerted the ability to inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, while enhancing the synthesis of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of inflammation-related proteins and NO production were suppressed.
|
|
Localization of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes administration in the mouse model.
|
Oral administration of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes and in vivo imaging in mice showed that Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes were first present in the stomach, diffused over time, and were able to enrich in the colon after 24h of administration, and finally disappeared after 48h.
|
|
Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes affected disease activity index and colon length in colitis mice.
|
By comparing mice receiving oral lipopolysaccharide or both lipopolysaccharide and Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes, it was found that treatment with Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes rescued weight loss and mouse death and attenuated the pathology of acute colitis and the levels of related factors involved in the inflammatory response, such as COX-2 and IL-1β, were also reduced as expected.
|
|
The anti-inflammatory action of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes involves the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
|
Western blotting assays revealed that treatment of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes increased the expression levels of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated proteins, which were eliminated by endoplasmic reticulum stress blockers. It was further found by targeted interference with CHOP siRNA that the anti-inflammatory effect of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes mediated by enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress may have involved the promotion of CHOP expression.
|
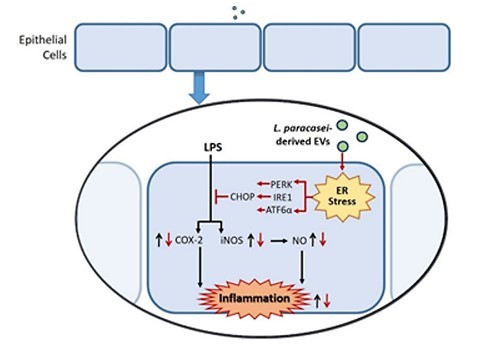 Fig. 1 Molecular mechanism of colitis suppression by Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Molecular mechanism of colitis suppression by Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes.1
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes on colon cancer cells and colon cancer tumors.
|
-
In vitro experiments demonstrated that Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes inhibited colon cancer cell invasion and promoted colon cancer cell death.
-
In a nude mouse model of xenograft tumors, subcutaneous injection of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes inhibited tumor growth.
|
|
Molecular mechanisms of colon cancer inhibition by Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes.
|
Combined analysis of transcriptome sequencing, western blotting, and immunohistochemistry assays showed that Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes anti-colon cancer involved inhibition of the PDK1/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway.
|
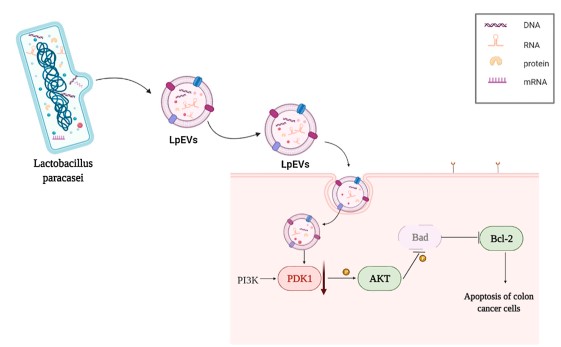 Fig. 2 Molecular mechanism of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes against colon cancer.2
Fig. 2 Molecular mechanism of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes against colon cancer.2
Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes show anti-inflammatory effects mediated by enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress in inflammation-induced colon cancer cellular and mouse models and are capable of fighting colorectal tumors, which raises the possibility of further applications of probiotic-derived vesicles. Creative Biolabs is committed to providing Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosome-related research, advancing their research and translation for intervention in colorectal-related diseases. Please contact us to learn more.
References
-
Choi, Ji Hyun, et al. "Lactobacillus paracasei-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate the intestinal inflammatory response by augmenting the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 52.3 (2020): 423-437.
-
Shi, Yangqian, et al. "Extracellular vesicles of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei PC-H1 induce colorectal cancer cells apoptosis via PDK1/AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway." Microbiological research 255 (2022): 126921.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Molecular mechanism of colitis suppression by Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Molecular mechanism of colitis suppression by Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Molecular mechanism of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes against colon cancer.2
Fig. 2 Molecular mechanism of Lactobacillus paracasei-derived exosomes against colon cancer.2








